
25 클래스
25.1 클래스는 프로토타입의 문법적 설탕인가?
자바스크립트는
-
프로토타입 기반 객체지향 언어다.
-
프로토타입 기반 객체지향 언어는 클래스가 필요없는 객체지향 프로그래밍 언어다.
- ES5에서는 클래스 없이도 생성자 함수와 프로토타입을 통해 객체지향 언어의 상속을 구현할 수 있었지만,
- 클래스 기반 언어에 익숙한 프로그래머들은 프로토타입 기반 프로그래밍 방식에 혼란을 느끼며,
- 자바스크립트를 어렵게 느끼는 요소 중 하나로 인식되어 ES6에서 클래스를 도입하게 된다
-
ES6에서 도입된 클래스는 기존 프로토타입 기반의 패턴을 클래스 기반 객체지향 프로그래밍에 익숙해지기 쉽도록 새로운 객체 생성 메커니즘을 제시한다.
-
기존 프로토타입 기반 객체지향 모델을 폐지하고 새롭게 클래스 기반 객체지향 모델을 제공하는 것은 아니다. 클래스는 생성자 함수와 매우 유사하게 동작하지만 다음 몇 가지 차이가 있다.
- 클래스를
new연산자 없이 호출하면 에러가 발생한다. 하지만 생성자 함수를new연산자 없이 호출하면 일반 함수로서 호출된다. - 클래스는 상속을 지원하는
extends와super키워드를 제공한다. 하지만 생성자 함수는extends와super키워드를 지원하지 않는다. - 클래스는 호이스팅이 발생하지 않는 것처럼 동작한다. 하지만 함수 선언문으로 정의된 생성자 함수는 함수 호이스팅이, 함수 표현식으로 정의한 생성자 함수는 변수 호이스팅이 발생한다.
- 클래스를
- 클래스 내의 모든 코드에는 암묵적으로
strict mode가 지정되어 실행되며strict mode를 해제할 수 없다. 하지만 생성자 함수는 암묵적으로strict mode가 지정되지 않는다. - 클래스의
constructor, 프로토타입 메서드, 정적 메서드는 모두 프로퍼티 어트리뷰트[[Enumerable]]의 값이false다. 다시 말해, 열거되지 않는다.
➔ 따라서 클래스를 프로토타입 기반 객체 생성 패턴의 단순한 문법적 설탕이라고 보기보다는, 새로운 객체 생성 메커니즘으로 보는 것이 좀 더 합당하다.
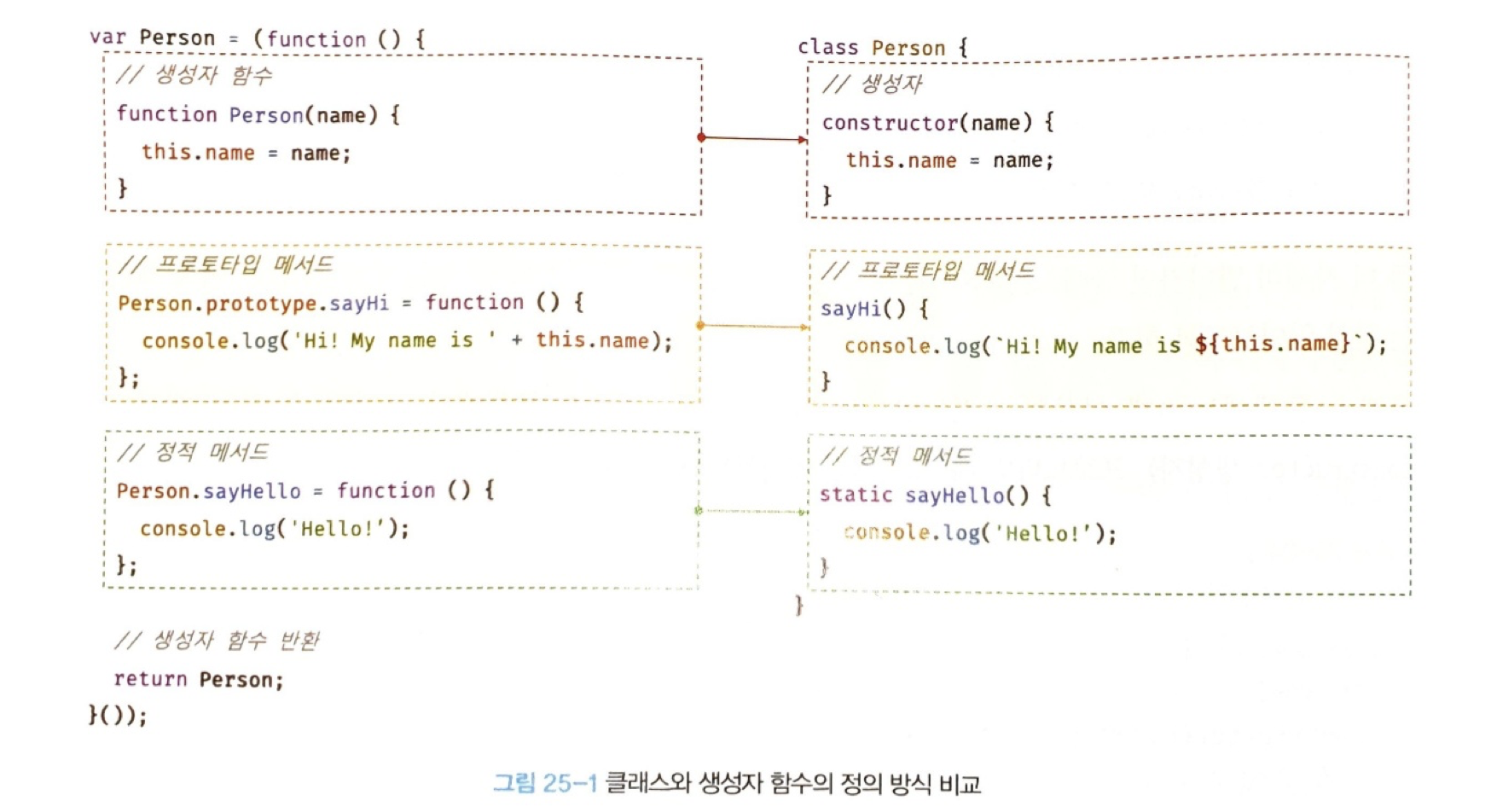
25.2 클래스 정의
클래스는 class 키워드를 사용해 정의하며 클래스 이름은 생성자 함수와 마찬가지로 파스칼 케이스를 사용하는 것이 일반적이다.
// 클래스 선언문
class Person {}클래스는 일급 객체로서 다음과 같은 특징을 갖는다.
- 무명의 리터럴로 생성할 수 있다. 즉, 런타임에 생성이 가능하다.
- 변수나 자료구조(객체, 배열 등)에 저장할 수 있다.
- 함수의 매개변수에게 전달할 수 있다.
- 함수의 반환값으로 사용할 수 있다.
