TileMaching 만들기

- 핵심 클래스 구조
- UMyGameInstance : 전역 게임 상태(점수, 남은 이동 횟수)를 관리하는 역할을 합니다.
게임의 전반적인 상태를 관리하며, 레벨 간에도 데이터가 유지됩니다. - ATile : 퍼즐 타일 개체를 나타내며, 색상 또는 모양과 같은 정보를 가집니다.
- ATileGrid : 타일의 그리드를 관리하며, 타일 생성, 매칭, 타일 이동 등을 담당합니다.
- AMatch3GameMode : 게임의 진행 상태를 관리하고, 게임 로직을 조율합니다.
- UMyGameInstance : 전역 게임 상태(점수, 남은 이동 횟수)를 관리하는 역할을 합니다.
MyGameInstance.h
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "Engine/GameInstance.h"
#include "MyGameInstance.generated.h"
UCLASS()
class PUZZLESTUDY_API UMyGameInstance : public UGameInstance
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
UMyGameInstance();
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, BlueprintReadWrite, Category = "Game Data")
int32 PlayerScore;
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, BlueprintReadWrite, Category = "Game Data")
int32 RemainingMoves;
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Game Functions")
void AddScore(int32 Points);
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Game Funcitons")
void DecreaseMoves();
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Game Functions")
void ResetGameState();
};MyGameInstance.cpp
#include "MyGameInstance.h"
UMyGameInstance::UMyGameInstance()
{
PlayerScore = 0;
RemainingMoves = 30;
}
void UMyGameInstance::AddScore(int32 Points)
{
PlayerScore += Points;
}
void UMyGameInstance::DecreaseMoves()
{
if (RemainingMoves > 0)
{
RemainingMoves--;
}
}
void UMyGameInstance::ResetGameState()
{
PlayerScore = 0;
RemainingMoves = 30;
}Tile.h
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "GameFramework/Actor.h"
#include "Tile.generated.h"
UCLASS()
class PUZZLESTUDY_API ATile : public AActor
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
// Sets default values for this actor's properties
ATile();
protected:
// Called when the game starts or when spawned
virtual void BeginPlay() override;
public:
// Called every frame
virtual void Tick(float DeltaTime) override;
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, BlueprintReadWrite, Category = "Tile Properties")
FColor TileColor;
bool IsMatching(ATile* OtherTile);
void ProcessDataInParallerl();
};Tile.cpp
#include "Tile.h"
#include "Async\ParallelFor.h"
// Sets default values
ATile::ATile()
{
// Set this actor to call Tick() every frame. You can turn this off to improve performance if you don't need it.
PrimaryActorTick.bCanEverTick = true;
}
// Called when the game starts or when spawned
void ATile::BeginPlay()
{
Super::BeginPlay();
}
// Called every frame
void ATile::Tick(float DeltaTime)
{
Super::Tick(DeltaTime);
}
bool ATile::IsMatching(ATile* OtherTile)
{
return TileColor == OtherTile->TileColor;
}
void ATile::ProcessDataInParallerl()
{
TArray<int32> DataArray;
DataArray.Init(0, 100);
ParallelFor(DataArray.Num(), [&](int32 Index)
{
DataArray[Index] = Index * 2;
}
);
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT("ParallerlForFinish"));
}TileGrid.h
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings.
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "GameFramework/Actor.h"
#include "TileGrid.generated.h"
class ATile;
UCLASS()
class PUZZLESTUDY_API ATileGrid : public AActor
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
// Sets default values for this actor's properties
ATileGrid();
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, BlueprintReadWrite, Category = "Grid")
int32 GridWidth;
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, BlueprintReadWrite, Category = "Grid")
int32 GridHeigh;
UPROPERTY()
TArray<ATile*> TileArray;
void InitializeGrid();
// 특정 타일의 위치를 얻는 함수
ATile* GetTile(int32 x, int32 y) const;
// 특정 타일의 위치를 설정하는 함수
void SetTile(int32 x, int32 y, ATile* Tile);
};TileGrid.cpp
#include "TileGrid.h"
#include "Tile.h"
#include "Async\ParallelFor.h"
// Sets default values
ATileGrid::ATileGrid()
{
// Set this actor to call Tick() every frame. You can turn this off to improve performance if you don't need it.
