Chapter 2. Implementation Algorithm
 알고리즘 스터디 2주차의 주제는 구현이다.
알고리즘 스터디 2주차의 주제는 구현이다.
Implementation이란?

구현은 머릿속으로 어찌저찌 해결하는 방법을 떠올릴 수 있으나 코드로 표현하는 것이 어려운 문제 유형을 칭한다.
문제풀이
이번 주는 컨베이어 벨트 위의 로봇(골드 4), 연구소(골드 4)라는 문제들을 풀어보았다.
컨베이어 벨트 위의 로봇(골드 4)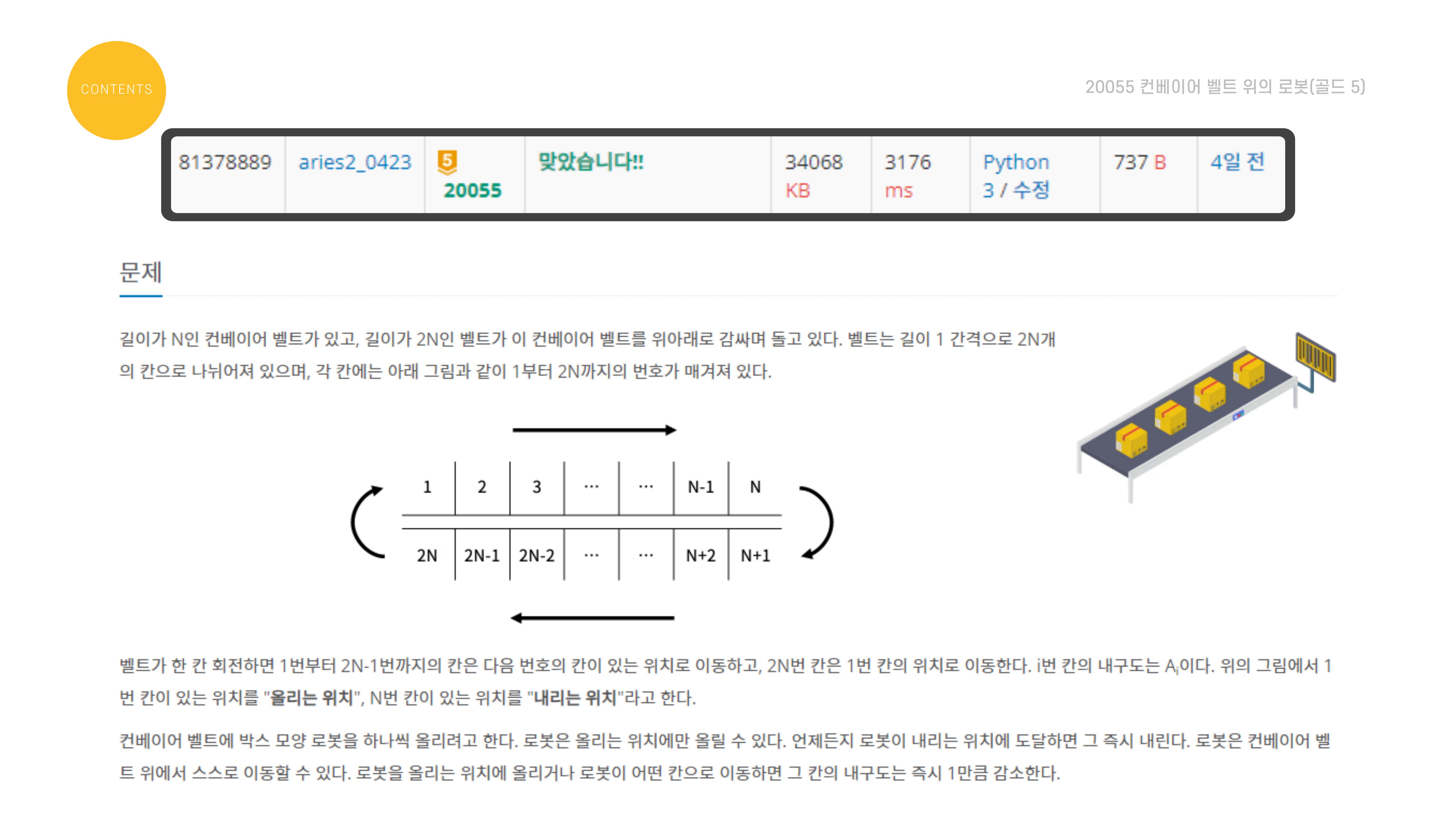
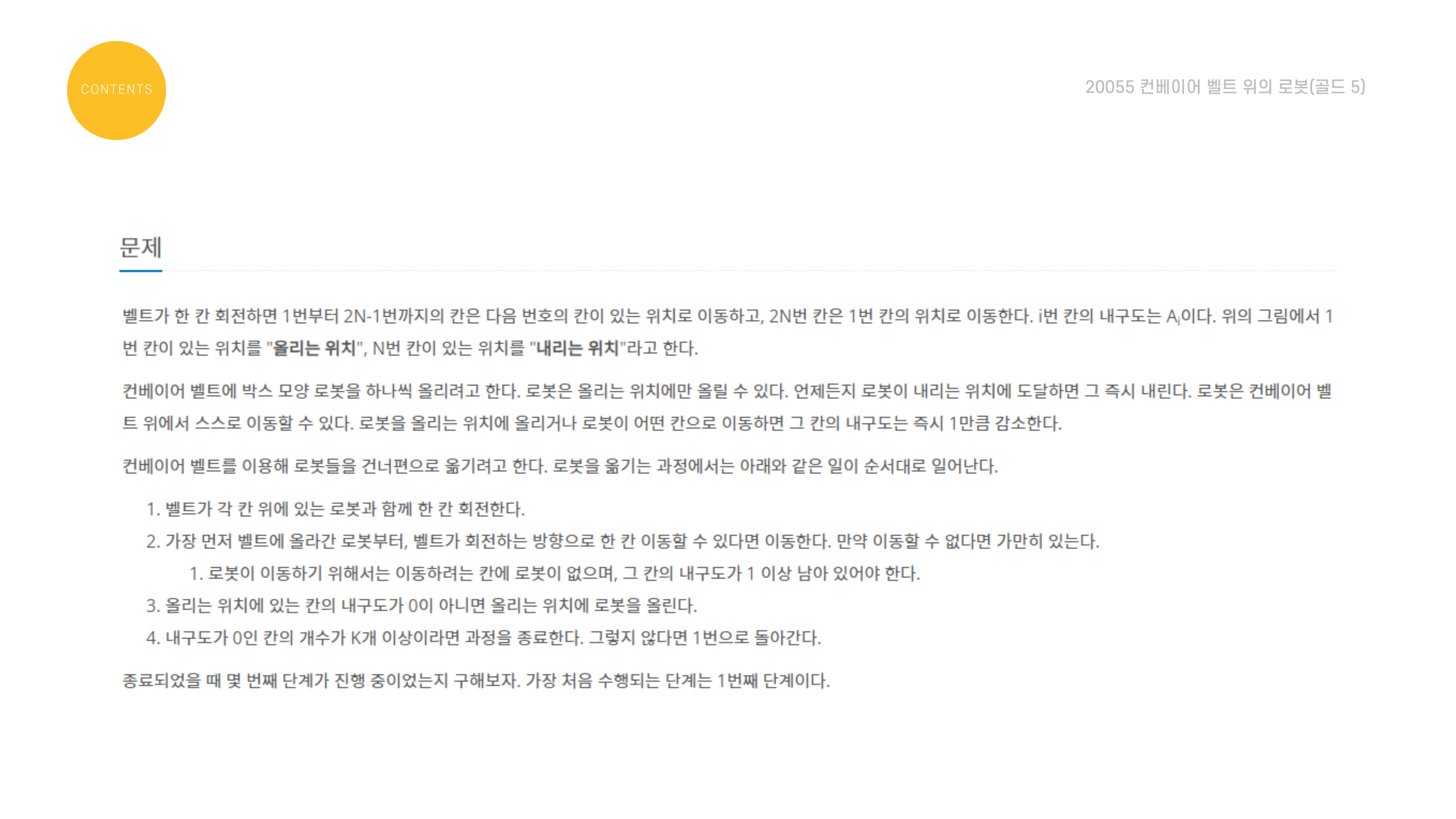
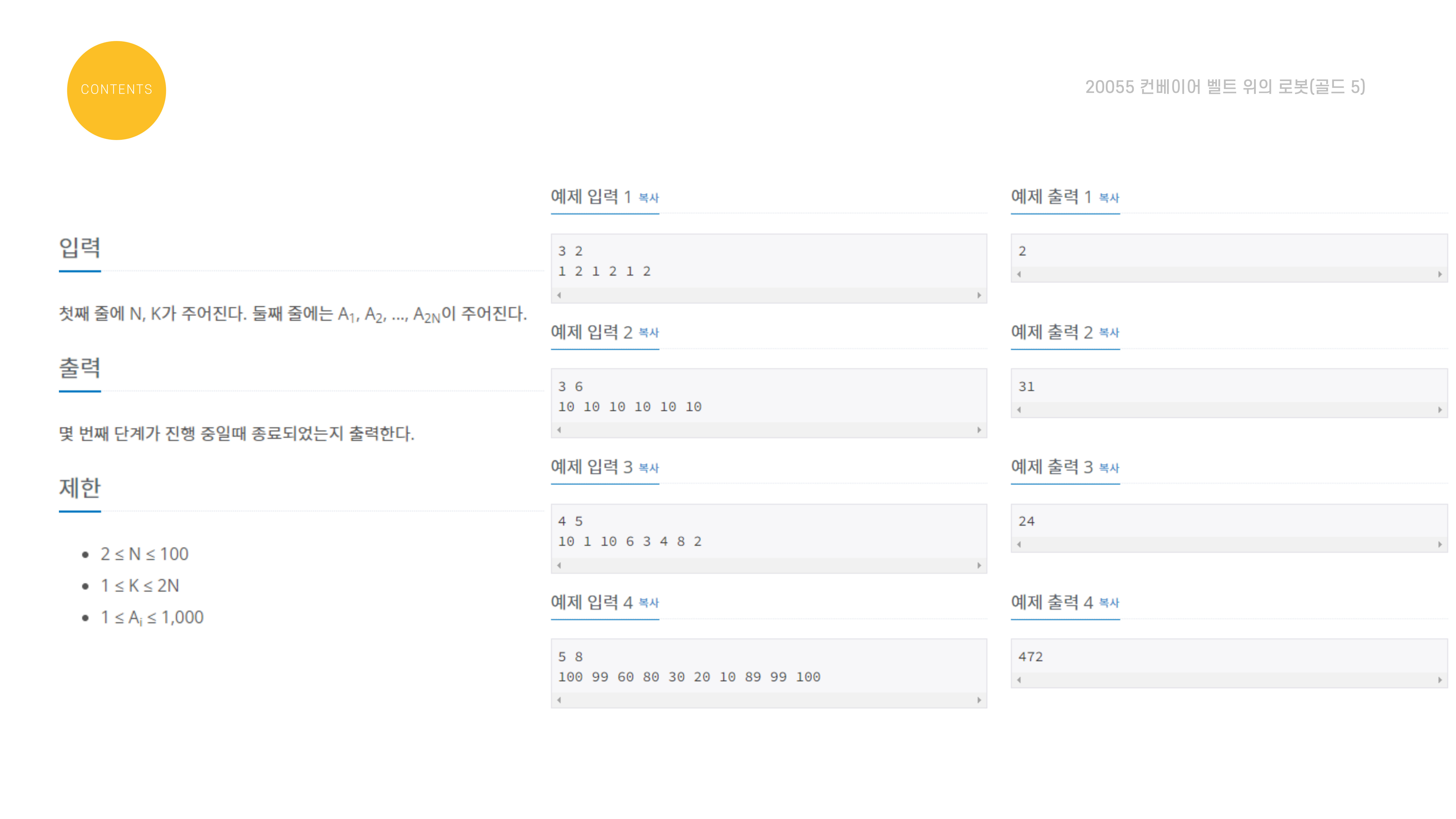
문제 설명은 다음과 같다.
