※문제 풀이의 경우 블로그 등에 작성이 가능하다는 답변을 확인하고 글을 작성했습니다.
혹시 정책이 변경되는 경우 알려주시면 해당 글을 비공개 처리하도록 하겠습니다.
감사합니다.
※ 확인한 글의 출처 : https://career.programmers.co.kr/questions/34688
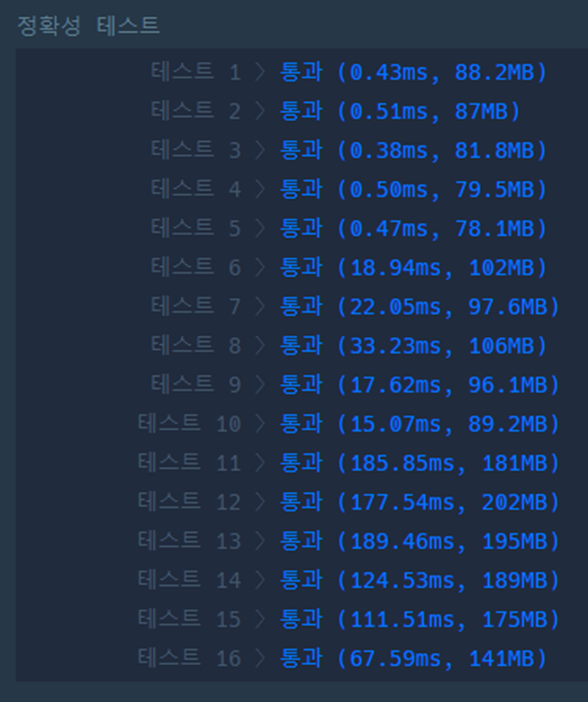
Q1
package com.company;
public class Quiz1 {
static public void main(String[] args) {
int[] X1 = {-2, 3, 0, 2, -5};
int[] X2 = {-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3};
int[] X3 = {-1, 1, -1, 1};
System.out.println(solution(X1) == 2);
System.out.println(solution(X2) == 5);
System.out.println(solution(X3) == 0);
}
static public int solution(int[] number) {
int answer = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < number.length - 2; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < number.length - 1; j++) {
for (int k = j + 1; k < number.length; k++) {
if((number[i] + number[j] + number[k]) == 0){
answer++;
}
}
}
}
return answer;
}
}
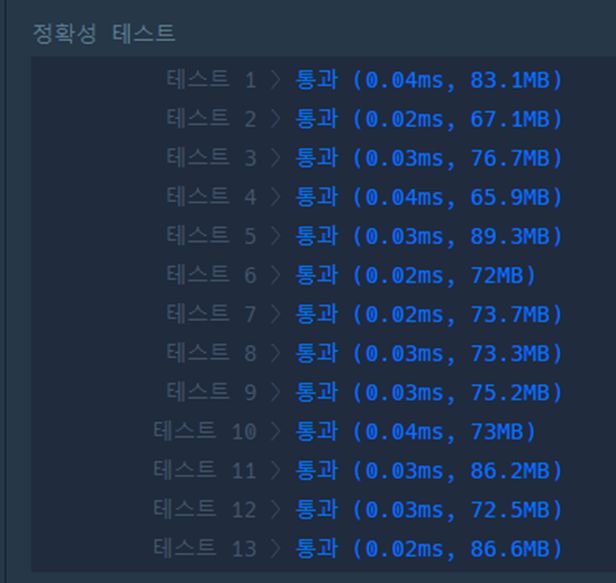
Q2
package com.company;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Quiz2 {
static public void main(String[] args) {
int[] topping1 = {1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 4, 1, 2};
int[] topping2 = {1, 2, 3, 1, 4};
System.out.println(solution(topping1) == 2);
System.out.println(solution(topping2) == 0);
}
//https://congsoony.tistory.com/283?category=961402 참고
static public int solution(int[] topping) {
int answer = 0;
Map<Integer,Integer> answerMap1 = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer,Integer> answerMap2 = new HashMap<>();
//전체의 종류를 구하기.
for (int topp : topping) {
answerMap1.put(topp, answerMap1.getOrDefault(topp, 0) + 1);
}
//1개씩 다른 Map 으로 옮기면서 (answerMap1 -> answerMap2) 사이즈를 비교하고 같으면 answer 를 ++ 시키자.