PrimaryActorTick.bCanEverTick = true;
GridWidth = 8;
GridHeigh = 8;
TileArray.SetNum(GridWidth * GridHeigh);
// 1차원 배열로 메모리 할당 8*8 형태
}
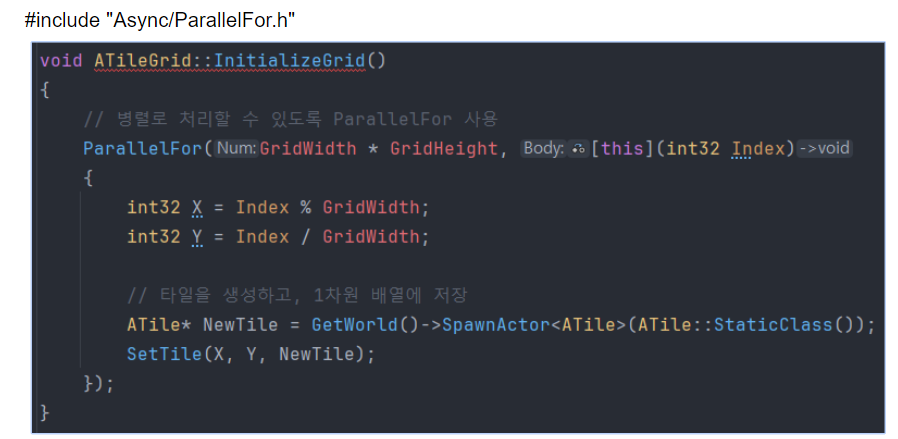
void ATileGrid::InitializeGrid()
{
// for문을 돌면서 타일 그리드 그리기
for (int32 x = 0; x < GridWidth; ++x)
{
for (int32 y = 0; y < GridHeigh; ++y)
{
// 타일을 생성하고, 1차원 배열에 저장
ATile* NewTile = GetWorld()->SpawnActor<ATile>(ATile::StaticClass());
SetTile(x, y, NewTile);
}
}
}
ATile* ATileGrid::GetTile(int32 x, int32 y) const
{
if (x < 0 || x >= GridWidth || y < 0 || y >= GridHeigh)
{
// 유효하지 않은 좌표 거리
return nullptr;
}
return TileArray[y * GridWidth + x];
}
void ATileGrid::SetTile(int32 x, int32 y, ATile* Tile)
{
if (x >= 0 && x < GridWidth && y >= 0 && y < GridHeigh)
{
TileArray[y * GridWidth + x] = Tile;
}
}Match3GameMmode.h
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "GameFramework/GameModeBase.h"
#include "Match3GameMmode.generated.h"
UCLASS()
class PUZZLESTUDY_API AMatch3GameMmode : public AGameModeBase
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
virtual void BeginPlay() override;
};Match3GameMmode.cpp
#include "Match3GameMmode.h"
#include "MyGameInstance.h"
#include "TileGrid.h"
#include "Kismet\GameplayStatics.h"
void AMatch3GameMmode::BeginPlay()
{
Super::BeginPlay();
// 어느 클래스에서 가져오던 GetWorld내에 하나밖에 없으므로 내가 만든 MyGameInstance 이다
