스프링 시큐리티 내부 구조

SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication();
authentication.getPrincipal();
authentication.getCredentials();
authentication.getAuthorities();코드와 그림으로 보면 알수있듯이 내부 구조가 아래와 같다.
SecurityContextHolder -> SecurityContext -> Authentication -> Principal & Credentials & Authorities
SecurityContesxtHolder
스프링 시큐리티로 인증한 사용자의 상세 정보를 저장한다.
SecurityContext
Authentication 객체를 가지고 있다.
Authentication
- principal - 사용자를 식별, 대부분의 경우 Principal로 UserDetails를 반환
- credentials - 주로 비밀번호에 사용하며 유출되지 않도록 사용자를 인증한 다음 비운다.
- authorities -= 사용자에게 부여한 권한은 GrantedAuthority로 추상화
GrantedAuthroity
Authentication.getAuthorities() 메소드로 접근 가능
권한은 여러개 일 수 있기 때문에GrantedAuthority 객체의 Collection을 리턴하며 인증한 사람의 부여된 권한이다.
prefixfh 'ROLE_'가 붙고 인증 이후에 인가할 때 사용한다.
ex)ROLE_ADMIN, ROLE_USER
principal과 GrantAuthority로 인증,인가를 판단한다.
SecurityContext 디버그걸어서 확인한 사진
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();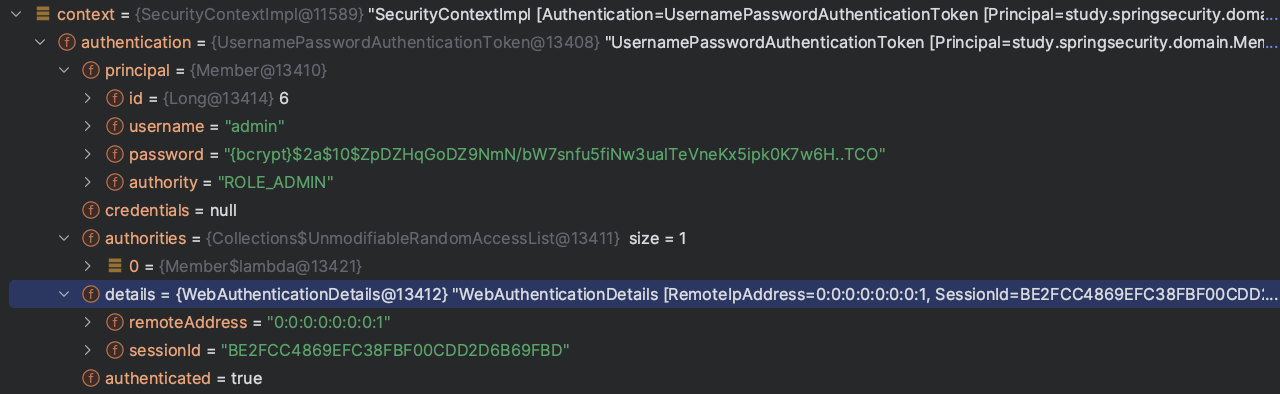
authority = "ROLE_ADMIN"확인가능
여기서 의문점!! 어떤 유저인지에 관한 내용이 없는데 getContext를 했을뿐인데 유저가 누군인지를 알고 유저마다 각각 고유한 securityContext를 줄 수 있었을까?
@GetMapping
public String getAlram(Model model) {
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
List<Alarm> alarm = alarmService.findAll();
return "alram/index";
}바로 ThreadLocal 때문이다.

출처 : 토리맘의 한글라리즈 프로젝트
