ResponseEntityExceptionHandler
@ControllerAdvice?
스프링 부트를 통해 애플리케이션을 개발하면, 예외를 전역적으로 처리하게 됩니다.
주로 @ControllerAdvice(혹은 @RestControllerAdvice)를 통해 다음과 같이 작성하게 됩니다.
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalControllerAdvice {
// 생략
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
private ResponseEntity<ExceptionResponse> handleException(Exception ex) {
logger.warn("Exception : ", ex);
return ResponseEntity.internalServerError().body(new ExceptionResponse("예상치 못한 문제가 발생했습니다."));
}
}이를 통해 다음과 같은 장점을 얻을 수 있습니다.
- 예외 처리 로직을 분리할 수 있습니다.
- 코드의 중복을 방지할 수 있습니다.
- 관심사를 분리해 코드의 가독성을 높일 수 있습니다.
- 한 곳에서 예외를 처리할 수 있습니다.
- 일관성을 유지하며 예외를 처리할 수 있습니다.
- 가독성, 유지보수성에 이점이 있습니다.
여러 개의 @ControllerAdvice?
하나의 Controller에 하나의 @ControllerAdvice에서 예외 처리를 한다고 가정하겠습니다.
@Controller
public class AController {
// 생략
}
@RestControllerAdvice(assignableTypes = AController.class)
public class AControllerAdvice {
// 생략
}
@Controller
public class BController {
// 생략
}
@RestControllerAdvice(assignableTypes = BController.class)
public class BControllerAdvice {
// 생략
}이렇게 사용하면, @ControllerAdvice를 사용해 예외 처리 로직을 분리하면서 얻은 이점의 상당수를 잃어버리게 됩니다.
- 예외 처리 로직이 분산됩니다.
- 일관성이 없어질 가능성이 큽니다.
- 코드의 중복이 발생할 수 있습니다.
@ControllerAdvice, @RestControllerAdvice의 우선순위를 신경써야 합니다.- 가독성, 유지보수성이 떨어지게 됩니다.
하나의 클래스에서 예외를 처리하는게 분산하는 것보다 장점이 많은 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
그러므로 다음과 같이 결론을 내릴 수 있습니다.
@ControllerAdvice를 통해 예외 처리를 하고자 한다면 하나의 클래스에서 전역적으로 처리하는 것을 지향해야 한다.
문제 상황
UserController라는 회원 관련한 단 하나의 Controller만 존재하고, 해당 Controller에서 발생하는 예외를 GlobalControllerAdvice에서 처리한다고 가정하겠습니다.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<UserResponse> findUser() {
// 생략
}
}
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalControllerAdvice {
// 생략
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
private ResponseEntity<ExceptionResponse> handleException(Exception ex) {
logger.warn("Exception : ", ex);
return ResponseEntity.internalServerError().body(new ExceptionResponse("예상치 못한 문제가 발생했습니다."));
}
}예상치 못한 문제가 발생했을 때, 클라이언트에게 관련된 정보를 전파하지 않도록 Exception으로 예외 처리를 하고 있습니다.
실행
이제 @PostMapping이지만 HTTP DELETE METHOD로 요청을 해보겠습니다.
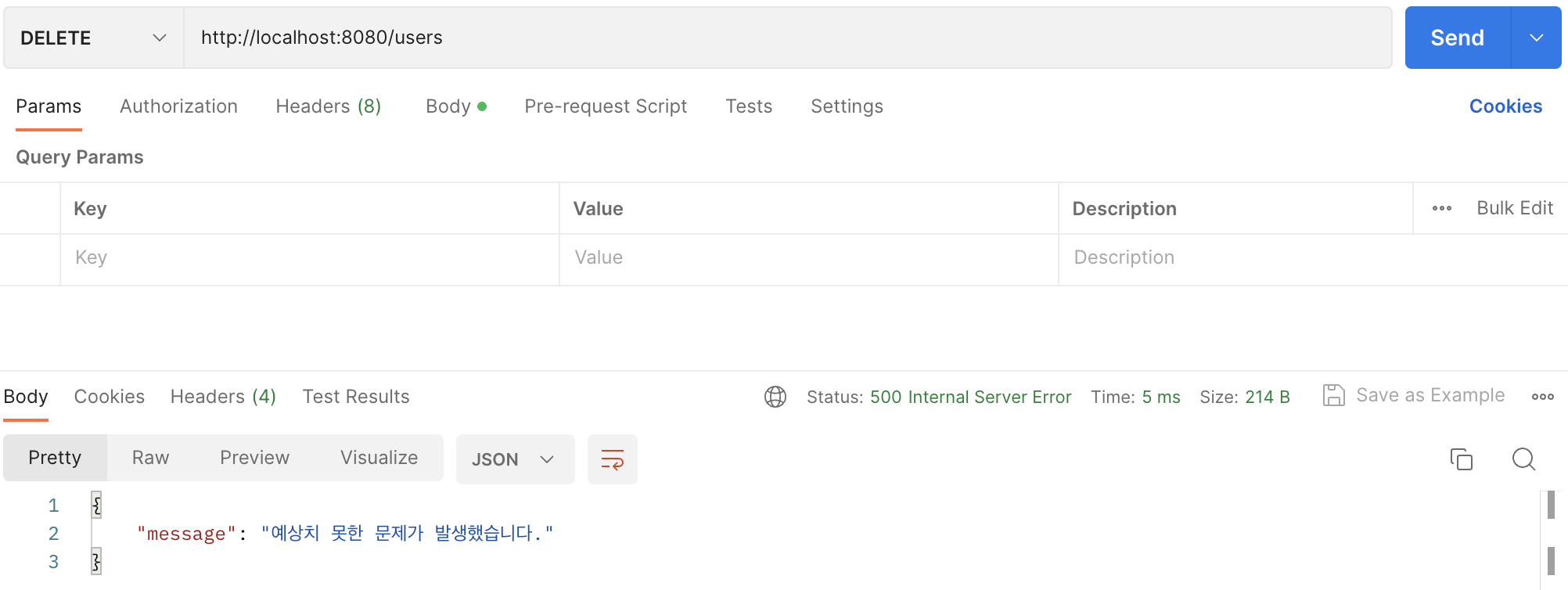
500 Internal Server Error가 발생합니다.
Exception으로 예외를 처리하고 있어, HTTP DELETE METHOD로 요청한 클라이언트의 잘못이지만 서버의 잘못이 되어 버린 것입니다.