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/20055
 rotate()는 배열을 시계 방향(default)으로 회전시켜 저장하는 기능을 가지고 있다. 벨트의 내구도와 로봇의 위치를 나타내는 배열인 durability와 robots를 회전하는 벨트에 맞춰 rotate()를 사용하면 쉽게 풀 수 있다.
rotate()는 배열을 시계 방향(default)으로 회전시켜 저장하는 기능을 가지고 있다. 벨트의 내구도와 로봇의 위치를 나타내는 배열인 durability와 robots를 회전하는 벨트에 맞춰 rotate()를 사용하면 쉽게 풀 수 있다.
전체코드
import sys
from collections import deque
input = sys.stdin.readline
N, K = map(int, input().split())
durability = deque(list(map(int, input().split())))
robots = deque([False]*N)
level = 0
while 1:
level += 1
# 과정 1
durability.rotate()
robots.rotate()
robots[N-1] = False
# 과정 2
for i in range(N-2, 0, -1):
if robots[i] == True:
if robots[i+1] == False and durability[i+1] > 0:
robots[i+1] = True
robots[i] = False
durability[i+1] -= 1
robots[N-1] = False
# 과정 3
if durability[0] != 0:
robots[0] = True
durability[0] -= 1
# 과정 4
if durability.count(0) >= K:
break
print(level)
연구소(골드 4)
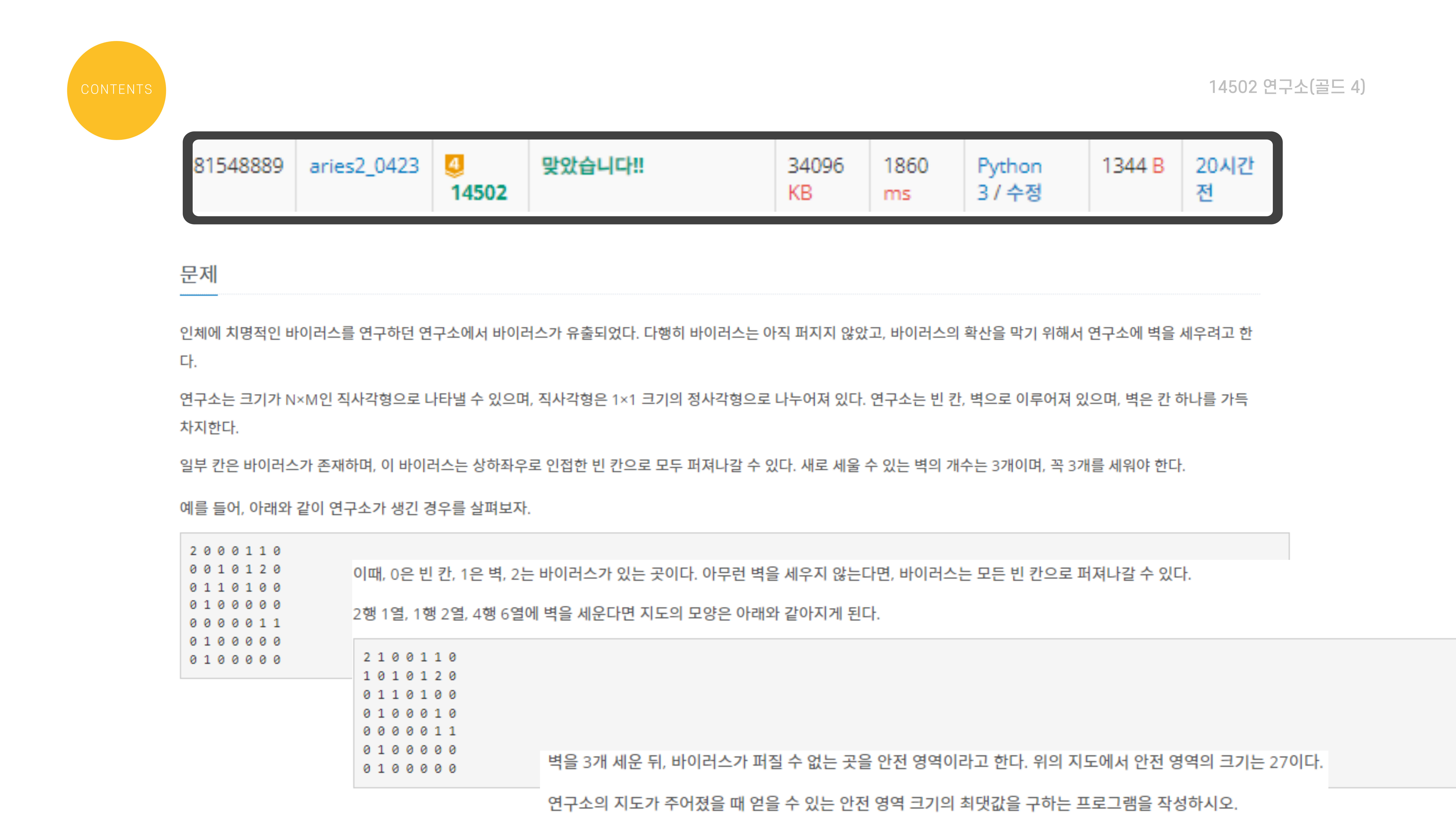
 문제 설명은 다음과 같다.
문제 설명은 다음과 같다.
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/14502
 빈 공간에 대해서 empth_rooms에 좌표를 저장하고, empty_rooms에서 combinations를 통해 3개씩 뽑는 모든 경우에 대해서 벽을 세우고 바이러스를 퍼뜨려 보았다. 바이러스를 퍼뜨린 방법은 아래와 같다.
빈 공간에 대해서 empth_rooms에 좌표를 저장하고, empty_rooms에서 combinations를 통해 3개씩 뽑는 모든 경우에 대해서 벽을 세우고 바이러스를 퍼뜨려 보았다. 바이러스를 퍼뜨린 방법은 아래와 같다.