25.3 클래스 호이스팅
클래스는 함수로 평가된다
const Person = '';
{
// 호이스팅이 발생하지 않는다면 ''이 출력되어야 한다.
console.log(Person);
// ReferenceError: Cannot access 'Person' before initialization
// 클래스 선언문
class Person {}
}클래스 선언문으로 정의한 클래스는
- 함수 선언문과 같이 소스코드 평가과정 즉, 런타임 이전에 먼저 평가되어 함수 객체를 생성한다.
- 이때 클래스가 평가되어 생성된 함수 객체는 생성자 함수로서 호출할 수 있는 함수, 즉
constructor다. - 생성자 함수로서 호출할 수 있는 함수는 함수 정의가 평가되어 함수 객체를 생성하는 시점에 프로토타입도 더불어 생성된다.
클래스 선언문도
- 변수 선언, 함수 정의와 마찬가지로 호이스팅이 발생한다.
- 단, 클래스는
let,const키워드로 선언한 변수처럼 호이스팅 되어 선언과 초기화가 분리되어 진행되기 때문에 - TDZ(일시적 사각지대)에 빠지게 되어 호이스팅이 발생하지 않는 것처럼 동작한다.
25.4 인스턴스 생성
클래스는 생성자 함수이며 new 연산자와 함께 호출되어 인스턴스를 생성한다.
함수는
new연산자의 사용 여부에 따라 일반 함수로 호출되거나- 인스턴스 생성을 위한 생성자 함수로 호출되지만
클래스는
- 인스턴스를 생성하는 것이 유일한 존재 이유이므로 반드시
new연산자와 함께 호출해야 한다.
class Person {}
// 인스턴스 생성
const me = new Person();
console.log(me); // Person {}
// 클래스를 new 연산자 없이 호출하면 타입 에러가 발생한다.
const you = Person();
// TypeError: Class constructor Foo cannot be invoked without 'new'25.5 메서드
클래스 몸체에는 0개 이상의 메서드만 선언할 수 있다.
클래스 몸체에서 정의할 수 있는 메서드는 세 가지가 있다.
constructor(생성자)- 프로토타입 메서드
- 정적 메서드
✔️ 25.5.1 constructor
constructor는
- 인스턴스를 생성하고
- 초기화하기 위한 특수한 메서드다
class Person {
// 생성자
constructor(name) {
// 인스턴스 생성 및 초기화
this.name = name;
}
}클래스는 평가되어 함수 객체가 되어
- 클래스도 함수 객체 고유의 프로퍼티를 모두 가지고 있다.
- 함수와 동일하게 프로토타입과 연결되어 있으며 자신의 스코프 체인을 구성한다.
