- 포인트컷 - 포인트컷 지시자
- 포인트컷 - 예제 만들기
- 포인트컷 - execution1
- 포인트컷 - execution2
- 포인트컷 - within
- 포인트컷 - args
- 포인트컷 - @target, @within
- 포인트컷 - @annotation, @args
- 포인트컷 - bean
- 포인트컷 - 매개변수 전달
- 포인트컷 - this, target
1. 포인트컷 - 포인트컷 지시자
포인트컷 표현식은 execution같은 포인트컷 지시자(Pointcut Designator)로 시작한다. 줄여서 PCD라 한다.
포인트컷 지시자의 종류
execution: 메소드 실행 조인 포인트를 매칭한다. 스프링 AOP에서 가장 많이 사용하고, 기능도 복잡하다.within: 특정 타입 내의 조인 포인트를 매칭한다.args: 인자가 주어진 타입의 인스턴스인 조인 포인트this: 스프링 빈 객체(스프링 AOP 프록시)를 대상으로 하는 조인 포인트target: Target 객체(스프링 AOP 프록시가 가르키는 실제 대상)를 대상으로 하는 조인 포인트@target: 실행 객체의 클래스에 주어진 타입의 애노테이션이 있는 조인 포인트@within: 주어진 애노테이션이 있는 타입 내 조인 포인트@annotation: 메서드가 주어진 애노테이션을 가지고 있는 조인 포인트를 매칭@args: 전달된 실제 인수의 런타임 타입이 주어진 타입의 애노테이션을 갖는 조인 포인트bean: 스프링 전용 포인트컷 지시자, 빈의 이름으로 포인트컷을 지정한다.
execution을 가장 많이 사용
2. 포인트컷 - 예제 만들기
ClassAop
package com.example.springaop.member.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ClassAop {
}MethodAop
package com.example.springaop.member.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MethodAop {
String value();
}
MemberService
package com.example.springaop.member;
public interface MemberService {
String hello(String param);
}
MemberServiceImpl
package com.example.springaop.member;
import com.example.springaop.member.annotation.ClassAop;
import com.example.springaop.member.annotation.MethodAop;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@ClassAop
@Component
public class MemberServiceImpl implements MemberService {
@Override
@MethodAop("test value")
public String hello(String param) {
return "ok";
}
public String internal(String param) {
return "ok";
}
}
ExecutionTest
package com.example.springaop.pointcut;
import com.example.springaop.member.MemberServiceImpl;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJExpressionPointcut;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Slf4j
public class ExecutionTest {
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut = new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
Method helloMethod;
@BeforeEach
public void init() throws NoSuchMethodException {
helloMethod = MemberServiceImpl.class.getMethod("hello", String.class);
}
@Test
void printMethod(){
log.info("helloMethod={}", helloMethod);
}
}
AspectJExpressionPointcut: 포인트컷 표현식을 처리해주는 클래스이다. 여기에 포인트컷 표현식을 지정하면 된다.
3. 포인트컷 - execution1
실제 코드를 보면서 execution을 이해해보자.
가장 정확한 포인트컷
ExecutionTest - exactMatch()추가
@Test
void exxactMatch(){
// public java.lang.String com.example.springaop.member.MemberServiceImpl.hello(java.lang.String)
pointcut.setExpression("execution(String com.example.springaop.member.MemberServiceImpl.hello(String))");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}AspectJExpressionPointcut에pointcut.setExpression을 통해서 포인트컷 표현식을 적용할 수 있다.pointcut.matches(메서드, 대상 클래스)를 실행하면 지정한 포인트컷 표현식의 매칭 여부를true,false로 반환한다.
테스트 결과
가장 많이 생략한 포인트컷
ExecutionTest - allMatch()추가
@Test
void allMatch() {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* *(..))");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
메서드 이름 매칭 관련 포인트컷
ExecutionTest - nameMatch~()추가
@Test
void nameMatch() {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* hello(..))");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
@Test
void nameMatchStar1() {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* hel*(..))");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
@Test
void nameMatchStar2() {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* *el*(..))");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
@Test
void nameMatchFalse() {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* nono(..))");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isFalse();
}- 메서드 이름 앞 뒤에
*을 사용해서 매칭할 수 있다.
