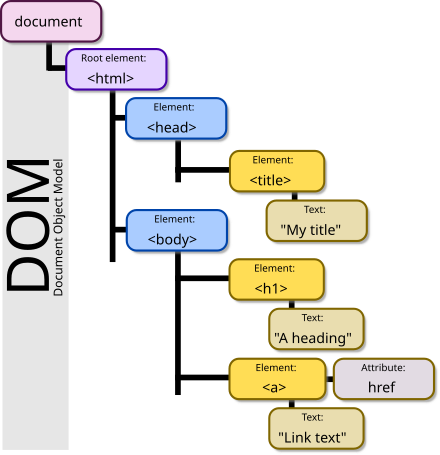
1. DOM이란?
DOM(Document Object Model)은 웹 브라우저가 HTML, XML 문서를 읽어들이고 이를 메모리 내에서 트리 구조의 객체 모델로 만드는 표준 모델입니다.
즉, 브라우저는 HTML 문서를 단순한 텍스트가 아니라 객체들의 집합(트리)으로 변환하여, 자바스크립트를 통해 이 객체들을 동적으로 조작할 수 있도록 합니다.
2. DOM의 기본 구조
DOM은 계층적(Tree) 구조로 구성됩니다.
HTML 문서가 계층적 구조를 가지므로, 브라우저는 이를 노드(Node)들의 집합인 트리로 전환할 수 있습니다.
2.1 DOM 트리 구성 요소
DOM은 여러 종류의 노드(Node)로 구성된 계층적 트리 구조입니다.
브라우저는 HTML 문서를 파싱하면서 아래와 같은 다양한 노드들을 생성합니다.
2.1.1 Document 노드
- DOM 트리의 최상위(root) 노드입니다.
- 문서 전체를 나타내는 루트 노드이며, 자바스크립트에서는 document라는 전역 객체로 제공됩니다.
- DOM 탐색이나 조작은 대부분 document 객체에서 시작됩니다.
console.log(document); // Document 전체 출력
console.log(document.body); // <body> 요소 접근
console.log(document.getElementByID("main")); // 특정 요소 접근2.1.2 Element 노드
- HTML의 각 태그(
<body>, <p>, <div>, <span> ... 등)는 모두 Element 노드입니다. - DOM 조작에서 가장 많이 다루는 노드이며, 스타일, 내용, 이벤트 등 거의 모든 상호작용이 이 노드를 통해 이루어집니다.
- 자바스크립트로 선택 후 속성과 메서드를 이용해 조작할 수 있습니다.
<!--html-->
<p id="greeting">안녕하세요</p>// JavaScript
const p = document.getElementById("greeting");
console.log(p.tagName); // "P"2.1.3 Text 노드
- 텍스트 노드는 HTML 요소 안에 포함된 실제 문자열 데이터를 나타냅니다.
- 즉,
<p>Hello</p>에서 "Hello"는 Text 노드입니다. - 텍스트는 요소의 textContent 또는 innerText 속성을 통해 읽거나 수정할 수 있습니다.
<!--html-->
<p id="greeting">안녕하세요</p>// JavaScript
const p = document.getElementById("greeting");
console.log(p.firstChild.nodeType); // 3 (Text 노드)
console.log(p.firstChild.nodeValue); // "안녕하세요"| nodeType 값 | 의미 |
|---|---|
| 1 | Element 노드 (<div>, <p>, ... 등) |
| 3 | Text 노드 |
| 8 | Comment 노드 |
2.1.4 Attribute 노드
- HTML 태그가 갖는 id, class, href, style 같은 속성(attribute)들도 DOM 트리에서 Attribute 노드로 존재합니다.
- 하지만 실무나 자바스크립트 코드에서는 이 속성들을 별도의 “노드”처럼 다루기보다는,
그냥 해당 요소의 "속성값(Property)"으로 간단하게 접근하는 방식을 사용합니다.