모든 함수 객체가 가지고 있는 prototype 프로퍼티가 가리키는 프로토타입 객체의 constructor 프로퍼티는 클래스 자신을 가리킨다
- 이는 클래스가 인스턴스를 생성하는 생성자 함수라는 것을 의미
- 즉
new연산자와 함께 클래스를 호출하면 클래스는 인스턴스를 생성한다.
- 즉
constructor는 메서드로 해석되는 것이 아니라 클래스가 평가되어 생성한 함수 객체 코드의 일부가 된다. constructor는 생성자 함수와 유사하지만 몇가지 차이가 있는데,
-
constructor는 클래스 내에 최대 한 개만 존재할 수 있다. -
constructor를 생략하면 빈 객체를 생성한다.- 초기화된 인스턴스를 생성하려면
constructor내부에서 this에 인스턴스 프로퍼티를 추가한다. - 클래스 외부에서 인스턴스 프로퍼티의 초기값을 전달하려면 매개변수로 전달하면 된다
- 따라서 인스턴스를 초기화하려면
constructor를 생략해서는 안된다.
- 초기화된 인스턴스를 생성하려면
-
constructor는 별도의 반환문을 갖지 않아야 한다.new연산자와 함께 클래스가 호출되면 생성자 함수와 동일하게 암묵적으로this, 즉 인스턴스를 반환하기 때문- 만약
this가 아닌 다른 객체를 명시적으로 반환하면 인스턴스(this)가 반환되지 못하로return문에 명시한 객체가 반환된다. constructor내부에서 명시적으로this가 아닌 다른 값을 반환하는 것은 클래스의 기본 동작을 훼손하므로constructor내부에서return문은 반드시 생략해야 한다
✔️ 25.5.2 프로토타입 메서드
생성자 함수를 사용하여 인스턴스를 생성하는 경우
- 프로토타입 메서드를 생성하기 위해서는 명시적으로 프로토타입에 메서드를 추가해야 한다
- 클래스 몸체에서 정의한 메서드는
- 생성자 함수에 의한 객체 생성 방식과는 다르게
- 클래스의
prototype프로퍼티에 메서드를 추가하지 않아도 기본적으로 프로토타입 메서드가 된다.
class Person {
// 생성자
constructor(name) {
// 인스턴스 생성 및 초기화
this.name = name;
}
// 프로토타입 메서드
sayHi() {
console.log(`Hi! My name is ${this.name}`);
}
}
const me = new Person('Lee');
me.sayHi(); // Hi! My name is Lee
// me 객체의 프로토타입은 Person.prototype이다.
Object.getPrototypeOf(me) === Person.prototype; // -> true
me instanceof Person; // -> true
// Person.prototype의 프로토타입은 Object.prototype이다.
Object.getPrototypeOf(Person.prototype) === Object.prototype; // -> true
me instanceof Object; // -> true
// me 객체의 constructor는 Person 클래스다.
me.constructor === Person; // -> true클래스가 생성한 인스턴스는
- 프로토타입 체인의 일원이 되어 프로토타입 메서드를 상속받아 사용할수 있다.
결국 클래스는 생성자 함수와 같이 인스턴스를 생성하는 생성자 함수라고 볼 수 있다.
다시 말해, 클래스는 생성자 함수와 마찬가지로 프로토타입 기반의 객체 생성 메커니즘이다.
✔️ 25.5.3 정적(static) 메서드
정적 메서드는 인스턴스를 생성하지 않아도 호출할 수 있는 메서드를 말한다
- 생성자 함수의 경우 정적 메서드를 생성하기 위해서는 명시적으로 생성자 함수에 메서드를 추가해야 하는데
- 클래스에서는 메서드에
static키워드를 붙이면 정적 메서드가 된다.
class Person {
// 생성자
constructor(name) {
// 인스턴스 생성 및 초기화
this.name = name;
}
// 정적 메서드
static sayHi() {
console.log('Hi!');
}
}
// 정적 메서드는 클래스로 호출한다.
// 정적 메서드는 인스턴스 없이도 호출할 수 있다.
Person.sayHi(); // Hi!
// 인스턴스 생성
const me = new Person('April');
me.sayHi(); // TypeError: me.sayHi is not a function정적 메서드는
- 클래스에 바인딩된 메서드가 되고
- 클래스는 함수 객체로 평가되므로 자신의 프로퍼티/메서드를 소유할 수 있다
- 클래스는 클래스 정의(선언문이나 표현식)가 평가되는 시점에 함수 객체가 되므로 별다른 생성과정이 필요없다
- 따라서 정적 메서드는 클래스 정의 이후 인스턴스를 생성하지 않아도 호출할 수 있다
- 정적 메서드는 인스턴스로 호출할수 없고 클래스로 호출하는데
- 정적 메서드가 바인딩 된 클래스는 인스턴스의 프로토타입 체인상에 존재하지 않기 때문이다.