UMyGameInstance* GameInstance = Cast<UMyGameInstance>(UGameplayStatics::GetGameInstance(GetWorld()));
if (GameInstance)
{
GameInstance->ResetGameState();
}
ATileGrid* TileGrid = GetWorld()->SpawnActor<ATileGrid>(ATileGrid::StaticClass());
if (TileGrid)
{
TileGrid->InitializeGrid();
}
}비동기 처리( Asynchronous )
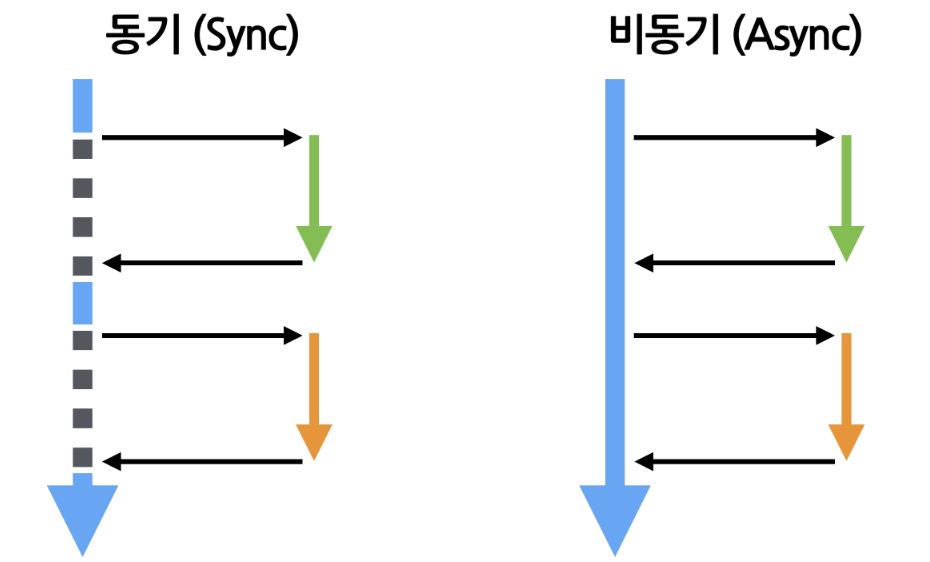
- 동기 처리 (Synchronous)
- 동기는 코드가 순차적으로 실행되는 방식을 의미합니다.
- 한 작업이 완료되기 전까지 다음 작업이 시작되지 않습니다.
- 예를 들어, 함수 호출이 끝나야만 다음 줄 코드가 실행됩니다.
- 코드의 흐름이 직관적이어서 디버깅하기 쉽습니다.
- 비동기 처리 (Asynchronous)
- 비동기는 작업이 완료될 때까지 기다리지 않고, 다른 작업을 동시에 수행할 수 있는 방식을 의미합니다.
- 긴 시간이 걸리는 작업을 비동기로 처리하면, 다른 작업이 해당 작업의 완료를 기다리지 않고 계속 진행됩니다.
- 긴 시간 소요 작업(파일 입출력, 네트워크, AI 처리 등)을 처리할 때 프로그램의 응답성을 유지할 수 있습니다.
멀티 비동기 처리 ( ParallelFor )
-
ParallelFor의 기본 개념
- ParallelFor는 반복 작업(루프)을 여러 스레드로 분할하여 병렬로 처리하는 함수입니다.
- 일반적인 for 루프는 순차적으로 실행되지만, ParallelFor는 각각의 루프가 서로 독립적이라면 동시에 여러 스레드에서 실행할 수 있도록 최적화합니다.
-
멀티스레딩을 활용한 타일 생성 최적화
-
ParallelFor의 장점
- 성능 최적화 : 멀티코어 CPU에서 병렬로 작업을 처리하기 때문에, 타일 그리드와 같이 작업이 큰 경우 전체 처리 시간을 줄일 수 있습니다.
- 자동 스레드 분배 : ParallelFor는 시스템의 CPU 코어 개수에 맞춰 자동으로 작업을 분배합니다. 따라서 복잡한 스레드 관리가 필요 없습니다.
- 확장성 : 작업 크기가 증가할수록 멀티스레딩의 이점이 더욱 커지며, 큰 그리드를 처리할 때 특히 유리합니다.
-
주의 사항
- 스레드 안전성 :
- ParallelFor 내부에서 실행되는 모든 작업은 스레드 안전성을 보장해야 합니다. 즉, 다른 스레드와 충돌하지 않도록 주의해야 합니다.