 3개의 벽을 세운 해당 경우에 대해 BFS를 통해 바이러스를 퍼뜨리고 안전 영역의 수를 세어 임시로 저장했다. 그리고 combinations를 통한 모든 경우에 대해서 answer에 저장된 값보다 현재 임시로 저장한 값이 크면 임시값을 answer에 저장하는 방식을 사용했다.
3개의 벽을 세운 해당 경우에 대해 BFS를 통해 바이러스를 퍼뜨리고 안전 영역의 수를 세어 임시로 저장했다. 그리고 combinations를 통한 모든 경우에 대해서 answer에 저장된 값보다 현재 임시로 저장한 값이 크면 임시값을 answer에 저장하는 방식을 사용했다.
전체 코드
from itertools import combinations
from collections import deque
N, M = map(int, input().split())
graph = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(N)]
answer = 0
dx = [0, 0, -1, 1]
dy = [1, -1, 0, 0]
def virus(graph):
tmp_graph = [row[:] for row in graph]
virus_loc_queue = deque()
for i in range(N):
for j in range(M):
if tmp_graph[i][j]==2:
virus_loc_queue.append((i, j))
while virus_loc_queue:
x, y = virus_loc_queue.popleft()
for i in range(4):
new_x, new_y = x + dx[i], y + dy[i]
if 0<=new_x<N and 0<=new_y<M and tmp_graph[new_x][new_y]==0:
tmp_graph[new_x][new_y] = 2
virus_loc_queue.append((new_x, new_y))
return sum(row.count(0) for row in tmp_graph)
empty_rooms = []
for i in range(N):
for j in range(M):
if graph[i][j]==0:
empty_rooms.append((i, j))
for walls in combinations(empty_rooms, 3):
for x, y in walls:
graph[x][y]=1
answer = max(answer, virus(graph))
for x, y in walls:
graph[x][y]=0
print(answer)