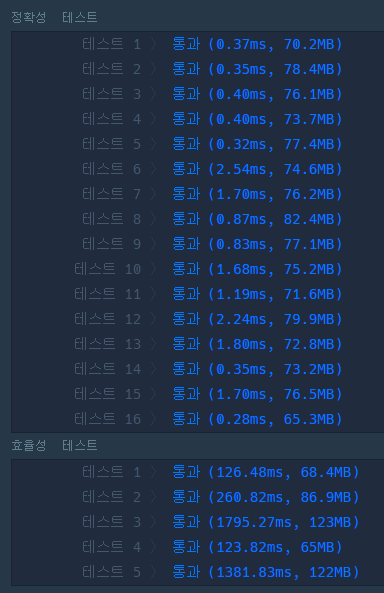
PriorityQueue를 사용하지 않을 경우 효율성 테스트를 통과하지 못한다.
참고용 블로그 추천
-
https://coding-factory.tistory.com/603 [[Java] PriorityQueue(우선순위 큐) 클래스 사용법 & 예제 총정리]
-
https://st-lab.tistory.com/205 [배열을 이용한 Heap (힙) 구현하기]
package com.company;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Solution {
static public void main(String[] args) {
// int[] scoville1 = { 1, 2, 3, 9, 10, 12 };
int[] scoville1 = { 1,1,1};
int[] scoville2 = { 3, 3, 3, 9, 10, 12 };
int K = 3;
System.out.println(solution(scoville1, K));
System.out.println(solution(scoville2, K));
}
// 참고용 블로그 추천
// 1. https://coding-factory.tistory.com/603 [[Java] PriorityQueue(우선순위 큐) 클래스 사용법 & 예제 총정리]
// 2. https://st-lab.tistory.com/205 [배열을 이용한 Heap (힙) 구현하기]
static public int solution(int[] scoville, int K) {
int answer = 0;
//PriorityQueue 생성 : minValue를 제일 위로 보낸다. , maxHeap을 하려면 Collections.reverseOrder() 를 넣자.
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
//PriorityQueue의 내용을 채운다.
for (int sco : scoville) {
pq.add(sco);
}
//사이즈가 1 초과 일때 계속해서 비교를 한다.
while ( pq.size() > 1 ) {
//PriorityQueue의 제일 Min 값이 K보다 높으면 루프를 멈춘다.
if(pq.peek() >= K)
return answer;
//합치기 위해서 2개의 값을 꺼낸다.
int scoville0 = pq.poll();
int scoville1 = pq.poll();
//2개의 스코빌을 합친다.
int newScoville = scoville0 + scoville1 * 2;
//합친 스코빌을 다시 PriorityQueue에 넣는다.
pq.add(newScoville);
//섞었기 때문에 answer을 1개 올린다.
answer++;
}
//PriorityQueue의 사이즈가 1인데 해당 원소가 K보다 작을 경우 -1을 리턴한다.
if(pq.peek() >= K)
return answer;
return -1;
}
}