- 예를 들어, 여러 스레드에서 동시에 동일한 데이터를 수정하려고 할 때는 동기화(mutex, critical section 등)를 고려해야 합니다.
- 게임 스레드에서의 작업 제한 :
- 언리얼 엔진의 특정 함수(예: SpawnActor 등)는 게임 스레드에서만 호출되어야 합니다.
- ParallelFor 내부에서 이러한 함수를 호출할 때는 게임 스레드에서만 실행되도록 보장해야 합니다. 이를 위해 작업을 게임 스레드로 전달하는 것이 필요할 수 있습니다.
- AsyncTask(ENamedThreads::GameThread, ...)를 사용하여 게임 스레드에서 필요한 작업을 처리할 수 있습니다.
- 예를 들어, 타일 생성은 반드시 게임 스레드에서 실행해야 하므로 다음과 같이 수정할 수 있습니다.
- 스레드 안전성 :
ParallelFor 기본 문법
ParallelFor(int32 Num, [&](int32 Index)
{
// 반복될 작업 로직 작성
});ParallelFor 예제
TArray<int32> DataArray;
DataArray.Init(0, 100);
// 배열의 각 요소를 병렬로 수정하는 예시
ParallelFor(DataArray.Num(), [&](int32 Index)
{
DataArray[Index] = Index * 2;
});비동기 타일 생성 ( Asynchronous Tile Creation )
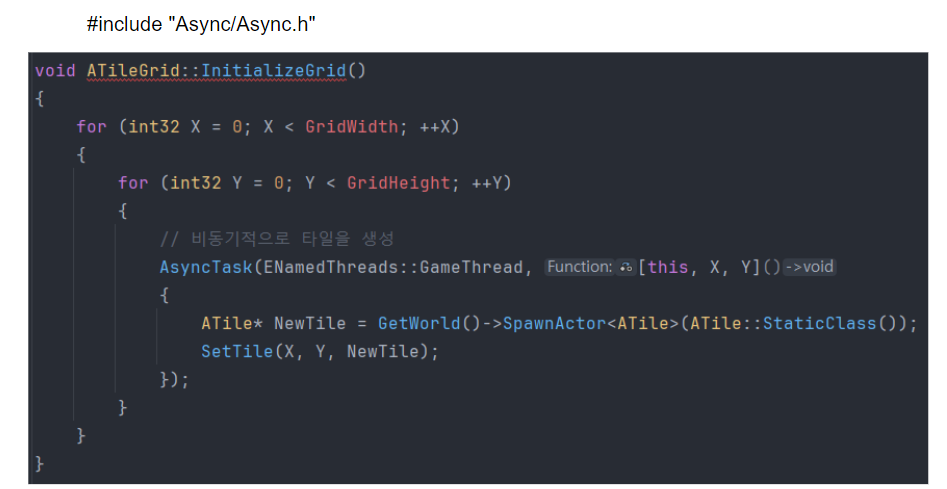
-
AsyncTask
- Unreal Engine에서 비동기 작업을 쉽게 수행할 수 있도록 제공하는 템플릿 기반의 유틸리티이다
- 주로 긴 시간이 걸리는 작업(예: 파일 입출력, AI 계산, 네트워크 요청 등)을 게임의 메인 스레드를 막지 않고 비동기로 처리할 때 사용
- AsyncTask는 새로운 스레드에서 작업을 실행한 뒤, 해당 작업이 완료되면 메인 스레드에서 결과를 처리할 수 있도록 합니다.
-
기본 개념
- 비동기 처리 : AsyncTask는 백그라운드 스레드에서 작업을 수행하여 게임의 메인 스레드가 다른 작업을 계속할 수 있게 합니다.
- 콜백 : 작업이 완료되면 메인 스레드에서 후속 작업(콜백 함수)을 호출하여 결과를 처리하거나 UI를 업데이트할 수 있습니다.
