JavaScript, postgreSQL, DBeaver, apollogrphql 이용해서 간단한 백엔드 만들기
- 프론트엔드를 공부 중 이지만 나중에 백엔드 개발자, 프로젝트 매니저분들과 원활한 커뮤니케이션을 백엔드의 기본을 알아야 한다고 하셨다!
- 그래서
JavaScript, postgreSQL, DBeaver, apollogrphql를 이용해서 간단한 백엔드를 만들어보았다.
📔 먼저 index.ts를 만들어서 postgreSQL과 연결하기 위한 코드를 작성해준다.
createConnection({
type: "postgres",
database: "****",
username: "****",
password: "****",
port: ****,
host: "3*.**.***.***",
entities: [__dirname + "/*.postgres.ts"],
logging: true,
synchronize: true,
}).then(() => {
console.log("접속완료!!!");
server.listen({ port: **** });
});
DBeaver 를 실행시켜서 postgreSQL를 선택해서 연결해준다. DBeaver 란 SQL 데이터베이스 관리도구로써 SQL에 담긴 데이터들을 관리 할 수 있다!
📔 TypeORM을 만들어서 type을 지정해준다
import { BaseEntity, Column, Entity, PrimaryGeneratedColumn } from "typeorm";
@Entity()
export default class Product extends BaseEntity {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn("increment")
number!: number;
@Column({ type: "text" })
name!: string;
@Column({ type: "text" })
detail!: string;
@Column({ type: "text" })
seller!: string;
@Column({ type: "integer" })
price!: number;
@Column({ type: "timestamp", default: null, nullable: true })
deletedAt?: Date;
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn("uuid")
_id!: string;
}
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn
자동생성되는 ID값을 표현하는 방식을 아래와 같이 2가지 옵션을 사용할 수 있도록 도와줍니다.
increment: AUTO_INCREMENT를 사용해서 1씩 증가하는 ID를 부여한다. 기본 옵션이다.
uuid: 유니크한 uuid를 사용할 수 있다.
@Column
entity의 속성을 테이블 칼럼으로 표시합니다.
📔 index.ts 작성
- 위에서 만든
TypeORM인 Product 를 import해온다.
import { createConnection } from "typeorm";
import { ApolloServer, gql } from "apollo-server";
import Product from "./Product.postgres";
gql 을 선언해준다. (선언해준것들이 apollogrphql에 뜨게 된다)
const typeDefs = gql`
input CreateProductInput {
name: String
detail: String
price: Int
}