당연히 Exception을 통해 예외를 처리하는 곳에서는 로그를 표시할테고, 이를 통해 어떤 예외가 발생했는지 파악하고 @ExceptionHandler를 추가할 수 있을 것입니다.
다만 예시를 위해 어떠한 예외가 발생했는지 파악하는데 실패했고, 차라리 스프링에서 해주는 예외 처리를 사용하는 상황이라고 가정하겠습니다.
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalControllerAdvice {
// 주석 처리
/*
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
private ResponseEntity<ExceptionResponse> handleException(Exception ex) {
logger.warn("Exception : ", ex);
return ResponseEntity.internalServerError().body(new ExceptionResponse("예상치 못한 문제가 발생했습니다."));
}
*/
}다시 동일한 요청을 보내면, 다음과 같은 응답을 받을 수 있습니다.
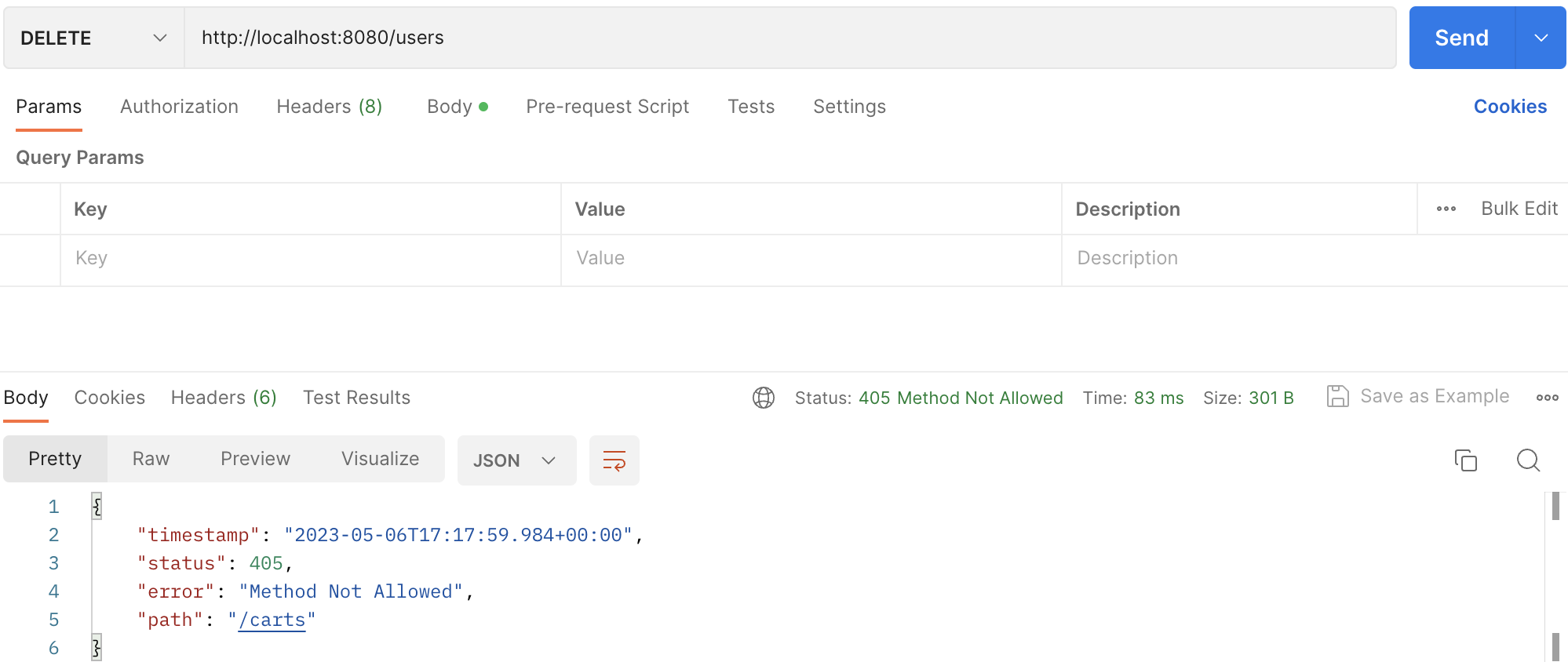
405 Method Not Allowed가 발생합니다.
500을 반환하던 이전보다는 나아졌지만, 다음과 같은 문제가 발생합니다.
- 응답 메세지를 커스터마이징할 수 없음
- 예외 처리를 하나의 클래스에서 전역적으로 처리할 수 없음
왜 전역적으로 처리할 수 없는지 살펴보겠습니다.
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
WARN 1568 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] .w.s.m.s.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver : Resolved [org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException: Request method 'DELETE' not supported]로그를 통해 어떤 클래스에서 예외를 처리하는지, 예외 메세지가 무엇인지 확인할 수 있습니다.
// DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
@Override
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView doResolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) {
try {
if (ex instanceof HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException) {
return handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported(
(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException) {
return handleHttpMediaTypeNotSupported(
(HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException) {
return handleHttpMediaTypeNotAcceptable(
(HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof MissingPathVariableException) {
return handleMissingPathVariable(
(MissingPathVariableException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof MissingServletRequestParameterException) {
return handleMissingServletRequestParameter(
(MissingServletRequestParameterException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof ServletRequestBindingException) {
return handleServletRequestBindingException(
(ServletRequestBindingException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof ConversionNotSupportedException) {
return handleConversionNotSupported(
(ConversionNotSupportedException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof TypeMismatchException) {
return handleTypeMismatch(
(TypeMismatchException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMessageNotReadableException) {
return handleHttpMessageNotReadable(
(HttpMessageNotReadableException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMessageNotWritableException) {
return handleHttpMessageNotWritable(
(HttpMessageNotWritableException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException) {
return handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(
(MethodArgumentNotValidException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof MissingServletRequestPartException) {
return handleMissingServletRequestPartException(
(MissingServletRequestPartException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof BindException) {
return handleBindException((BindException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof NoHandlerFoundException) {
return handleNoHandlerFoundException(
(NoHandlerFoundException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof AsyncRequestTimeoutException) {
return handleAsyncRequestTimeoutException(
(AsyncRequestTimeoutException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
}
catch (Exception handlerEx) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Failure while trying to resolve exception [" + ex.getClass().getName() + "]", handlerEx);
}
}
return null;
}DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver.doResolveException()을 확인해보면 여러 예외(Spring MVC Exception)를 처리하고 있음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
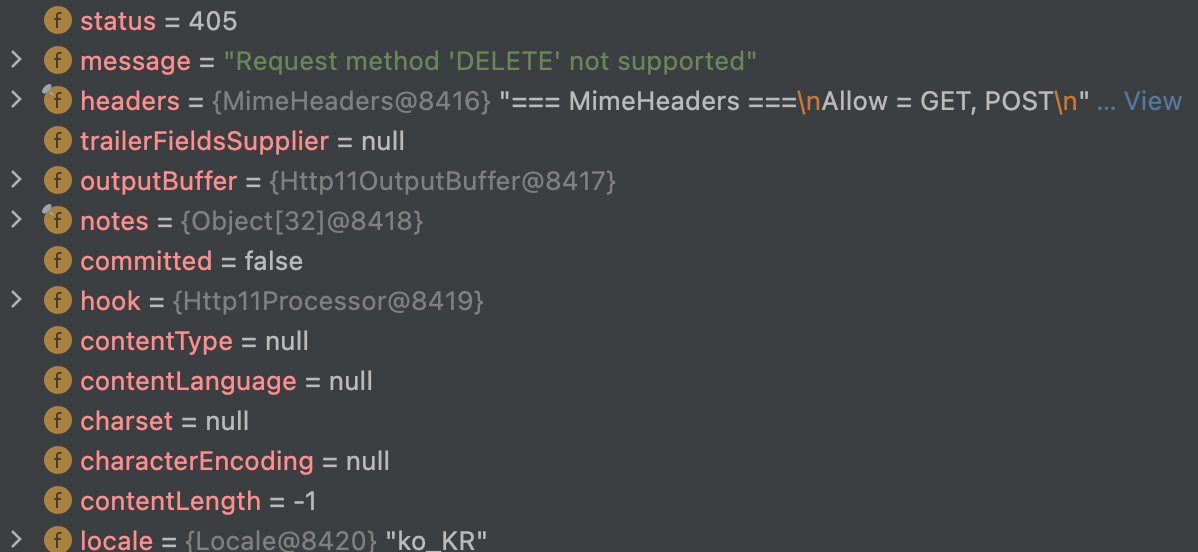
필요한 값들을 HttpServletResponse에 담는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
그렇다면, @ExceptionHandler를 사용한다면 어디서 처리될까요?
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
@ControllerAdvice, @RestControllerAdvice를 사용한 경우, ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver에 해당 클래스를 저장합니다.
이후 예외가 발생하면, 저장한 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver에서 해당 예외를 처리할 수 있는 클래스를 찾아 리플렉션으로 @ExceptionHandler로 명시한 메소드를 사용하게 됩니다.
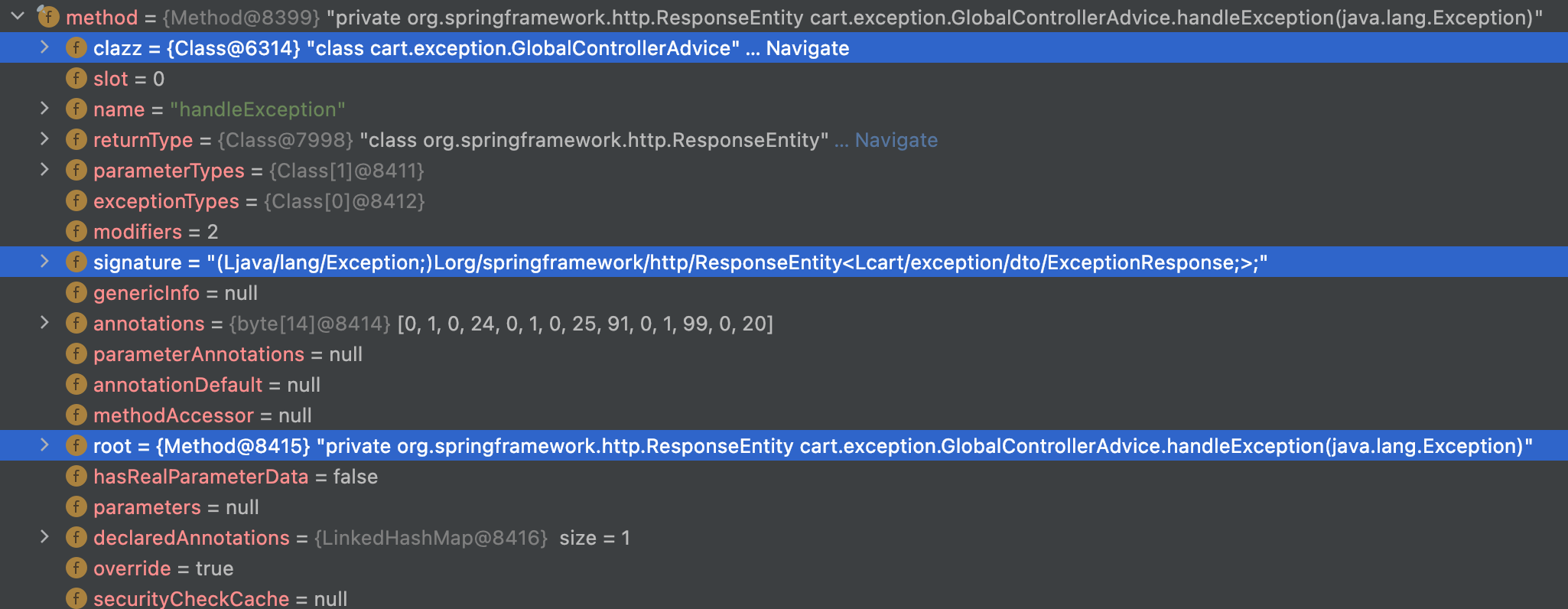
지정한 GlobalControllerAdvice 클래스의 handleException(Exception) 메소드를 호출할 것임을 확인할 수 있습니다.