AsyncTask 기본예제
AsyncTask(ENamedThreads::ThreadType, TaskFunction);
// 비동기 처리 ( 비동기 타입, 실행될 함수 ) - ThreadType : 작업을 수행할 스레드 타입을 지정합니다. 일반적으로 백그라운드 스레드나 게임 스레드로 작업을 지정할 수 있습니다.
- TaskFunction : 해당 스레드에서 수행할 함수를 람다식으로 전달합니다.
AsyncTask 사용 예제
#include "Async/Async.h"
void MyAsyncTask()
{
// 비동기 작업을 수행
Async(ENameThreads::AnyBackgroundThreadNormalTask, []()
{
// 백그라운드 스레드에서 실행될 작업
FPlatformProcess::Sleep(2.0f); // 예: 2초 동안 대기 (긴 작업을 시뮬레이션)
int32 Result = 42;
// 메인 스레드에서 후속 작업 실행
Async(ENameThreads::GameThread, [Result]()
{
// 메인 스레드에서 결과를 처리
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT("AsyncTask completed! Result: %d"), Result);
});
});
}- 주요 스레드 타입
- ENamedThreads::AnyBackgroundThreadNormalTask : 일반적인 백그라운드 스레드에서 작업을 처리합니다. 시간이 오래 걸리는 작업을 비동기적으로 처리하고 싶을 때 사용합니다.
- ENamedThreads::GameThread : 작업을 메인 게임 스레드에서 실행합니다. UI 업데이트나 게임 객체 조작 등 메인 스레드에서만 처리해야 하는 작업이 있을 때 사용합니다.
ENameThreads
- ENameThreads는 주로 작업이 실행될 스레드나 스레드 그룹을 명시적으로 지정할 때 사용됩니다. Unreal Engine은 여러 스레드와 스레드 풀(Task Graph)을 사용하여 작업을 효율적으로 분산 처리합니다.
- 주요 역할
- 스레드에 이름을 지정하거나 특정 스레드 그룹을 정의합니다.
- 예시
- 메인 게임 스레드, 렌더 스레드, 또는 Task Graph에서 정의된 특정 스레드 그룹.
- 사용 상황
- 주로 FGraphEvent나 FGraphEventRef와 같은 Task Graph 작업에서 사용되며, 특정 작업을 특정 스레드에서 실행되도록 명시할 때 활용됩니다.
ENameThreads 예시 코드// 특정 스레드에서 실행될 작업 정의 FGraphEventRef Task = FFunctionGraphTask::CreateAndDispatchWhenReady([]() { UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT("This is running on a named thread!")); }, TStatId(), nullptr, ENamedThreads::GameThread);
- ENamedThreads::GameThread : 이 코드는 작업을 메인 게임 스레드에서 실행하도록 지정합니다.
EAsyncExecution
- EAsyncExecution은 Unreal Engine에서 비동기 작업의 실행 방식을 정의하는 열거형입니다. 비동기 작업을 스레드풀에서 실행하거나 특정 스레드에서 실행하도록 설정할 때 사용됩니다. Async 함수를 호출할 때 이 열거형을 사용해 작업을 어느 스레드 그룹에서 처리할지 결정할 수 있습니다.
- 주요 역할
- 비동기 작업의 실행 환경을 설정합니다.
- 예시
- 메인 스레드, 백그라운드 스레드, 스레드풀 등.
사용 상황- Async 함수를 호출할 때 어떤 스레드에서 비동기 작업이 실행될지 선택합니다.
