Singly Linked List는 컴퓨터 과학에서 중요한 자료구조 중 하나로, 노드들이 한 방향으로 연결된 구조를 가지고 있다. 각 노드는 데이터 요소와 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터로 구성되어 있다. 이러한 특징으로 인해 링크드 리스트는 다양한 프로그래밍 문제와 애플리케이션에서 유용하게 사용된다.
하지만 한계도 분명한 자료구조이다. 싱글 링크드 리스트의 경우, 한쪽 방향으로 연결되었기 때문에 반대 방향으로 순회할 수 없다. 또한 특정 노드를 탐색하거나 삭제할 경우, 첫번째 노드부터 찾아야 하므로 배열의 랜덤 액세스보다 시간이 더 오래 걸린다. 한쪽 방향으로 연결된 한계점은 “Doubly Linked List”를 통해 극복할 수 있다. 또한 추후에 배열과 링크드 리스트를 비교해보도록 하자.
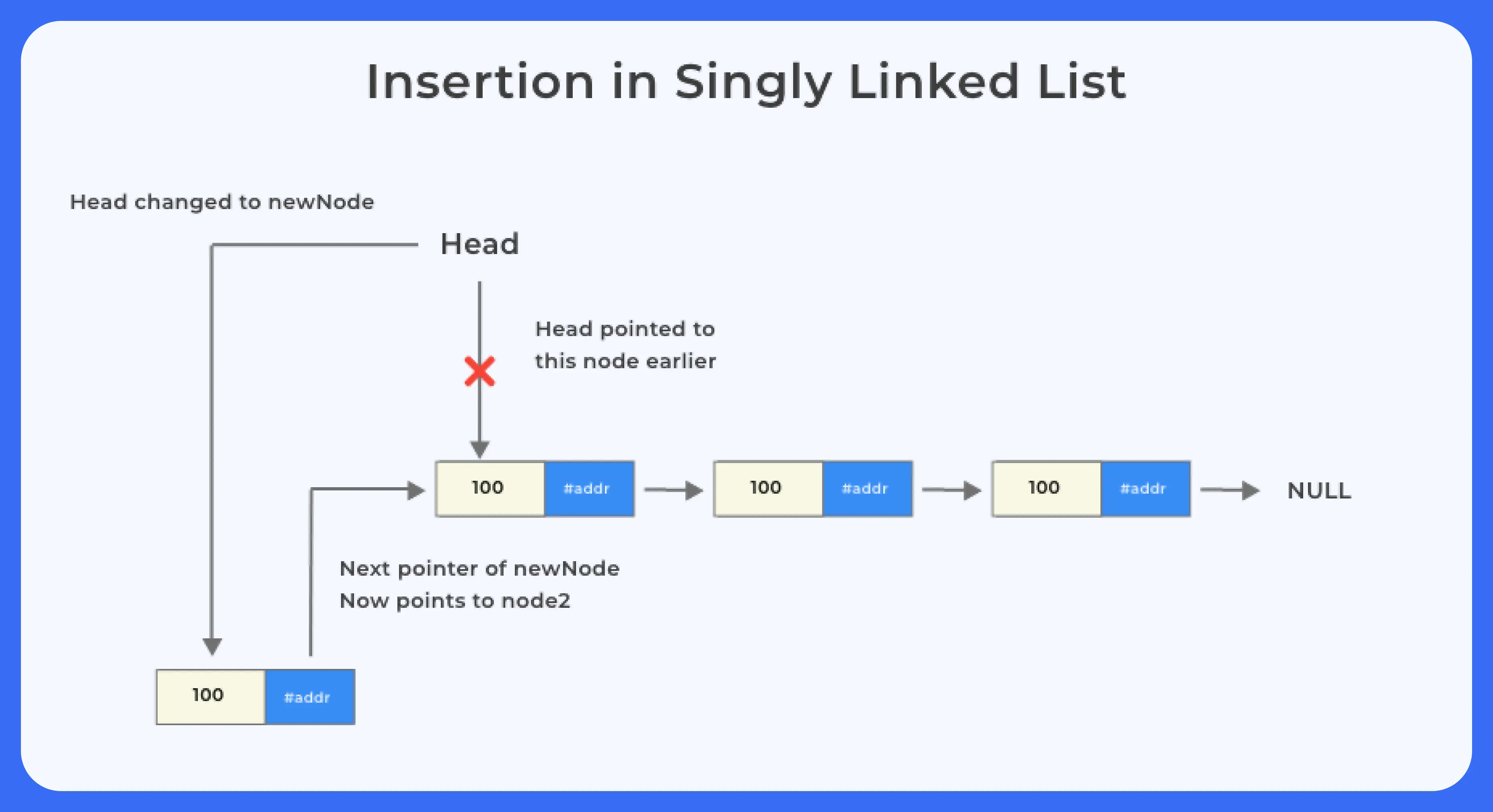
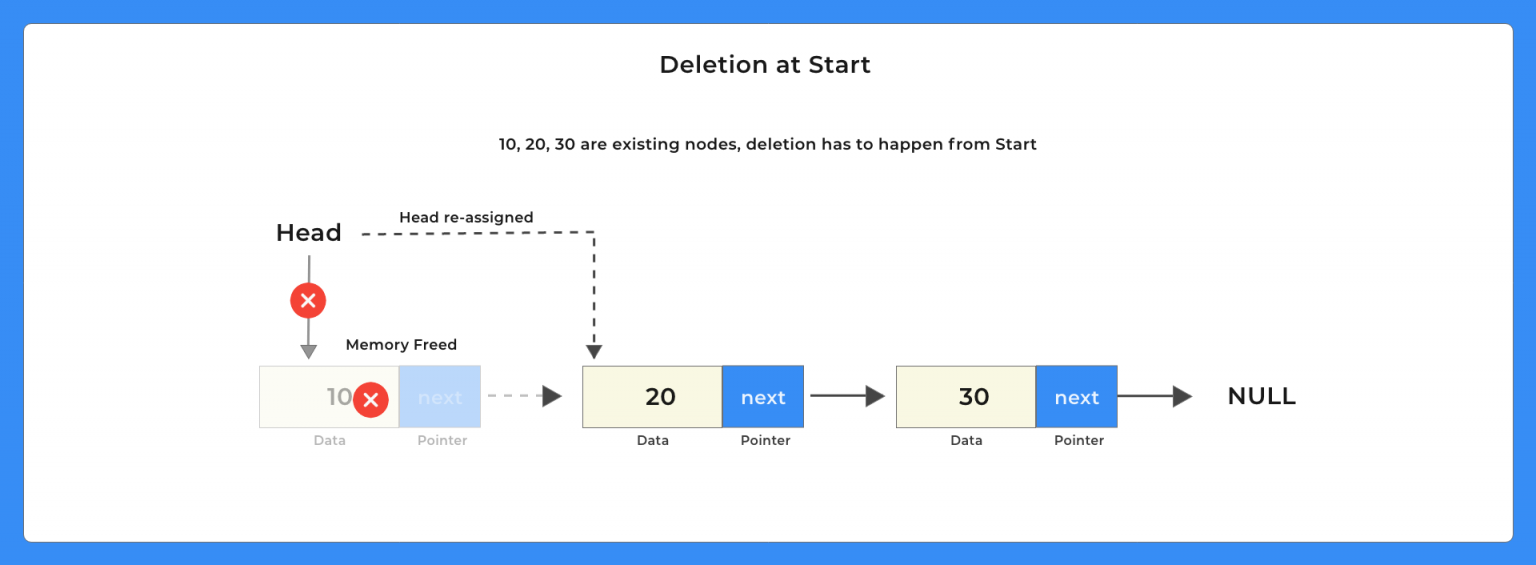
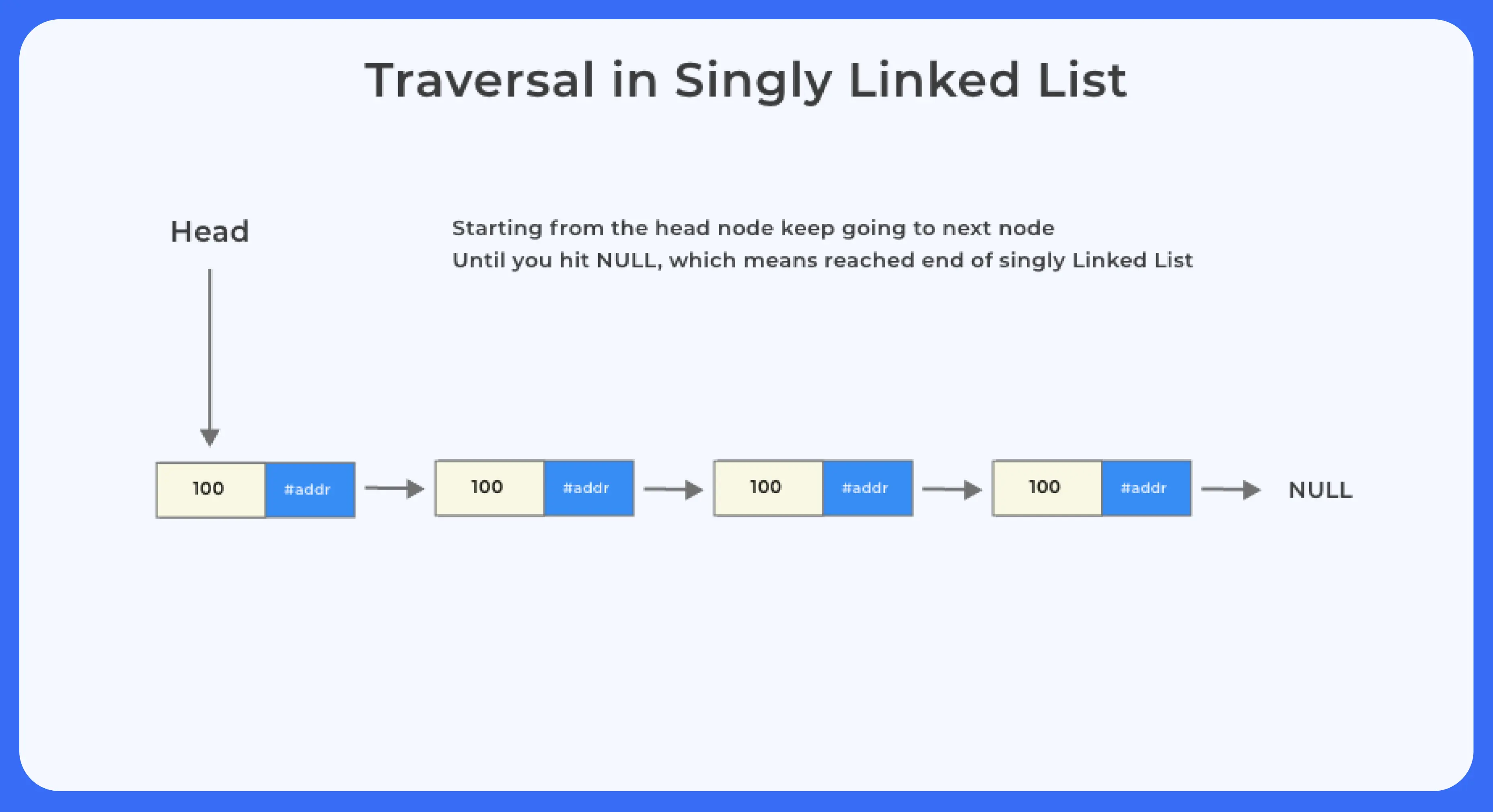
이미지 출처 : https://prepinsta.com/c-program/singly-linked-list/
위 그림은 싱글 링크드 리스트의 삽입, 삭제, 순회를 이미지로 표현한 것이다.해당 자료를 참조하며 아래 구현 코드를 본다면 쉽게 이해할 수 있다.
Singly Linked List는 다음과 같은 주요 연산들을 포함하는 추상 데이터 타입이다.
ADT
- insert: 리스트의 특정 위치에 새로운 요소를 추가한다.
- delete: 리스트의 특정 위치에서 요소를 제거한다.
- search: 리스트에서 특정 요소를 찾는다.
- is_empty: 리스트가 비어 있는지 여부를 확인한다.
이제 Single Linked List를 구현해보자.
구현
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
Node* create_node(int data) {
Node* new_node = (Node*) malloc(sizeof(Node));
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
return new_node;
}
void insert_node(Node** head, int data) {
Node* new_node = create_node(data);
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
}
void delete_node(Node** head, int key) {
Node* temp = *head, *prev;
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key) {
*head = temp->next;
free(temp);
return;
}
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
if (temp == NULL) return;
prev->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
Node* search_node(Node* head, int key) {
Node* current = head;
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->data == key) {
return current;
}
current = current->next;
}
return NULL;
}
int is_empty(Node* head) {
return head == NULL;
}