정리
@ControllerAdvice + @ExceptionHandlerExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver에 의해 처리
- 명시하지 않은 예외 중
Spring MVC ExceptionDefaultHandlerExceptionResolver에 의해 처리
이렇게 @ControllerAdvice, @RestControllerAdvice를 사용했다고 하더라도, 실제 예외를 처리하는 구간은 두 개로 나뉠 수 있습니다.
위에서 살펴본 것처럼, 예외 처리는 하나의 클래스에서 전역적으로 처리하는 것을 지향해야 하므로 이러한 상황은 개선해야 할 것입니다.
Spring MVC Exception
현재 문제점은 다음과 같습니다.
Exception을 통해Spring MVC Exception을 처리하는 경우- 클라이언트의 잘못이 명확한 상황에서도 서버의 잘못으로 처리될 수 있음
- 예상치 못한 서버의 예외를 처리해야 하는 메소드가 원인이 명확한 예외까지 처리하게 됨
Exception을 통해Spring MVC Exception을 처리하지 않는 경우- 모든
Spring MVC Exception에 대한 예외 처리를 직접 작성해야 함
- 모든
결국 @ControllerAdvice, @RestControllerAdvice를 의도에 맞게 사용하기 위해서는 Spring MVC Exception을 처리해야 합니다.
이를 위해 Spring MVC Exception이 무엇인지 살펴보겠습니다.
Spring MVC Exception은Spring MVC요청 처리 도중 발생할 수 있는 예외를 의미합니다.
Spring MVC에서는 HTTP 요청 / 응답을 처리하는 데 사용되는 다양한 구성 요소(HandlerMethod, DataBinder, Validation, ViewResolver 등등)들이 있습니다.
이러한 구성 요소들은 요청을 처리하는 도중, 예외가 발생할 수 있습니다.
이러한 예외들을 Spring MVC에서 별도의 예외 클래스를 통해 제공합니다.
이를 통해 다음과 같은 장점을 얻을 수 있습니다.
- 일관성 있는 예외 처리
- 코드 중복 방지
- 유지보수
다음으로 Spring MVC Exception에는 어떠한 종류가 있고, 기본적으로 어떤 HTTP 상태 코드로 반환되는지 살펴보도록 하겠습니다.
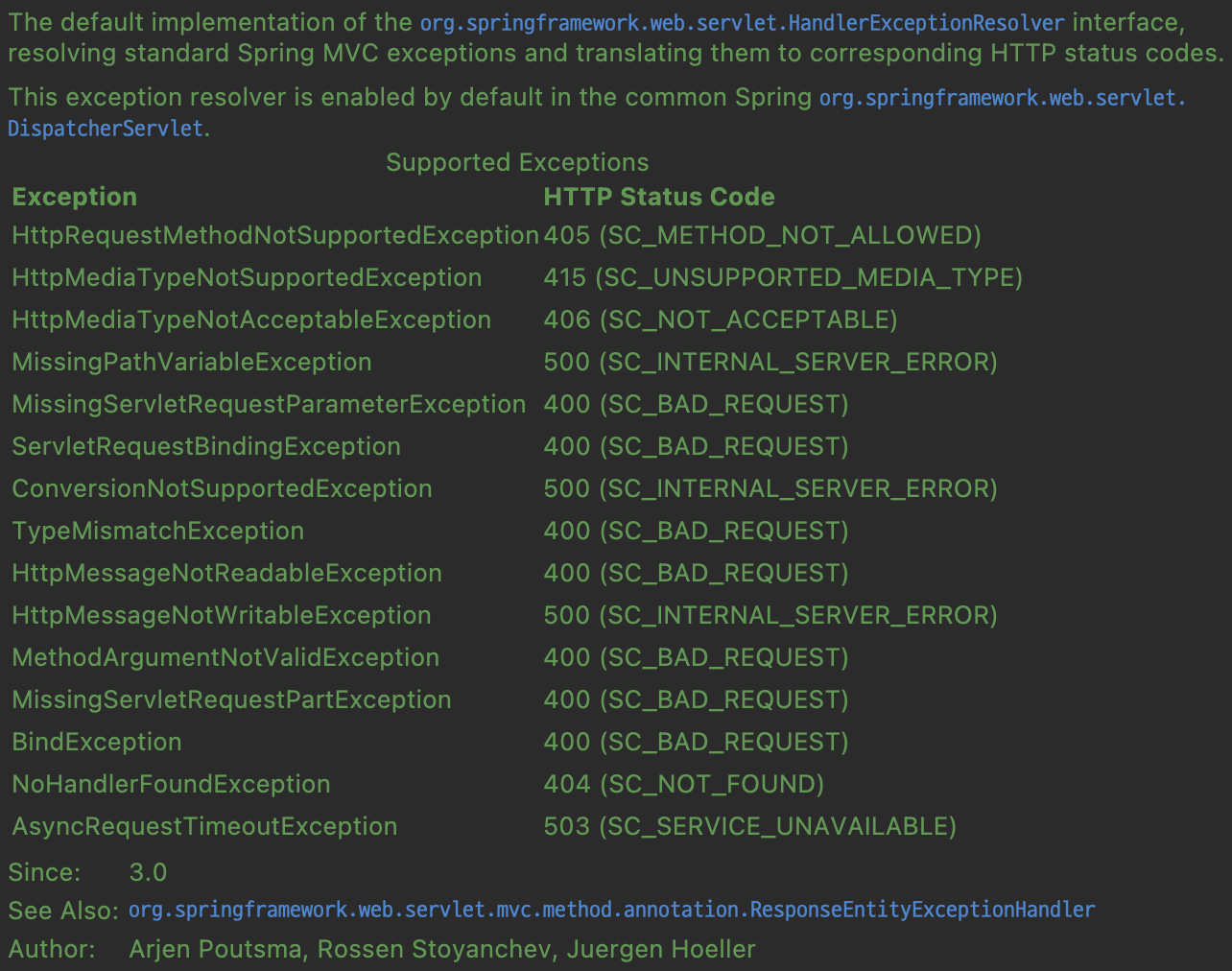
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver API docs에 잘 명시되어 있기는 하지만, 그래도 조금 더 정리해보겠습니다.