input UpdateProductInput {
name: String
detail: String
price: Int
}
type Return {
_id: String
message: String
number: Int
}
type Product {
number: Int
seller: String
name: String
detail: String
price: Int
_id: String
type Query {
fetchProduct(productId: ID): Product
fetchProducts: [Product]
}
createProduct(
seller: String
createProductInput: CreateProductInput
): Return
updateProduct(
productId: ID
updateProductInput: UpdateProductInput!
): Return
deleteProduct(productId: ID): Return
`;
📔 resolvers 안에 Query와 Mutation을 선언해준다
fetch는 Query 안에, create, update, delete는 Mutation 안에 적어준다.
const resolvers = {
Query: {
fetchProduct: async (_: any, args: any) => {
const result = await Product.findOne({
where: { _id: args.productId, deletedAt: null },
});
return result;
},
fetchProducts: async (_: any, args: any) => {
const result = await Product.find({
where: { deletedAt: null },
});
return result;
},
}
Mutation: {
createProduct: async (_: any, args: any) => {
const result = await Product.insert({
seller: args.seller,
...args.createProductInput,
});
return {
message: "상품이 등록되었습니다.",
number: result.identifiers[0].number,
_id: result.identifiers[0]._id,
};
},
updateProduct: async (_: any, args: any) => {
const result = await Product.update(
{
_id: args.productId,
},
{
...args.updateProductInput,
}
);
return {
message: " 상품이 수정되었습니다.",
_id: args.productId,
};
},
deleteProduct: async (_: any, args: any) => {
await Product.update({ _id: args.productId }, { deletedAt: new Date() });
return { message: "상품을 삭제했습니다.", _id: args.productId };
},
}
}
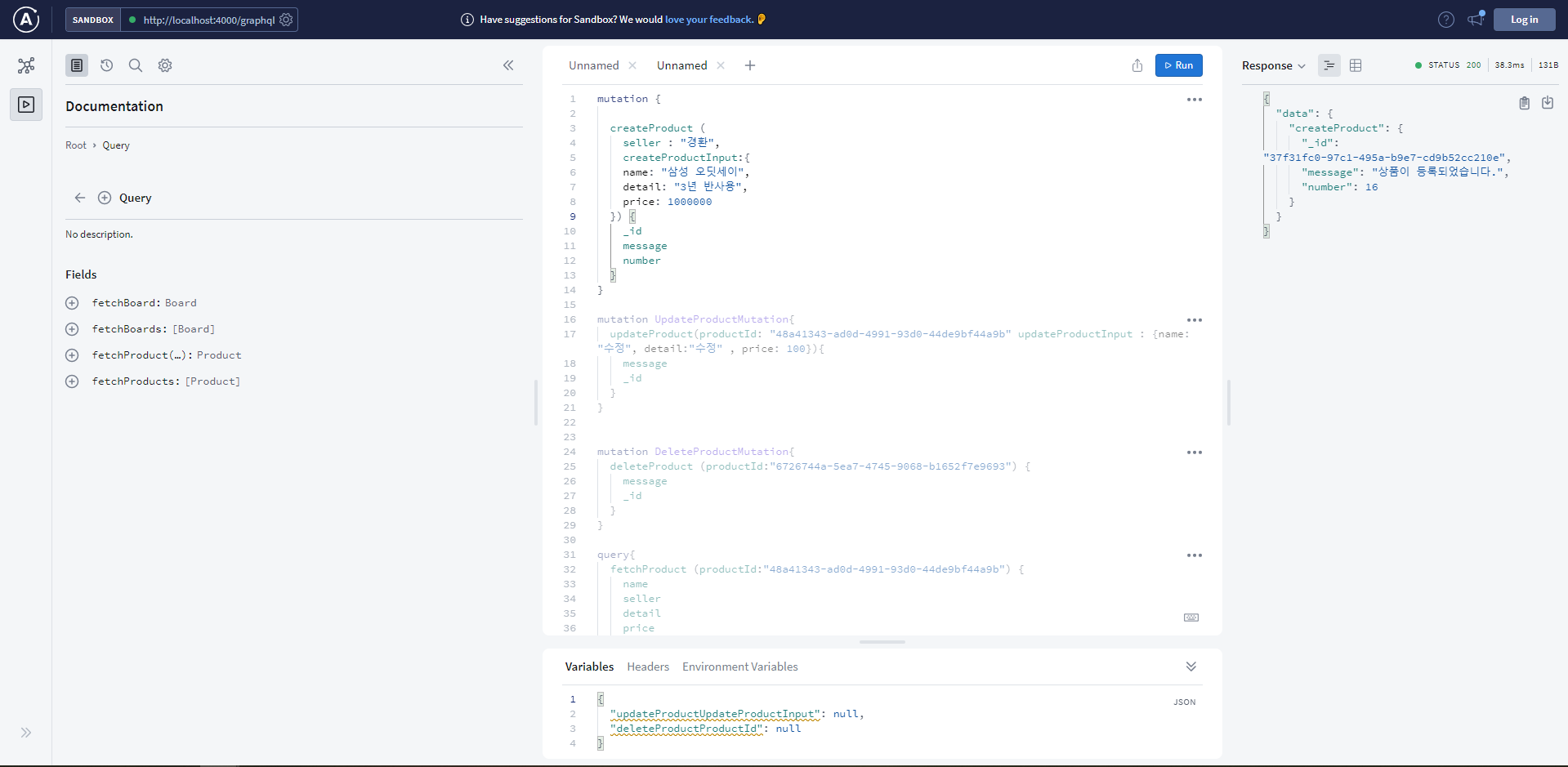
📔 apollographql 을 이용해서 mutation 과 query를 해본다.
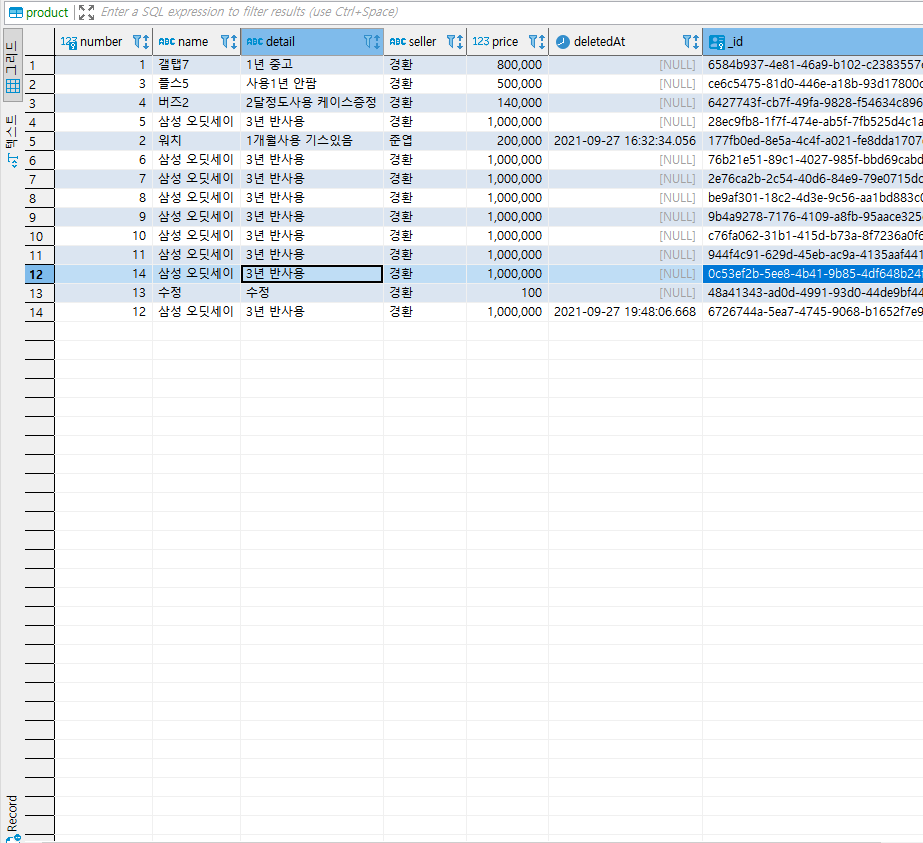
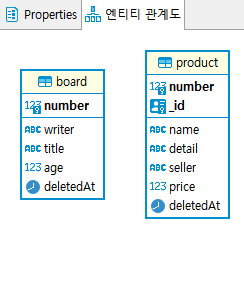
📔 DBeaver로 데이터를 조회, 확인해본다.
📔 데이터가 잘 등록,수정, 삭제, 조회되었다면 완성!!