✔️ 25.5.4 정적 메서드와 프로토타입 메서드의 차이
- 정적 메서드와 프로토타입 메서드는 자신이 속해 있는 프로토타입 체인이 다르다.
- 정적 메서드는 클래스로 호출하고 프로토타입 메서드는 인스턴스로 호출한다.
- 정적 메서드는 인스턴스 프로퍼티를 참조할 수 없지만 프로토타입 메서드는 인스턴스 프로퍼티를 참조할 수 있다.
class Square {
// 정적 메서드
static area(width, height) {
return width * height;
}
}
console.log(Square.area(10, 10)) // 100
class Square {
constructor(width, height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
// 프로토타입 메서드
area() {
return this.width * this.height;
}
}
const square = new Square(10, 10)
console.log(square.area()) // 100프로토타입 메서드와 정적 메서드는 내부의 this 바인딩이 다르다
- 따라서 메서드 내부에서 인스턴스 프로퍼티를 참조할 필요가 있다면
this를 사용해야 하며,- 이러한 경우 프로포타입 메서드로 정의해야 하지만
- 메서드 내부에서 인스턴스 프로퍼티를 참조해야 할 필요가 없다면
this를 사용하지 않게된다 - 물론 메서드 내부에서
this를 사용하지 않더라도 프로토타입 메서드로 정의할 수 있지만 - 반드시 인스턴스를 생성한 다음 인스턴스로 호출해야 하므로
this를 사용하지 않는 메서드는 정적 메서드로 정의하는 것이 좋다
💡 표준 빌트인 객체인
Math,Number,JSON,Object,Reflect등은 다양한 정적 메서드를 가지고 있어
애플리케이션 전역에서 사용할 유틸리티 함수다
✔️ 25.5.5 클래스에서 정의한 메서드 특징
function키워드를 생략한 메서드 축약 표현을 사용한다.- 객체 리터럴과는 다르게 클래스에 메서드를 정의할 때는 콤마가 필요 없다.
- 암묵적으로
strict mode로 실행된다. for ... in문이나Object.keys메서드 등으로 열거할 수 없다. 즉, 프로퍼티의 열거 가능 여부를 나타내며, 불리언 값을 갖는 프로퍼티 어트리뷰트[[Enumerable]]의 값이false다.- 내부 메서드
[[Construct]]를 갖지 않는non-constructor다. 따라서new연산자와 함께 호출할 수 없다.
25.6 클래스의 인스턴스 생성 과정
new 연산자와 함께 클래스를 호출하면 생성자 함수와 마찬가지로 클래스의 내부 메서드 [[Construct]]가 호출된다.
이때 아래의 과정을 거쳐 인스턴스가 생성된다
- 인스턴스 생성과
this바인딩new연산자와 함께 클래스를 호출하면constructor내부 코드가 실행되기에 앞서 암묵적으로 빈 객체가 생성- 이때 클래스가 생성한 인스턴스의 프로토타입으로 클래스의
prototype프로퍼티가 가리키는 객체가 설정 - 그리고 암묵적으로 생성된 빈 객체, 즉 인스턴스는
this에 바인딩된다
- 인스턴스 초기화
this에 바인딩되어 있는 인스턴스에 프로퍼티를 추가하고constructor가 인수로 전달받은 초기값으로 인스턴스의 프로퍼티 값을 초기화한다
- 인스턴스 반환
- 클래스의 모든 처리가 끝나면 완성된 인스턴스가 바인딩된
this가 암묵적으로 반환된다.
- 클래스의 모든 처리가 끝나면 완성된 인스턴스가 바인딩된
25.7 프로퍼티
✔️ 25.7.1 인스턴스 프로퍼티
인스턴스 프로퍼티는 constructor 내부에서 정의해야 한다
constructor 내부에서 this에 추가한 프로퍼티는 언제나 클래스가 생성한 인스턴스의 프로퍼티가 된다.
class Person {
constructor(name) {
// 인스턴스 프로퍼티
this.name = name;
}
}
const me = new Person('April');
console.log(me); // Person {name: "April"}
class Person {
constructor(name) {
// 인스턴스 프로퍼티
this.name = name; // name 프로퍼티는 public하다.
}
}
const me = new Person('April');
// name은 public하다.
console.log(me.name); // April✔️ 25.7.2 접근자 프로퍼티
접근자 프로퍼티는
- 자체적으로는 값
[[Value]]을 갖지 않고 - 다른 데이터 프로퍼티의 값을 읽거나 저장할 때 사용하는 접근자 함수, 즉
getter함수와setter함수로 구성되어 있다.getter는 인스턴스 프로퍼티에 접근할 때setter는 인스턴스 프로퍼티에 값을 할당할 때
getter는 이름 그대로 무언가를 취득할 때 사용하므로 반드시 무언가를 반환해야 하고setter는 무언가를 프로퍼티에 할당 해야할 때 사용하므로 반드시 매개변수가 있어야 한다.setter는 단 하나의 값만 할당받기 때문에 단 하나의 매개변수만 선언할 수 있다.