테스트 결과
4. 포인트컷 - execution2
타입 매칭 - 부모 타입 허용
ExecutionTest - type~()추가
@Test
void typeExactMatch() {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* com.example.springaop.member.MemberServiceImpl.*(..))");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
@Test
void typeMatchSuperType() {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* com.example.springaop.member.MemberService.*(..))");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}typeExactMatch()는 타입 정보가 정확하게 일치하기 때문에 매칭된다.execution에서는MemberService처럼 부모 타입을 선언해도 그 자식 타입은 매칭된다.
테스트 결과
타입 매칭 - 부모 타입에 있는 메서드만 허용
@Test
void typeMatchInternal() throws NoSuchMethodException {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* com.example.springaop.member.MemberServiceImpl.*(..))");
Method internalMethod = MemberServiceImpl.class.getMethod("internal", String.class); // 자식 타입에 있는 메소드는 매칭 o
assertThat(pointcut.matches(internalMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
//포인트컷으로 지정한 MemberService는 internal이라는 이름의 메서드가 없다.
@Test
void typeMatchNoSuperTypeMethodFalse() throws NoSuchMethodException {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* com.example.springaop.member.MemberService.*(..))"); // 자식 타입에 있는 다른 메서드도 매칭 될까?? -> x
Method internalMethod = MemberServiceImpl.class.getMethod("internal", String.class);
assertThat(pointcut.matches(internalMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isFalse();
}- 부모 타입을 표현식에 선언한 경우 부모 타입에서 선언한 메서드가 자식 타입에 있어야 매칭에 성공한다. 그래서 부모 타입에 있는
hello(String)메서드는 매칭에 성공하지만, 부모 타입에 없는internal(String)는 매칭에 실패한다.
테스트 결과
파라미터 매칭
ExecutionTest - argsMatch~()추가
//String 타입의 파라미터 허용
//(String)
@Test
void argsMatch() {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* *(String))");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
//파라미터가 없어야 함
@Test
void argsMatchNoArgs() {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* *())");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isFalse();
}
//정확히 하나의 파라미터 허용, 모든 타입 허용
@Test
void argsMatchStar() {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* *(*))");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
//숫자와 무관하게 모든 파라미터, 모든 타입 허용
//파라미터가 없어도 됨
@Test
void argsMatchAll() {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* *(..))");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
//String 타입으로 시작, 숫자와 무관하게 모든 파라미터, 모든 타입 허용
//(String), (String, Xxx), (String, Xxx, Xxx) 허용
@Test
void argsMatchComplex() {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* *(String, ..))");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}execution 파라미터 매칭 규칙
(String): 정확하게 String 타입 파라미터(): 파라미터가 없어야 한다.(*): 정확히 하나의 파라미터, 단 모든 타입을 허용한다.(*, *): 정확히 두 개의 파라미터, 단 모든 타입을 허용한다.(..): 숫자와 무관하게 모든 파라미터, 모든 타입을 허용한다. 참고로 파라미터가 없어도 된다.0..*로 이해하면 된다.(String, ..): String 타입으로 시작해야 한다. 숫자와 무관하게 모든 파라미터, 모든 타입을 허용한다.- 예)
(String),(String, Xxx),(String, Xxx, Xxx)허용
- 예)
테스트 결과
5. 포인트컷 - within
within지시자는 특정 타입 내의 조인 포인트들로 매칭을 제한한다.execution에서 타입 부분만 사용한다고 보면 된다.
WithinTest
package com.example.springaop.pointcut;
import com.example.springaop.member.MemberServiceImpl;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJExpressionPointcut;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
public class WithinTest {
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut = new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
Method helloMethod;
@BeforeEach
public void init() throws NoSuchMethodException {
helloMethod = MemberServiceImpl.class.getMethod("hello", String.class);
}
@Test
void withinExact() {
pointcut.setExpression("within(com.example.springaop.member.MemberServiceImpl)");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
@Test
void withinStar() {
pointcut.setExpression("within(com.example.springaop.member.*Service*)");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
@Test
void withinSubPackage() {
pointcut.setExpression("within(com.example.springaop..*)");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
@Test
@DisplayName("타켓의 타입에만 직접 적용, 인터페이스를 선정하면 안됨")
void withinSuperTypeFalse() {
pointcut.setExpression("within(com.example.springaop.member.MemberService)");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isFalse();
}
@Test
@DisplayName("execution은 타입 기반, 인터페이스를 선정 가능")
void executionSuperTypeTrue() {
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* com.example.springaop.member.MemberService.*(..))");
assertThat(pointcut.matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
}
within사용시 주의해야 할 점이 있다. 표현식에 부모 타입을 지정하면 안된다는 점이다. 정확하게 타입이 맞아야 한다. 이 부분에서execution과 차이가 난다.- 부모 타입(여기서는
MemberService인터페이스) 지정시within은 실패하고,execution은 성공하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
테스트 결과
6. 포인트컷 - args
args: 인자가 주어진 타입의 인스턴스인 조인 포인트로 매칭- 기본 문법은
execution의args부분과 같다. args는 부모 타입을 허용한다.args는 실제 넘어온 파라미터 객체 인스턴스를 보고 판단한다.