| 예외 | 설명 | HTTP 상태 코드 |
|---|---|---|
| HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException | 허용되지 않은 HTTP 메소드를 사용한 경우 | 405 (Method Not Allowed) |
| HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException | 지원되지 않는 미디어 타입을 사용한 경우 | 415 (Unsupported Media Type) |
| HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException | 요청에 대해 지원되는 미디어 타입이 없는 경우 | 406 (Not Acceptable) |
| MissingPathVariableException | 경로 변수(@PathVariable)가 누락된 경우 | 500 (Internal Server Error) |
| MissingServletRequestParameterException | 요청 매개 변수가 누락된 경우 | 400 (Bad Request) |
| ServletRequestBindingException | 요청 매개 변수 바인딩에 실패한 경우 | 400 (Bad Request) |
| ConversionNotSupportedException | 타입 변환이 실패한 경우 | 500 (Internal Server Error) |
| TypeMismatchException | 타입 불일치가 발생한 경우 | 400 (Bad Request) |
| HttpMessageNotReadableException | 요청 메세지를 읽을 수 없는 경우 | 400 (Bad Request) |
| HttpMessageNotWritableException | 응답 메세지를 쓸 수 없는 경우 | 500 (Internal Server Error) |
| MethodArgumentNotValidException | @Valid 애노테이션으로 검증에 실패한 경우 | 400 (Bad Request) |
| MissingServletRequestPartException | Part 타입 데이터가 누락된 경우 | 400 (Bad Request) |
| BindException | 폼 데이터 바인딩에 실패한 경우 | 400 (Bad Request) |
| NoHandlerFoundException | 요청에 대한 핸들러를 찾을 수 없는 경우 | 404 (Not Found) |
| AsyncRequestTimeoutException | 비동기 요청 처리 시간을 초과한 경우 | 503 (Service Unavailable) |
예외 개수가 상당한 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
이 모든 예외를 일일히 수작업으로 명시하는 것은 비용이 상당할 것입니다.
애플리케이션 환경에 따라 발생할 가능성이 낮은 예외들도 존재합니다.
HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException- 요청을 전송할 때 응답으로 받고자 하는 미디어 유형을 명시적으로 지정하는 경우 발생합니다.
- 대부분의 클라이언트는 암시적으로
Accept 헤더를 전달하거나,*/*로 명시합니다.
ConversionNotSupportedExceptionCustom Converter를 사용할 때 발생합니다.
AsyncRequestTimeoutException- 비동기 요청을 사용할 때 발생합니다.
NoHandlerFoundException- 기본적으로
DispatcherServlet이 처리하므로, 설정을 하지 않는 이상NoHandlerFoundException을 직접 처리할 수 없습니다.
- 기본적으로
재정의를 고려할만한 예외 또한 존재합니다.
MissingPathVariableException- 해당 예외를 클라이언트의 잘못으로 본다면,
500을 적합하지 않다고 판단할 수도 있습니다.
- 해당 예외를 클라이언트의 잘못으로 본다면,
MethodArgumentNotValidException- 클라이언트에게 명확한 메세지를 전달하고자 할 수도 있습니다.
Spring MVC Exception은 그 양이 상당하며, 애플리케이션 환경에 따라 일부만 취사 선택해 예외 처리를 하면 된다는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
다만, 하나의 @ControllerAdvice, @RestControllerAdvice만을 통해 전역적으로 예외를 처리하고고자 한다면, 어쩔 수 없이 모든 Spring MVC Exception을 명시해야 합니다.
이럴 때 고려해볼 수 있는 클래스가 바로 ResponseEntityExceptionHandler 입니다.
ResponseEntityExceptionHandler?
문서를 살펴보면, 다음과 같이 ResponseEntityExceptionHandler를 설명하고 있습니다.
A class with an
@ExceptionHandlermethod that handles allSpring MVCraised exceptions by returning a ResponseEntity withRFC 7807 formattederror details in the body.
@ExceptionHandler가 존재하는 클래스로, 본문에서RFC 7807 형식의 예외 세부 정보가 포함된ResponseEntity를 반환하여Spring MVC에서 발생한 모든 예외를 처리합니다.