- 클래스의 메서드는 기본적으로 프로토타입 메서드가 된다. 따라서 클래스의 접근자 프로퍼티 또한 인스턴스 프로퍼티가 아닌 프로토타입의 프로퍼티가 된다.
✔️ 25.7.3 클래스 필드 정의 제안
클래스 필드(필드 또는 멤버)란
- 클래스 기반 객체지향 언어에서 클래스가 생성할 인스턴스의 프로퍼티를 가리키는 용어다.
- 참고: 자바에서는 마치 클래스 내부에서 변수처럼 사용된다
- 자바스크립트의 클래스 몸체에는 메서드만 선언할 수 있다. 따라서 자바와 유사하게 클래스 필드를 선언하면 문법 에러가 발생한다
- 하지만 최신 브라우저(Chrome 72 이상) 또는 최신 Node.js에서 실행하면 문법 에러가 발생하지 않고 정상 동작하는데, 그 이유는
- 자바스크립트에서도 새로운 표준 사양인 Class field declarations가 제안되었다. 이로 인해 인스턴스 프로퍼티를 정의하는 방식은 두 가지가 되었다.
- 인스턴스를 생성할 때 외부 초기값으로 클래스 필드를 초기화할 필요가 있다면
constuctor에서 인스턴스 프로퍼티를 정의하는 기존방식을 사용하고,
- 인스턴스를 생성할 때 외부 초기값으로 클래스 필드를 초기화할 필요가 없다면
- 기존의
constructor에서 인스턴스 프로퍼티를 정의하는 방식과 - 클래스 필드 정의 제안 모두 사용할 수 있다.
- 기존의
- 인스턴스를 생성할 때 외부 초기값으로 클래스 필드를 초기화할 필요가 있다면
✔️ 25.7.4 private 필드 정의 제안
자바스크립트는 캡슐화를 완전하게 지원하지 않는다
-
private,public,protected키워드와 같은 접근 제한자를 지원하지 않는다. 언제나public이다 -
하지만 자바스크립트에서도
private필드를 정의할 수 있는 새로운 표준 사양이 제안되어 있다. (아직 표준 사양은 아님.. 그러나 최신 브라우저와 최신 Node.js에서는 이미 구현되어 있음)private필드의 선두에는#을 붙여준다.private필드를 참조할 때도#을 붙여주어야 한다.private필드는 클래스 내부에서만 참조할 수 있다. 또한,private필드는 반드시 클래스 몸체에 정의해야 한다.
접근 가능성 publicprivate클래스 내부 O O 자식 클래스 내부 O X 클래스 인스턴스를 통한 접근 O X
class Person {
// private 필드 정의
#name = '';
constructor(name) {
// private 필드 참조
this.#name = name;
}
}
const me = new Person('Lee');
// private 필드 #name은 클래스 외부에서 참조할 수 없다.
console.log(me.#name);
// SyntaxError: Private field '#name' must be declared in an enclosing class✔️ 25.7.5 static 필드 정의 제안
static public필드, static private 필드, static private 메서드를 정의할 수 있는 새로운 표준 사양인 Static class features가 제안되어 있다.