<!--html-->
<a id="link" href="https://example.com">Example</a>Attribute 노드처럼 다루는 방식 (거의 안 씀)
// JavaScript
const link = document.getElementById("link");
const attrs = link.attributes;
console.log(attrs["href"].value); // "https://example.com"일반적인 접근 방식 (가장 많이 씀)
console.log(link.href); // "https://example.com"
console.log(link.getAttribute("href")); // "https://example.com"- link.href → DOM 요소의 속성(property)으로 직접 접근
- getAttribute("href") → HTML 속성 값을 문자열로 반환
- attributes → 실제 DOM 트리 상의 Attribute 노드 목록 (거의 안 씀)
2.1.5 Comment 노드
- HTML 문서 내의 주석(
<!--주석입니다-->)도 DOM의 노드로 저장됩니다. - 일반적인 경우 사용자에게 보이지 않으며, DOM 탐색을 통해 접근하거나 삭제할 수 있습니다.
<!-- html -->
<!-- 여기는 설명 주석입니다. -->// JavaScript
const comments = document.body.childNodes;
for (let node of comments) {
if (node.nodeType === Node.COMMENT_NODE) {
console.log("주석 내용: ", node.nodeValue);
}
}2.2 예시로 보는 DOM 트리
<body>
<h1></h1>
<p><span></span></p>
</body>이 HTML은 DOM 트리에서는 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있습니다.
Document
└── html
└── body
├── h1 (id="title")
│ └── Text: "Hello World"
└── p
├── Text: "이것은 "
├── span
│ └── Text: "DOM 예제"
└── Text: " 입니다."- 각 HTML 태그는 Element 노드가 되고, 태그 사이에 있는 글자들은 Text 노드로 구분되어 저장됩니다.
3. DOM 노드의 종류와 역할
3.1 Document 노드
- HTML 문서 전체를 대표하는 루트 노드
- DOM 트리 탐색과 조작의 출발점이 되는 객체
- 자바스크립트에서는 전역 객체인 document로 접근 가능
console.log(document); // 전체 DOM 트리 출력
console.log(document.body); // <body> 요소 접근
console.log(document.title); // 현재 문서의 제목(title) 가져오기3.2 Element 노드
- HTML 태그 하나하나가 모두 Element 노드로 표현됨
- 실질적으로 가장 많이 조작하는 노드
- 자바스크립트에서는 속성과 메서드를 통해 다양한 조작 가능
- 주요 속성
- id, className, innerHTML, textContent, style 등
- 주요 메서드
- getAttribute(), setAttribute(), appendChild(), removeChild() 등
<p id="firstP">Sample Text</p>위 요소(firstP)는 자바스크립트에서 다음과 같이 다룰 수 있습니다.
let firstP = document.getElementById("firstP");
console.log(firstP.tagName); // "P"
console.log(firstP.textContent); // "Sample Text"
firstP.style.color = "red"; // 글자색 변경3.3 Text 노드
- HTML 요소 안에 있는 실제 텍스트 문자열을 담는 노드
- 텍스트 노드는 일반적으로 Element 노드의 자식 노드로 존재
- DOM 조작 시 텍스트는 .textContent 또는 .nodeValue로 읽거나 수정할 수 있음
<!--html-->
<p id="firstP">Sample Text</p>// JavaScript
let textNode = firstP.firstChild; // Text 노드
console.log(textNode.nodeType); // 3 (Text 노드)
console.log(textNode.nodeValue); // "Sample Text"
textNode.nodeValue = "수정된 텍스트"; // 텍스트 내용 변경3.4 Attribute 노드
- HTML 태그의 속성(id, class, style 등)을 나타내는 노드
- DOM 트리 내부에는 독립된 Attribute 노드로 존재
- 하지만 실무나 자바스크립트 코드에서는 이 속성들을 별도의 “노드”처럼 다루기보다는,
그냥 해당 요소의 "속성값(Property)"으로 간단하게 접근하는 방식을 사용
<!--html-->
<a id="link" href="https://example.com">예제</a>// JavaScript
let link = document.getElementById("link");
// 일반적인 접근 방법 (속성처럼 다룸)
console.log(link.href); // 전체 URL 반환
console.log(link.getAttribute("href")); // "https://example.com"
// 속성 변경
link.setAttribute("title", "타이틀입니다");참고: attributes 속성을 통해 Attribute 노드 자체에 접근할 수도 있지만, 실무에서는 거의 사용하지 않음
console.log(link.attributes["href"].value); // "https://example.com"3.5 Comment 노드
- HTML 안의 주석도 DOM에서는 하나의 노드로 처리됨
- 화면에는 표시되지 않지만, DOM 트리를 탐색하면 찾을 수 있음
- 일반적으로 잘 사용하지는 않지만, 동적으로 주석을 처리해야 할 일이 있다면 사용할 수 있음
<!--html-->
<!-- 이것은 주석입니다 -->// JavaScript
const nodes = document.body.childNodes;
for (let node of nodes) {
if (node.nodeType === Node.COMMENT_NODE) {
console.log("주석 내용:", node.nodeValue);
}
}4. DOM의 생성 과정
웹 브라우저는 HTML 문서를 단순한 텍스트가 아닌, 객체 구조로 변환해 웹 페이지를 화면에 표시합니다. 이 과정에서 DOM(Document Object Model)이 생성됩니다. 전체 흐름은 다음과 같습니다.
