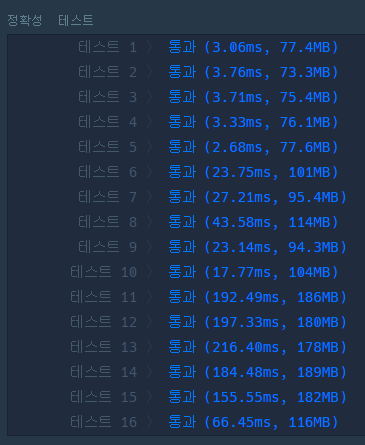
처음에 그냥 sources 에서 destination 까지 bfs로 풀었었다. 그렇게 하면 몇개의 케이스에 대해서 시간초과가 난다.
-> destination에서 sources로의 거리를 구하고 해당 값을 return하면 풀이 완료! [다익스트라 사용함]
다익스트라 사용할때 PriorityQueue를 사용하면 더 빠르다. 나는 오랜만에 풀어서 그런지 PriorityQueue는 생각도 못하고 있었다.
Deque 사용
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
int totalNode;
int gDestination;
Map<Integer, Integer> saveMap;
int[] distances;
public int[] solution(int n, int[][] roads, int[] sources, int destination) {
totalNode = n;
gDestination = destination;
saveMap = new HashMap<>();
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
//n개 만큼 List 생성
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] road : roads) {
graph.get(road[0]).add(road[1]);
graph.get(road[1]).add(road[0]);
}
distances = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(distances, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
dijkstra(sources, graph);
List<Integer> answer = new ArrayList<>();
for (int source : sources) {
answer.add(distances[source] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : distances[source]);
}
return answer.stream().mapToInt(i -> i).toArray();
}
private void dijkstra(final int[] sources, final List<List<Integer>> graph) {
Deque<Info> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.addLast(new Info(gDestination, 0));
distances[gDestination] = 0;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
final Info info = deque.pollFirst();
int curValue = info.value;
int curDistance = info.distance;
if (distances[curValue] != curDistance) {
continue;
}
for (int next : graph.get(curValue)) {
if (distances[next] > curDistance + 1) {
distances[next] = curDistance + 1;
deque.addLast(new Info(next, curDistance + 1));
}
}
}
}
class Info {
int value;
int distance;
Info(int value, int distance) {
this.value = value;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
}
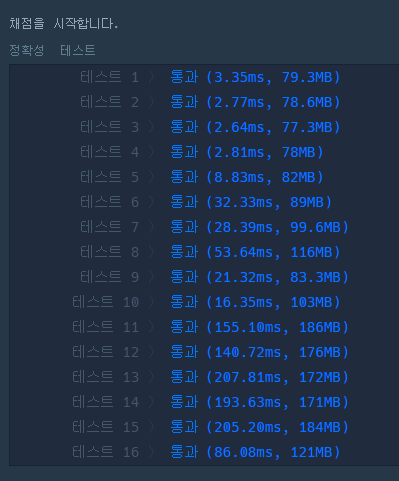
PriorityQueue 사용
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
int totalNode;
int gDestination;
Map<Integer, Integer> saveMap;
int[] distances;
public int[] solution(int n, int[][] roads, int[] sources, int destination) {
totalNode = n;
gDestination = destination;
saveMap = new HashMap<>();
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
//n개 만큼 List 생성
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] road : roads) {
graph.get(road[0]).add(road[1]);
graph.get(road[1]).add(road[0]);
}
distances = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(distances, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
dijkstra(graph);
List<Integer> answer = new ArrayList<>();
for (int source : sources) {
answer.add(distances[source] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : distances[source]);
}
return answer.stream().mapToInt(i -> i).toArray();
}
private void dijkstra(final List<List<Integer>> graph) {
Queue<Info> deque = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Info>() {
@Override
public int compare(final Info o1, final Info o2) {
return Integer.compare(o1.distance, o2.distance);
}
});
deque.add(new Info(gDestination, 0));
distances[gDestination] = 0;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
final Info info = deque.poll();
int curValue = info.value;
int curDistance = info.distance;
if (distances[curValue] != curDistance) {
continue;
}
for (int next : graph.get(curValue)) {
if (distances[next] > curDistance + 1) {
distances[next] = curDistance + 1;
deque.add(new Info(next, curDistance + 1));
}
}
}
}
class Info {
int value;
int distance;
Info(int value, int distance) {
this.value = value;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
}