** **
class MyMath {
// static public 필드 정의
static PI = 22 / 7;
// static private 필드 정의
static #num = 10;
// static 메서드
static increment() {
return ++MyMath.#num;
}
}
console.log(MyMath.PI); // 3.142857142857143
console.log(MyMath.increment()); // 1125.8 상속에 의한 클래스 확장
✔️ 25.8.1 클래스 상속과 생성자 함수 상속
상속에 의한 클래스 확장은
- 기존 클래스를 상속받아 새로운 클래스를 확장(
extends)하여 정의하는 것
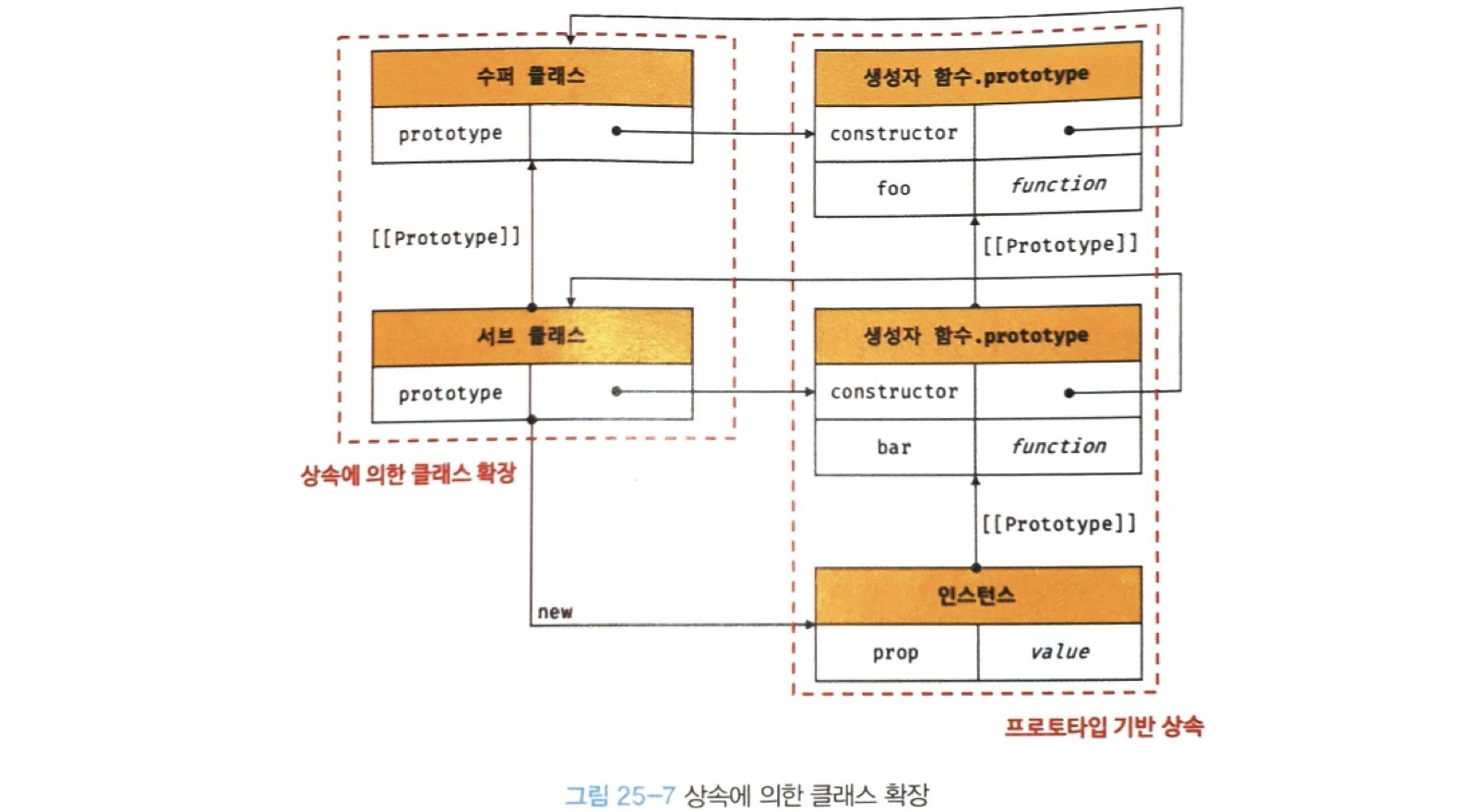
클래스와 생성자 함수는 인스턴스를 생성할 수 있는 함수라는 점에서 매유 유사하지만,
- 클래스는 상속을 통해 기존 클래스를 확장할 수 있는 문법이 기본적으로 제공되지만
- 클래스는 상속을 통해 다른 클래스를 확장할 수 있는 문법인
extends키워드가 기본적으로 제공된다.
- 클래스는 상속을 통해 다른 클래스를 확장할 수 있는 문법인
- 생성자 함수를 그렇지 않다
✔️ 25.8.2 extends 키워드
상속을 통해 클래스를 확장하려면 extends 키워드를 사용하여 상속받을 클래스를 정의한다.
// 수퍼(베이스/부모)클래스
class Base {}
// 서브(파생/자식)클래스
class Derived extends Base {}- 상속을 통해 확장된 클래스를 서브클래스라 부르고,
- 서브클래스에게 상속된 클래스를 수퍼클래스라 부른다
extends 키워드의 역할은
- 수퍼클래스와 서브클래스 간의 상속 관계를 설정하는 것
- 클래스도 프로토타입을 통해 상속관계를 구현한다.
- 수퍼클래스와 서브클래스는 인스턴스의 프로토타입 체인뿐 아니라 클래스 간의 프로토타입 체인도 생성한다.
- 이를 통해 프로토타입 메서드, 정적 메서드 모두 상속이 가능하다.