4.1 HTML 파싱
- 브라우저는 HTML 문서를 위에서 아래로 한 줄씩 순차적으로 읽어들입니다.
4.2 토큰화
- 각 태그, 속성, 텍스트 등을 작은 단위(토큰)로 나눠서 분석합니다.
- 이 과정을 통해 HTML 요소들이 어떤 구조인지, 어떤 관계인지 판단할 수 있습니다.
4.3 DOM 트리 구성
- 파싱된 토큰들을 바탕으로 DOM 트리를 구성합니다.
이 트리는 HTML 문서의 계층 구조를 객체 형태로 표현한 자료구조입니다. - 이 과정에서
<script>태그를 만나면 브라우저는 해당 자바스크립트를 즉시 실행합니다.
→ 이때 DOM을 읽거나 조작할 수 있습니다.
4.4 렌더 트리 생성
- DOM 트리와 함께, CSS 정보로부터 CSSOM(CSS Object Model)도 생성됩니다.
- DOM + CSSOM을 결합하면 → Render Tree(렌더 트리)가 됩니다.
- 브라우저는 렌더 트리를 기반으로 요소들의 위치(Layout)를 계산하고,
그 다음 화면에 그리기(Paint) 과정을 거쳐 사용자에게 페이지를 보여줍니다.
5. DOM 조작의 필요성과 활용
DOM을 자바스크립트로 조작할 수 있다는 것은 곧, 웹 페이지의 구조나 내용을 실시간으로 동적으로 변경할 수 있다는 것을 의미합니다.
사용자와의 상호작용, 실시간 업데이트, 조건부 렌더링 등 인터랙티브한 웹 페이지를 만들기 위해 DOM 조작은 필수적입니다.
활용 예시
1. 컨텐츠 업데이트
서버에서 데이터를 가져온 후, DOM을 통해 웹 페이지 내용을 변경합니다.
document.getElementById("result").textContent = "검색 결과를 가져왔습니다.";2. 인터랙션 처리
버튼 클릭, 입력 등 사용자 이벤트에 따라 스타일이나 내용을 실시간으로 변경합니다.
document.getElementById("btn").onclick = function () {
document.body.style.backgroundColor = "lightyellow";
};3. 요소 동적 생성 및 삭제
document.createElement() 등을 활용하여 새로운 요소를 추가하거나 제거할 수 있습니다.
// 새로운 리스트 항목을 동적으로 추가하는 예시
let newItem = document.createElement("li");
newItem.textContent = "동적 생성된 항목";
document.getElementById("list").appendChild(newItem);정리
- DOM 조작은 웹 페이지를 정적인 문서에서 동적인 애플리케이션으로 변화시키는 핵심입니다.
- 자바스크립트를 통해 DOM을 선택하고, 읽고, 쓰고, 바꾸고, 삭제하고, 이벤트를 연결하는 모든 동작이 가능하며,
- 이 모든 것이 가능한 이유는 브라우저가 HTML을 DOM 구조로 바꿔서 메모리에 저장하고 있기 때문입니다.
