문제를 이해하고 있다면 바로 풀이를 보면 됨
전체 코드로 바로 넘어가도 됨
마음대로 번역해서 오역이 있을 수 있음
Problem
정렬된 연결 리스트 head가 주어질 때, 중복되는 모든 요소를 삭제하고, 각 요소가 오직 한번만 나타나게 해라. 정렬된 상태로 연결 리스트를 반환해라.
Example
#1
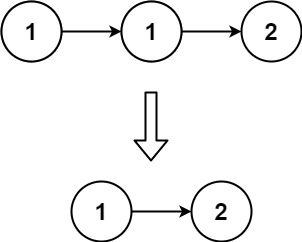
Input: head = [1, 1, 2]
Output: [1, 2]
#2
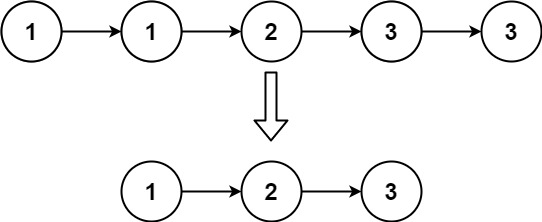
Input: head = [1, 1, 2, 3, 3]
Output: [1, 2, 3]
Constraints
- 연결 리스트의 노드 수는 [0, 300] 범위에 있다.
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
- 리스트는 오름차순으로 정렬되어 있는 것을 보장한다.
Solved
이 문제 상단에 주석으로 ListNode 클래스가 주석으로 나와있다.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/메서드의 매개변수로 ListNode head를 받는다. head가 null이거나 head의 next가 null이면 head를 반환한다.
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
}head의 next가 있다면 deleteDuplicates()를 호출하고 인자로 head.next를 전달해서 head.next를 바꿔준다.
head.next = deleteDuplicates(head.next);만약 head의 val과 head의 next의 val이 같다면 head.next를 반황한다.
if(head.val == head.next.val) {
return head.next;
}다 빠져나왔다면 마지막에 head를 반환한다.
return head;All Code
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
head.next = deleteDuplicates(head.next);
if(head.val == head.next.val){
return head.next;
}
return head;
}
}