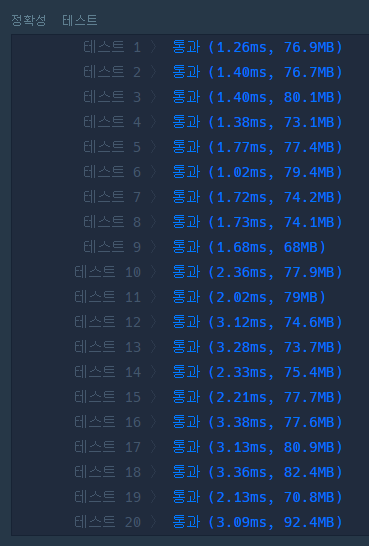
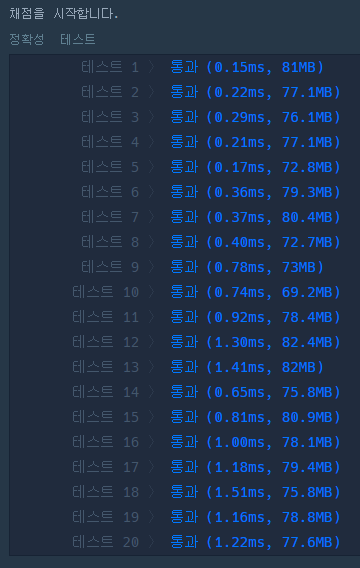
LocalDate 쓰는 것보다 일자로 풀어서 푸는게 훨씬 빠르다.
그냥 일자로 변환하여 계산 후 풀이
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
class Solution {
public int[] solution(String today, String[] terms, String[] privacies) {
int todayDayCounts = getDays(today);
Map<String, String> termMap = new HashMap<>();
for (String term : terms) {
String[] words = term.split(" ");
String alpha = words[0];
String month = words[1];
termMap.put(alpha, month);
}
List<Integer> destroyList = new ArrayList<>();
int idx = 1;
for (String privacy : privacies) {
String[] words = privacy.split(" ");
String date = words[0];
String alpha = words[1];
int monthLimit = Integer.parseInt(termMap.get(alpha));
int limitDayDayCount = getDays(date) + getDays(monthLimit);
if (todayDayCounts >= limitDayDayCount) {
destroyList.add(idx);
}
idx++;
}
int[] answer = new int[destroyList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < destroyList.size(); i++) {
answer[i] = destroyList.get(i);
}
return answer;
}
private int getDays(String strOfDate) {
String[] todayWords = strOfDate.split("\\.");
int y = Integer.parseInt(todayWords[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(todayWords[1]);
int d = Integer.parseInt(todayWords[2]);
return (y * (28 * 12)) + (m * 28) + d;
}
private int getDays(int month) {
return (month * 28);
}
}
LocalDate를 이용하여 풀이
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
class Solution {
public int[] solution(String today, String[] terms, String[] privacies) {
String[] todayWords = today.split("\\.");
int y = Integer.parseInt(todayWords[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(todayWords[1]);
int d = Integer.parseInt(todayWords[2]);
LocalDate tdy = LocalDate.of(y, m, d);
Map<String, String> termMap = new HashMap<>();
for (String term : terms) {
String[] words = term.split(" ");
String alpha = words[0];
String month = words[1];
termMap.put(alpha, month);
}
List<Integer> tempList = new ArrayList<>();
int idx = 1;
for (String privacy : privacies) {
String[] words = privacy.split(" ");
String date = words[0];
String alpha = words[1];
if (isDestroied(tdy, date, termMap.get(alpha))) {
tempList.add(idx);
}
idx++;
}
int[] answer = new int[tempList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < tempList.size(); i++) {
answer[i] = tempList.get(i);
}
return answer;
}
private boolean isDestroied(LocalDate tdy, String date, String period) {
String[] words = date.split("\\.");
int y = Integer.parseInt(words[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(words[1]);
int d = Integer.parseInt(words[2]);
LocalDate getDate = LocalDate.of(y, m, d);
LocalDate afterDate = getDate.plusMonths(Integer.parseInt(period));
// System.out.println(afterDate + " " + tdy);
return afterDate.isBefore(tdy) || afterDate.isEqual(tdy);
}
}