ArgsTest
package com.example.springaop.pointcut;
import com.example.springaop.member.MemberServiceImpl;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJExpressionPointcut;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
public class ArgsTest {
Method helloMethod;
@BeforeEach
public void init() throws NoSuchMethodException {
helloMethod = MemberServiceImpl.class.getMethod("hello", String.class);
}
private AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut(String expression) {
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut = new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression(expression);
return pointcut;
}
@Test
void args() {
//hello(String)과 매칭
assertThat(pointcut("args(String)").matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
assertThat(pointcut("args(Object)").matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
assertThat(pointcut("args()").matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isFalse();
assertThat(pointcut("args(..)").matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
assertThat(pointcut("args(*)").matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
assertThat(pointcut("args(String,..)").matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
}
/**
* execution(* *(java.io.Serializable)): 메서드의 시그니처로 판단 (정적)
* args(java.io.Serializable): 런타임에 전달된 인수로 판단 (동적)
* java의 String은 Serializable를 구현하고 있다.
*/
@Test
void argsVsExecution() {
//Args
assertThat(pointcut("args(String)").matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
assertThat(pointcut("args(java.io.Serializable)").matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
assertThat(pointcut("args(Object)").matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
//Execution
assertThat(pointcut("execution(* *(String))").matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isTrue();
assertThat(pointcut("execution(* *(java.io.Serializable))").matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isFalse();
assertThat(pointcut("execution(* *(Object))").matches(helloMethod, MemberServiceImpl.class)).isFalse();
}
}
- 자바가 기본으로 제공하는
String은Object,java.io.Serializable의 하위 타입이다. - 정적으로 클래스에 선언된 정보만 보고 판단하는
execution(* *(Object))는 매칭에 실패한다. - 동적으로 실제 파라미터로 넘어온 객체 인스턴스로 판단하는
args(Object)는 매칭에 성공한다. (부모 타입 허용)
7. 포인트컷 - @target, @within
@target: 실행 객체의 클래스에 주어진 타입의 애노테이션이 있는 조인 포인트@within: 주어진 애노테이션이 있는 타입 내 조인 포인트
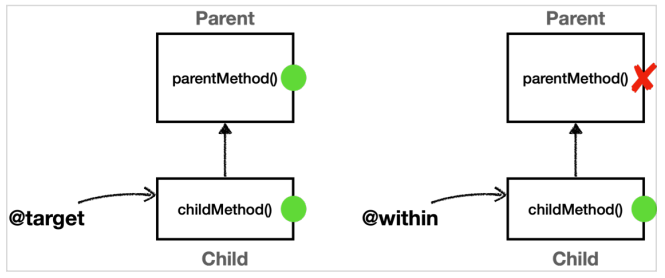
@target은 인스턴스의 모든 메서드를 조인 포인트로 적용한다.@within은 해당 타입 내에 있는 메서드만 조인 포인트로 적용한다.