for (int topp : topping) {
if(answerMap1.getOrDefault(topp,0) != 0){
int tempValue = answerMap1.get(topp);
if(tempValue - 1 == 0)
answerMap1.remove(topp);
else
answerMap1.put(topp, tempValue - 1);
}
answerMap2.put(topp, answerMap2.getOrDefault(topp, 0) + 1);
if(answerMap1.size() == answerMap2.size()){
answer++;
}
}
return answer;
}
}
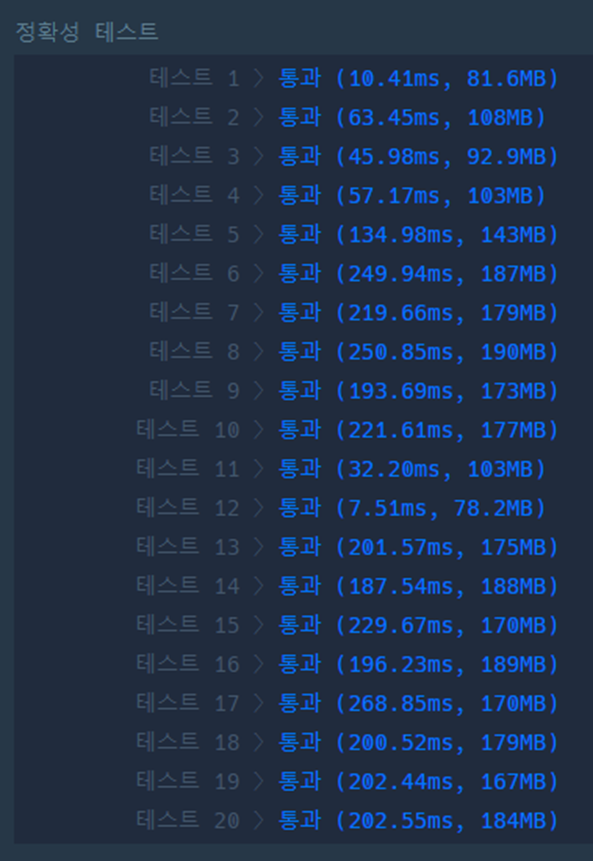
Q3
package com.company;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Quiz3 {
static public void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(solution(3, new int[][]{{1, 2}, {2, 3}}, new int[]{2, 3}, 1)));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(solution(5, new int[][]{{1, 2}, {1, 4}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {4, 5}}, new int[]{1, 3, 5}, 5)));
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(solution(6, new int[][]{{1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 5}, {3, 4},{3,6}, {4, 5},{4,6}}, new int[]{2,6,1,4,5}, 5)));
}
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph;
static int answerArrIndex;
static int dest;
static int[] visited;
static int[] answer;
static public int[] solution(int n, int[][] roads, int[] sources, int destination) {
answer = new int[sources.length];
dest = destination;
graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
//그래프 초기화 (node랑 Index랑 맞추기 위해서 + 1 해줌)
for (int i = 0; i < n+1; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
//그래프 내용 업데이트, 서로 연결이기 때문에 양쪽으로 연결해준다.
for (int[] road : roads) {
graph.get(road[0]).add(road[1]);
graph.get(road[1]).add(road[0]);
}
//visit을 확인해줄 배열 생성 , 초기값은 -1로 설정하여 값이 업데이트 되지 않으면 도달할 수 없는 영역
visited = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {
visited[i] = -1;
}
//source에 관해서 bfs가 아니라 destination에 관해서 bfs를 1번만 하면 모든 source에 관해서 거리를 알 수 있다 ==> 발상의 전환
bfs(dest, 0);
//answer 배열에 값을 넣는다. 넣을 때 index를 올려가면서 값을 넣는다.
answerArrIndex = 0;
for (int source : sources) {
answer[answerArrIndex] = visited[source];
answerArrIndex++;
}
return answer;
}
private static void bfs(int source, int distance) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
//집어넣기
queue.add(new Node(source, distance));
// visited 처리 , -1 이 아닌 곳은 방문한 곳 , 단순 true , false로 방문처리만 하는게 아니라 거리 값을 집어 넣는다.
visited[source] = distance;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node tempNode = queue.poll();
ArrayList<Integer> graphOfEachSource = graph.get(tempNode.source);
for (Integer eachSource : graphOfEachSource) {
// -1 이면 아직 방문하지 않은 것
if (visited[eachSource] == -1) {
queue.add(new Node(eachSource, tempNode.distance + 1));
visited[eachSource] = tempNode.distance + 1;
}
}
}
}
}
//bfs를 진행하기 위해 class를 만들고 멤버로 source 와 distance를 가진다.
class Node {
int source;
int distance;
public Node(int source, int distance) {
this.source = source;
this.distance = distance;
}
}