✔️ 25.8.3 동적 상속
extends 키워드는
- 클래스뿐만 아니라
- 생성자 함수를 상속받아 클래스를 확장할 수도 있다
- 단,
extends키워드 앞에는 반드시 클래스가 와야 한다
- 단,
// 생성자 함수
function Base (a) {
this.a = a;
}
// 생성자 함수를 상속받는 서브클래스
class Derived extends Base {}
const derived = new Derived(1);
console.log(derived); // Derived {a: 1}extends 키워드 다음에는
- 클래스뿐만이 아니라
[[Construct]]내부 메서드를 갖는 함수 객체로 평가될 수 있는 모든 표현식을 사용할 수 있다.- 이를 통해 동적으로 상속받을 대상을 결정할 수 있다.
function Base1() {}
class Base2 {}
let condition = true;
// 조건에 따라 동적으로 상속 대상을 결정하는 서브클래스
class Derived extends (condition ? Base1 : Base2) {}
const derived = new Derived();
console.log(derived); // Derived {}
console.log(derived instanceof Base1); // true
console.log(derived instanceof Base2); // false✔️ 25.8.4 서브 클래스의 constructor
- 클래스에서
constructor를 생략하면 암묵적으로 빈 객체가 정의되는데 - 서브클래스에서
constructor를 생략하면 클래스에 다음과 같은constructor가 암묵적으로 정의된다.args는new연산자와 함께 클래스를 호출할 때 전달한 인수의 리스트다
- 수퍼클래스에서
consturctor를 생략하면 빈 객체가 생성된다.- 서브클래스 마찬가지로
constructor를 생략하면 클래스에 다음과 같은constructor가 암묵적으로 정의된다.
- 서브클래스 마찬가지로
constructor(...args) { super(...args); }✔️ 25.8.5 super 키워드
super 키워드는
- 함수처럼 호출할 수도 있고
this와 같이 식별자처럼 참조할 수 있는
특수한 키워드다
super 키워드는 이렇게 동작한다.
super를 호출하면 수퍼클래스의constructor(super-constructor)를 호출super를 참조하면 수퍼클래스의 메서드를 호출할 수 있다
◼️ super 호출
super를 호출하면 수퍼클래스의 constructor(super-constructor)를 호출한다
super 호출할 때 주의할 점은,
- 서브클래스에서
constructor을 생략하지 않는 경우 서브클래스의constructor에서는 반드시super를 호출해야 한다.
class Base {}
class Derived extends Base {
constructor() {
// ReferenceError: Must call super constructor in derived class before accessing 'this' or returning from derived constructor
console.log('constructor call');
}
}
const derived = new Derived();- 서브클래스의
constructor에서super를 호출하기 전에는this를 참조할 수 없다.
class Base {}
class Derived extends Base {
constructor() {
// ReferenceError: Must call super constructor in derived class before accessing 'this' or returning from derived constructor
this.a = 1;
super();
}
}
const derived = new Derived(1);super는 반드시 서브클래스의constructor에서만 호출한다. 서브클래스가 아닌 클래스의constructor나 함수에서super를 호출하면 에러가 발생한다.
class Base {
constructor() {
super(); // SyntaxError: 'super' keyword unexpected here
}
}
function Foo() {
super(); // SyntaxError: 'super' keyword unexpected here
}◼️ super 참조
메서드 내에서 super를 참조하면 수퍼클래스의 메서드를 호출할 수 있다.
- 서브 클래스의 프로토타입 메서드 내에서 super.sayHi는 수퍼클래스의 프로토타입 메서드 sayHi를 가리킨다.
// 수퍼클래스
class Base {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
sayHi() {
return `Hi! ${this.name}`;
}
}
// 서브클래스
class Derived extends Base {
sayHi() {
// super.sayHi는 수퍼클래스의 프로토타입 메서드를 가리킨다.
return `${super.sayHi()}. how are you doing?`;
}
}
const derived = new Derived('April');
console.log(derived.sayHi()); // Hi! April. how are you doing?- 서브클래스의 정적 메서드 내에서 super.sayHi는 수퍼클래스의 정적 메서드 sayHi를 가리킨다.
// 수퍼클래스
class Base {
static sayHi() {
return 'Hi!';
}
}
// 서브클래스
class Derived extends Base {
static sayHi() {
// super.sayHi는 수퍼클래스의 정적 메서드를 가리킨다.
return `${super.sayHi()} how are you doing?`;
}
}
console.log(Derived.sayHi()); // Hi! how are you doing?✔️ 25.8.6 상속 클래스의 인스턴스 생성 과정
상속 관계에 있는 두 클래스가 어떻게 협업하며 인스턴스를 생성하는지 이해하면 super를 더욱 명확하게 이해할 수 있다
직사각형을 추상화한 Rectangle 클래스와 상속을 통해 Rectangle 클래스를 확장한 ColorRectangle 클래스다
// 수퍼클래스
class Rectangle {
constructor(width, height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
getArea() {
return this.width * this.height;
}
toString() {
return `width = ${this.width}, height = ${this.height}`;
}
}
// 서브클래스
class ColorRectangle extends Rectangle {
constructor(width, height, color) {
super(width, height);
this.color = color;
}
// 메서드 오버라이딩
toString() {
return super.toString() + `, color = ${this.color}`;
}
}
const colorRectangle = new ColorRectangle(2, 4, 'red');
console.log(colorRectangle); // ColorRectangle {width: 2, height: 4, color: "red"}
// 상속을 통해 getArea 메서드를 호출
console.log(colorRectangle.getArea()); // 8
// 오버라이딩된 toString 메서드를 호출
console.log(colorRectangle.toString()); // width = 2, height = 4, color = red서브클래스 colorRectangle이 new 연산자와 함께 호출되면 다음 과정을 통해 인스턴스를 생성한다.