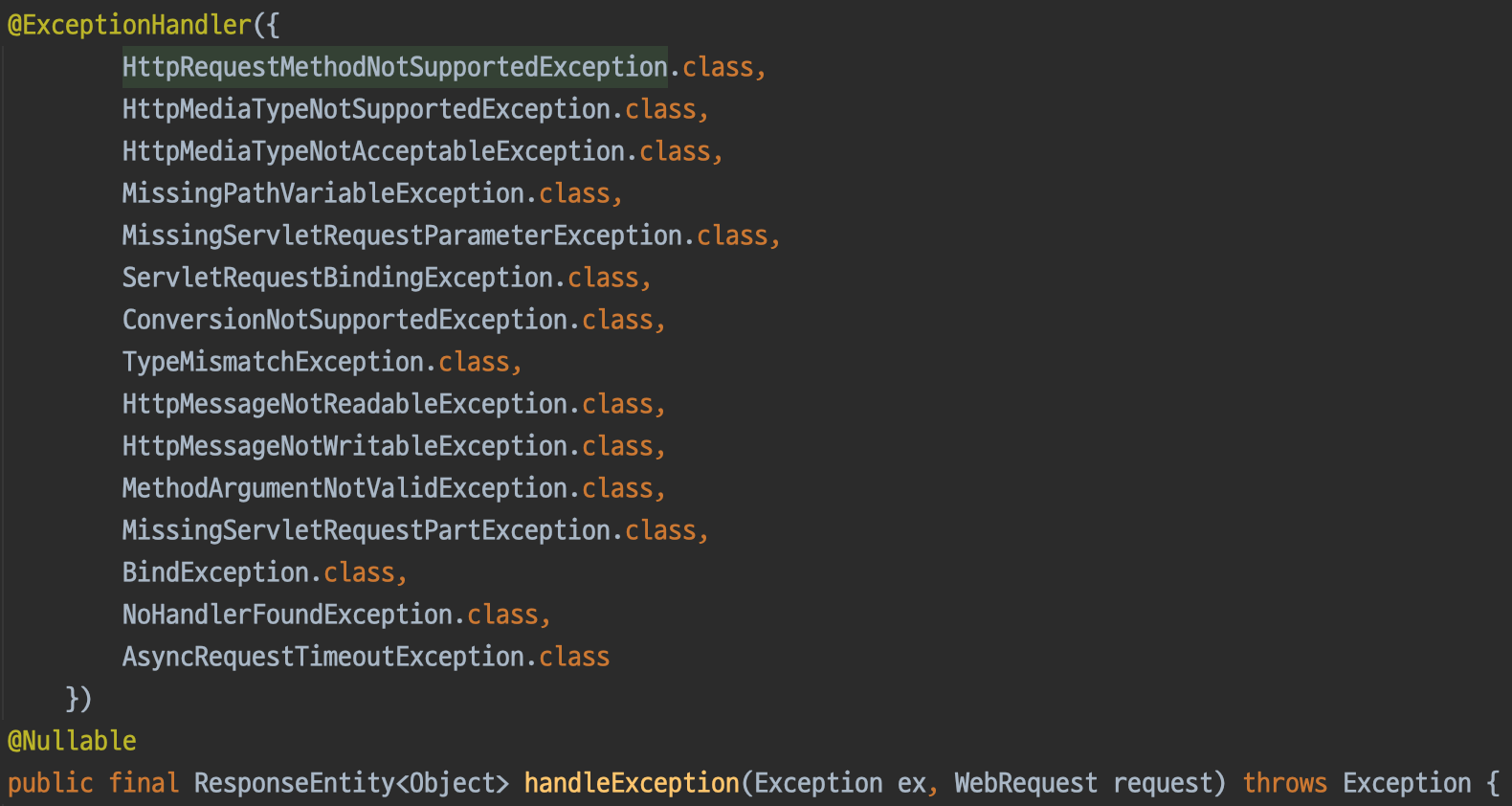
확인해보면, 실제로 모든 Spring MVC Exception을 @ExceptionHandler로 명시하고 있음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
public final ResponseEntity<Object> handleException(Exception ex, WebRequest request) throws Exception {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
if (ex instanceof HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED;
return handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported((HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE;
return handleHttpMediaTypeNotSupported((HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE;
return handleHttpMediaTypeNotAcceptable((HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof MissingPathVariableException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
return handleMissingPathVariable((MissingPathVariableException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof MissingServletRequestParameterException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
return handleMissingServletRequestParameter((MissingServletRequestParameterException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof ServletRequestBindingException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
return handleServletRequestBindingException((ServletRequestBindingException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof ConversionNotSupportedException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
return handleConversionNotSupported((ConversionNotSupportedException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof TypeMismatchException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
return handleTypeMismatch((TypeMismatchException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMessageNotReadableException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
return handleHttpMessageNotReadable((HttpMessageNotReadableException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMessageNotWritableException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
return handleHttpMessageNotWritable((HttpMessageNotWritableException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
return handleMethodArgumentNotValid((MethodArgumentNotValidException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof MissingServletRequestPartException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
return handleMissingServletRequestPart((MissingServletRequestPartException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof BindException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
return handleBindException((BindException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof NoHandlerFoundException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND;
return handleNoHandlerFoundException((NoHandlerFoundException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else if (ex instanceof AsyncRequestTimeoutException) {
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE;
return handleAsyncRequestTimeoutException((AsyncRequestTimeoutException) ex, headers, status, request);
}
else {
// Unknown exception, typically a wrapper with a common MVC exception as cause
// (since @ExceptionHandler type declarations also match first-level causes):
// We only deal with top-level MVC exceptions here, so let's rethrow the given
// exception for further processing through the HandlerExceptionResolver chain.
throw ex;
}
}코드는 DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver.doResolveException()와 유사하며, Spring MVC Exception이 아닌 다른 예외는 throw를 통해 다른 @ExceptionHandler가 처리하도록 진행하는 방식입니다.
이 중 HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException를 처리하는 메소드를 확인해보겠습니다.
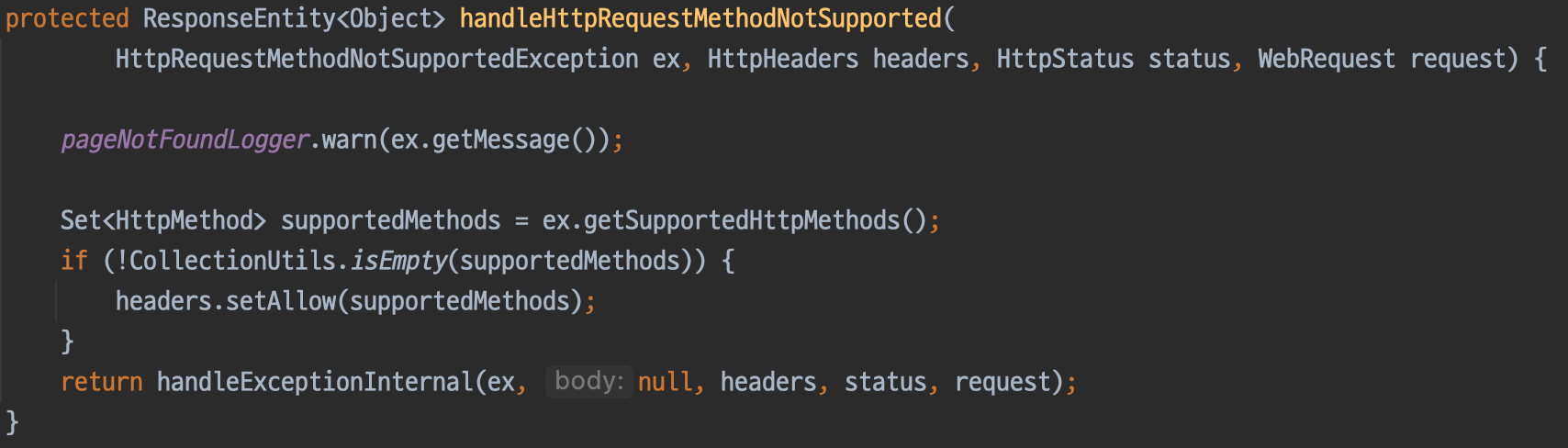
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver.handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported와 비슷하지만, 다음과 같은 차이점이 있습니다.