EAsyncExecution 예시 코드Async(EAsyncExecution::ThreadPool, []() { // 백그라운드 스레드풀에서 실행할 작업 UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT("This is running in the thread pool!")); });
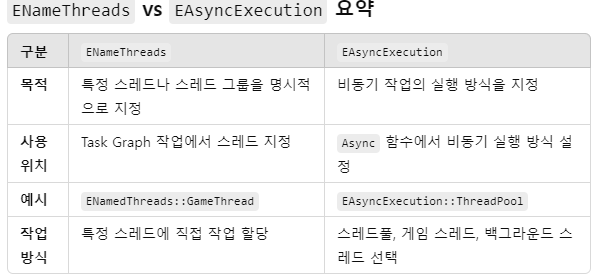
- 결론
- ENameThreads 는 특정 스레드나
스레드 그룹에서작업을 실행하도록 명시할 때 사용합니다. - EAsyncExecution은 비동기 작업의 실행 환경을 정의하여, 다양한 스레드풀 또는
특정 스레드에서작업을 처리할 수 있게 해줍니다 - 예시로 ENameThreads for문을 비동기 돌릴때 for문 작업이 시작하고 해당 각각의 for문안에 작은 작업을 행하는 하나의 작은 또다른 비동기 작업을 특정 지을땐, EAsyncExecution를 사용한다
- ENameThreads 는 특정 스레드나
쓰레드 풀( Thread Pool )
미리 생성된 스레드의 모음으로, 여러 개의 작업(작업 단위)을 동시에 처리할 수 있도록 하는 멀티스레딩 기법
- 쓰레드 풀의 개념
스레드 재사용: 새로운 작업이 있을 때마다 새로운 스레드를 생성하지 않고, 쓰레드 풀에서 이미 생성된 스레드를 할당해 작업을 수행합니다.작업 대기열: 작업이 생기면 큐(queue)에 추가되고, 풀에 있는 스레드들이 이를 가져가서 처리합니다. 모든 스레드가 바쁘면 새로운 작업은 대기열에 쌓이게 됩니다.성능 최적화: 스레드의 생성과 소멸은 비용이 많이 들기 때문에, 미리 생성된 스레드를 재사용함으로써 시스템 자원을 아끼고 처리 시간을 줄일 수 있습니다.- 쓰레드 풀이 필요한 이유
스레드 생성 오버헤드 감소: 스레드를 계속 생성하고 제거하는 과정은 비용이 많이 드므로, 풀을 사용하면 이 과정을 줄여 성능을 최적화할 수 있습니다.자원 관리: 많은 스레드가 동시에 생성되면 시스템 자원을 과도하게 사용할 수 있습니다. 풀의 크기를 제한하여 자원 사용을 효율적으로 관리할 수 있습니다.작업 분배: 작업을 자동으로 분배하여, 여러 작업을 동시에 처리하거나 특정 작업이 지연되는 것을 방지할 수 있습니다.
Unreal Engine 쓰레드 풀 예시
#include "Async/Async.h"
void ProcessHeavyTask()
{
// 쓰레드 풀에서 작업을 실행
Async(EAsyncExecution::ThreadPool, []()
{
// 이 작업은 쓰레드 풀의 스레드 중 하나에서 실행됩니다
FPlatformProcess::Sleep(2.0f); // 긴 작업 시뮬레이션
int32 Result = 100;
// 메인 스레드에서 후속 작업 실행
Async(EAsyncExecution::TaskGraphMainThread, [Result]()
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT("Heavy task completed! Result: %d"), Result);
});
});
}- 예시 설명
EAsyncExecution::ThreadPool: 비동기 작업을 쓰레드 풀에서 실행하도록 지정합니다. 여기서 풀에 있는 스레드 중 하나가 할당되어 작업을 처리합니다.긴 작업: 작업이 길어지더라도 쓰레드 풀이 사용되기 때문에 메인 스레드의 성능에 영향을 주지 않습니다.작업 완료 후 콜백: 작업이 완료되면 결과를 메인 스레드에서 처리할 수 있도록 EAsyncExecution::TaskGraphMainThread를 사용합니다.
- 쓰레드 풀의 장점
성능 최적화: 스레드 생성 및 소멸 비용이 줄어들어 성능이 향상됩니다.안정성: 시스템 자원을 제한적으로 사용하여, 과도한 스레드 생성으로 인한 시스템 불안정성을 방지합니다.확장성: 여러 작업을 효율적으로 분산 처리할 수 있어, 게임에서 대규모 연산을 수행할 때 유용합니다.