1. 서브클래스의 super 호출
자바스크립트 엔진은 클래스를 평가할 때 수퍼클래스와 서브클래스를 구분하기 위해 base 또는 derived를 값으로 갖는 내부 슬롯 [[ConstructorKind]]를 갖는다
base: 다른 클래스를 상속받지 않는 클래스, 그리고 생성자 함수derived: 다른 클래스를 상속받는 서브 클래스
이를 통해 new 연산자와 함께 호출되었을 때의 동작이 구분된다.
- 다른 클래스를 상속받지 않는 클래스(그리고 생성자 함수)는
new연산자가 함께 호출되었을 때 암묵적으로 빈 객체, 즉 인스턴스를 생성하고- 이를
this에 바인딩한다.
- 하지만 서브클래스는
- 자신이 직접 인스턴스를 생성하지 않고 수퍼클래스에게 인스턴스 생성을 위임한다.
이것이 바로 서브클래스의constructor에서 반드시super를 호출해야 하는 이유다.
- 자신이 직접 인스턴스를 생성하지 않고 수퍼클래스에게 인스턴스 생성을 위임한다.
2. 수퍼클래스의 인스턴스 생성과 this 바인딩
수퍼클래스 constructor의 내부의 코드가 실행되기 이전에 암묵적으로 빈 객체를 생성하고
- 이 빈 객체가(아직 완성되진 않았지만) 클래스가 생성한 인스턴스다
- 크리고 암묵적으로 생성된 빈 객체, 즉 인스턴스는
this에 바인딩된다.- 따라서 수퍼클래스의
constructor의 내부의this는 생성된 인스턴스(빈 객체)를 가리킨다. - 이 때
new와 함께 호출된 함수를 가리키는new.target은 서브클래스를 가리킨다.- 따라서 인스턴스는
new.target이 가리키는 서브클래스가 생성한 것으로 처리된다.
- 따라서 인스턴스는
- 따라서 수퍼클래스의
- 따라서 위의 코드에서 보면, 생성된 인스턴스의 프로토타입은
- 수퍼클래스의
prototype프로퍼티가 가리키는 객체(Rectangle.prototype)가 아니라
new.target, 즉 서브클래스의prototype프로퍼티가 가리키는 객체(ColorRectangle.prototype)이다.
- 수퍼클래스의
3. 수퍼클래스의 인스턴스 초기화
수퍼클래스의 constructor가 실행되어 this에 바인딩되어 있는 인스턴스를 초기화한다.
- 즉,
this에 바인딩 되어 있는 인스턴스에 프로퍼티를 추가하고 constructor가 인수로 전달받은 초기값으로 인스턴스의 프로퍼티를 초기화한다.
4. 서브클래스 constructor로의 복귀와 this 바인딩
super의 호출의 종료되고 제어 프름이 서브클래스 constructor로 돌아온다.
- 이때
super가 반환한 인스턴스가this에 바인딩된다. - 서브클래스는 별도의 인스턴스를 생성하지 않고
super가 반환한 인스턴스를this에 바인딩하여 그대로 사용한다. - 이처럼
super가 호출되지 않으면 인스턴스가 생성되지 않으며, this바인딩도 할 수 없다.- 서브클래스의
constructor에서super를 호출하기 전에는this를 참조할 수 없는 이유가 바로 이 때문이다.
5. 서브클래스의 인스턴스 초기화
super 호출 이후,
- 서브클래스의
consstructor에 기술되어 있는 인스턴스 초기화가 실행된다. - 즉,
this에 바인딩되어 있는 인스턴스에 프로퍼티를 추가하고constructor가 인수로 전달받은 초기값으로 인스턴스의 프로퍼티를 초기화한다.
6. 인스턴스 반환
클래스의 모든 처리가 끝나면 완성된 인스턴스가 바인딩된 this가 암묵적으로 반환된다.
✔️ 25.8.7 표준 빌트인 생성자 함수 확장
표준 빌트인 객체 또한 [[Construct]] 내부 메서드를 갖는 생성자 함수이므로 extends 키워드를 사용하여 확장할 수 있다.