- 반환 타입이
ModelAndView가 아닌ResponseEntity입니다. - 메소드 접근제어자가 protected 입니다.
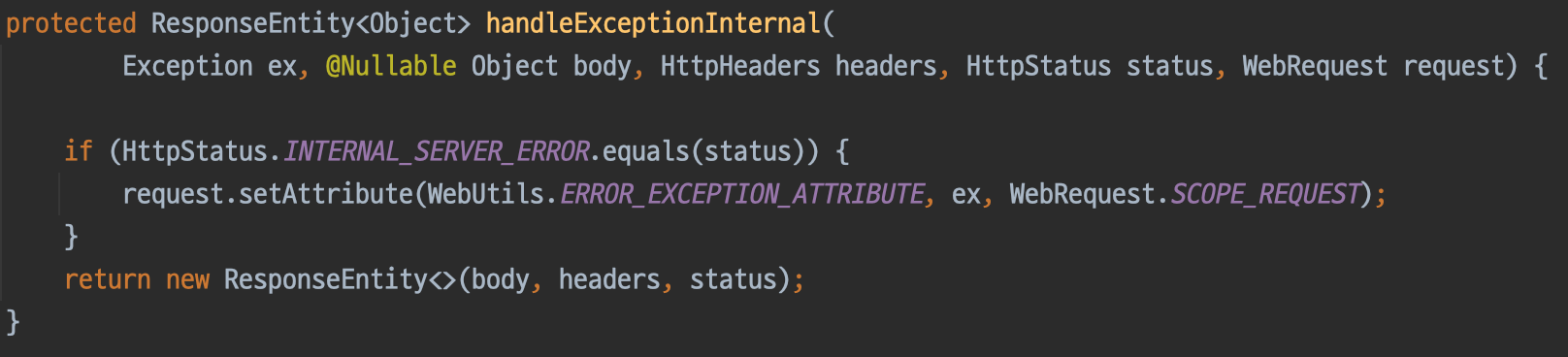
handleException() -> handle*() -> handleExceptioinInternal() 메소드에서 handle*() 뿐만 아니라 handleExceptioinInternal()까지 접근 제어자가 protected입니다.
이는 다음과 같은 의미를 가집니다.
handle*()- 특정 예외를 명시적으로 처리할 수 있음
handleExceptioinInternal()- 예외 처리 시 응답 형식을 재정의할 수 있음
ResponseEntityExceptionHandler에게 처리를 위임하더라도 일관성 있는 응답 가능
실행
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalControllerAdvice extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
private ResponseEntity<ExceptionResponse> handleException(Exception ex) {
logger.warn("Exception : ", ex);
return ResponseEntity.internalServerError().body(new ExceptionResponse("예상치 못한 문제가 발생했습니다."));
}
}GlobalControllerAdvice가 ResponseEntityExceptionHandler를 확장하고, Exception만을 처리하도록 설정했습니다.
이제 이전과 같이 @PostMapping으로 명시한 Handler를 HTTP DELETE METHOD로 요청해보도록 하겠습니다.
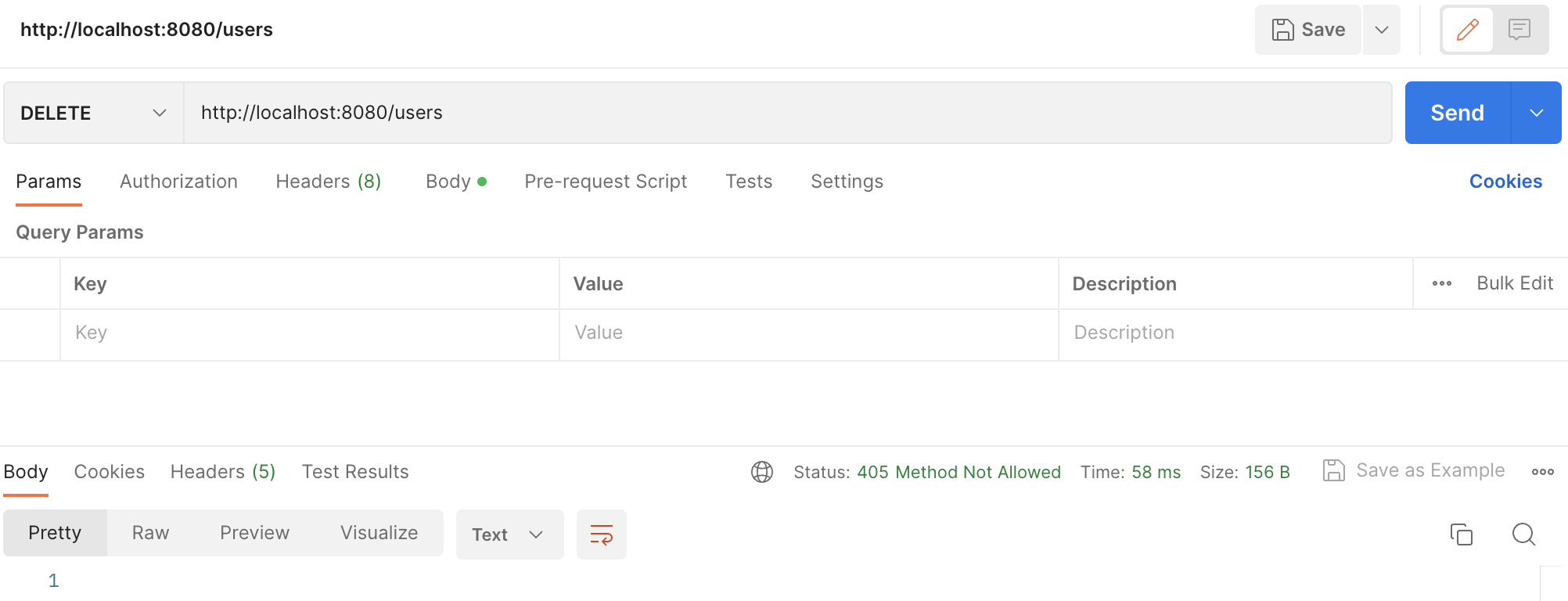
Exception으로 처리되지 않고, Spring MVC Exception이 정상적으로 처리되었음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
다만 HTTP Response Body가 존재하지 않습니다.
이를 명시해주기 위해서는 다음과 같이 오버라이딩을 활용할 수 있습니다.
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalControllerAdvice extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
private ResponseEntity<ExceptionResponse> handleException(Exception ex) {
logger.warn("Exception : ", ex);
return ResponseEntity.internalServerError().body(new ExceptionResponse("예상치 못한 문제가 발생했습니다."));
}
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported(
HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException ex,
HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status, final WebRequest request) {
logger.info("HttpRequestMethodNotSupported : ", ex);
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(new ExceptionResponse("적합한 HTTP Method로 요청해주세요."));
}
}
의도한 HTTP 상태 코드와 메세지를 확인할 수 있습니다.
기타
Logger
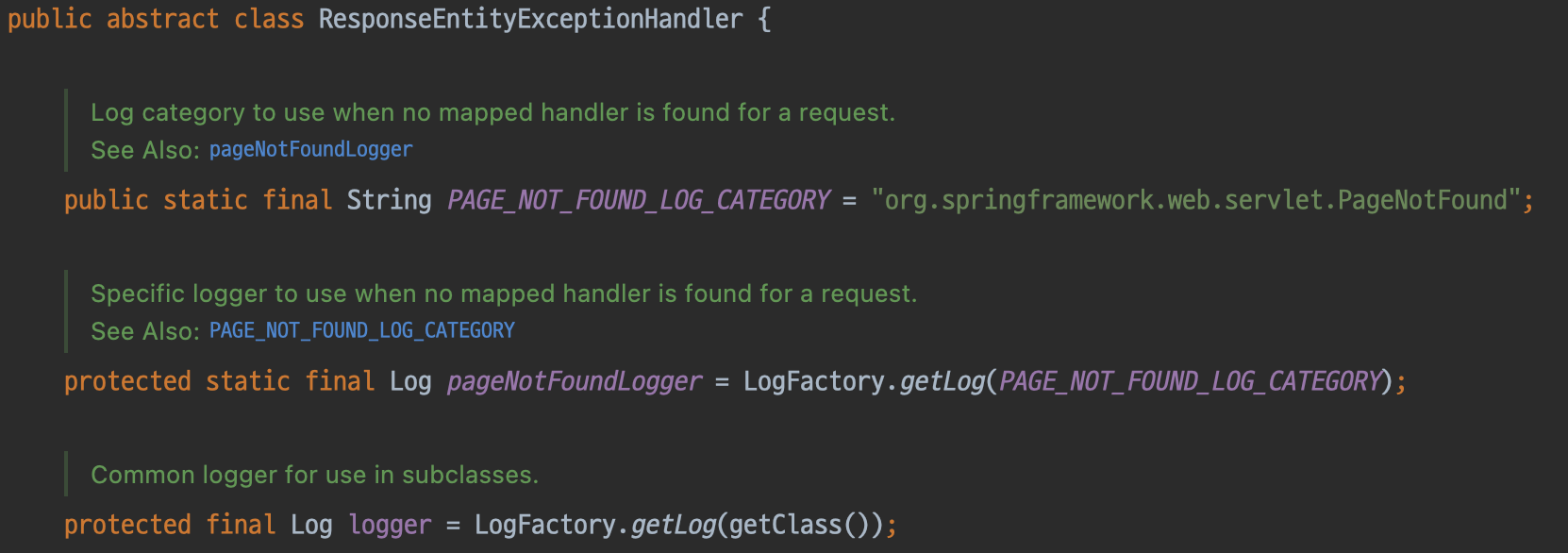
ResponseEntityExceptionHandler에서는 기본적으로 다음과 같은 두 가지의 Logger를 제공합니다.
pageNotFoundLogger- 요청을 처리하기 위한
Handler(Page)를 찾을 수 없을 때 사용하는Logger handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported()에서 사용
- 요청을 처리하기 위한
logger- 일반적인
Logger
- 일반적인
그렇기 때문에 ResponseEntityExceptionHandler를 확장한다면, 별도로 Logger를 선언할 필요가 없습니다.
정리
@ControllerAdvice, @RestControllerAdvice만을 사용할 경우Spring MVC Exception을 모두 처리하지 못할 수 있습니다.- 이 경우 사실상 하나의 클래스에서 전역적인 예외 처리가 불가능합니다.
- 모든
Spring MVC Exception을 수작업으로 처리할 수도 있지만, 매우 번거롭습니다.
ResponseEntityExceptionHandler를 확장하면Spring MVC Exception에 대한 최소한의 예외 처리가 가능합니다.- 필요한 경우 오버라이딩을 통해 예외 처리 관련 메소드를 커스터마이징 할 수 있습니다.
딱 이런 고민을 했었는데 해결책이 있었네요..! 좋은 포스트 감사합니다 ㅎㅎ 🥰