AtTargetAtWithinTest
package com.example.springaop.pointcut;
import com.example.springaop.member.annotation.ClassAop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@Slf4j
@Import({AtTargetAtWithinTest.Config.class})
@SpringBootTest
public class AtTargetAtWithinTest {
@Autowired
Child child;
@Test
void success() {
log.info("child Proxy={}", child.getClass());
child.childMethod(); //부모, 자식 모두 있는 메서드
child.parentMethod(); //부모 클래스만 있는 메서드
}
static class Config {
@Bean
public Parent parent() {
return new Parent();
}
@Bean
public Child child() {
return new Child();
}
@Bean
public AtTargetAtWithinAspect atTargetAtWithinAspect() {
return new AtTargetAtWithinAspect();
}
}
static class Parent {
public void parentMethod(){} //부모에만 있는 메서드
}
@ClassAop
static class Child extends Parent {
public void childMethod(){}
}
@Slf4j
@Aspect
static class AtTargetAtWithinAspect {
//@target: 인스턴스 기준으로 모든 메서드의 조인 포인트를 선정, 부모 타입의 메서드도 적용
@Around("execution(* com.example.springaop..*(..)) && @target(com.example.springaop.member.annotation.ClassAop)")
public Object atTarget(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("[@target] {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
//@within: 선택된 클래스 내부에 있는 메서드만 조인 포인트로 선정, 부모 타입의 메서드는적용되지 않음
@Around("execution(* com.example.springaop..*(..)) && @within(com.example.springaop.member.annotation.ClassAop)")
public Object atWithin(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("[@within] {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
}
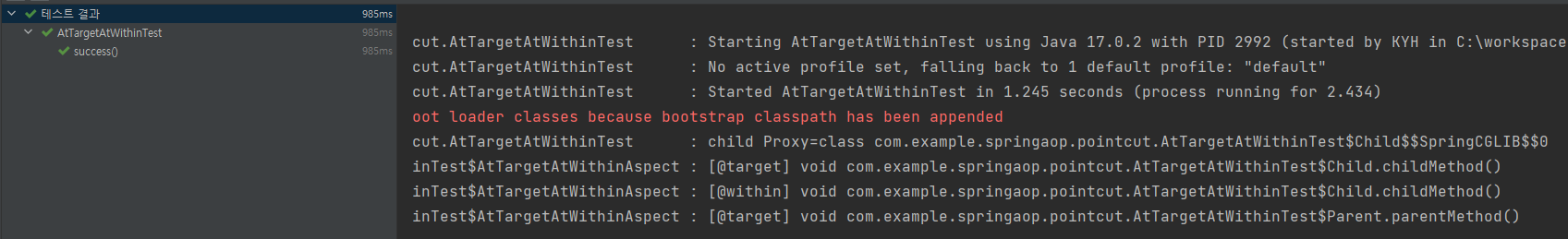
parentMethod()는 Parent클래스에만 정의되어 있고, Child클래스에 정의되어 있지 않기 때문에 @within에서 AOP 적용 대상이 되지 않는다.
8. 포인트컷 - @annotation, @args
@annotation: 메서드가 주어진 애노테이션을 가지고 있는 조인 포인트를 매칭- 메서드(조인 포인트)에 애노테이션이 있으면 매칭한다.
AtAnnotationTest
package com.example.springaop.pointcut;
import com.example.springaop.member.MemberService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@Slf4j
@Import(AtAnnotationTest.AtAnnotationAspect.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class AtAnnotationTest {
@Autowired
MemberService memberService;
@Test
void success() {
log.info("memberService Proxy={}", memberService.getClass());
memberService.hello("helloA");
}
@Slf4j
@Aspect
static class AtAnnotationAspect {
@Around("@annotation(com.example.springaop.member.annotation.MethodAop)")
public Object doAtAnnotation(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("[@annotation] {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
}

9. 포인트컷 - bean
bean: 스프링 전용 포인트컷 지시자, 빈의 이름으로 지정한다.- 스프링 빈의 이름으로 AOP 적용 여부를 지정한다. 이것은 스프링에서만 사용할 수 있는 특별한 지시자이다.
BeanTest
package com.example.springaop.pointcut;
import com.example.springaop.order.OrderService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@Slf4j
@Import(BeanTest.BeanAspect.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class BeanTest {
@Autowired
OrderService orderService;
@Test
void success() {
orderService.orderItem("itemA");
}
@Aspect
static class BeanAspect {
@Around("bean(orderService) || bean(*Repository)")
public Object doLog(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("[bean] {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
}

10. 포인트컷 - 매개변수 전달
다음은 포인트컷 표현식을 사용해서 어드바이스에 매개변수를 전달할 수 있다.
this, target, args,@target, @within, @annotation, @args
- 타입이 메서드에 지정한 타입으로 제한된다. 여기서는 메서드의 타입이
String으로 되어 있기 때문에 다음과 같이 정의되는 것으로 이해하면 된다.
ParameterTest
package com.example.springaop.pointcut;
import com.example.springaop.member.MemberService;
import com.example.springaop.member.annotation.ClassAop;
import com.example.springaop.member.annotation.MethodAop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@Slf4j
@Import(ParameterTest.ParameterAspect.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class ParameterTest {
@Autowired
MemberService memberService;
@Test
void success() {
log.info("memberService Proxy={}", memberService.getClass());
memberService.hello("helloA");
}
@Slf4j
@Aspect
static class ParameterAspect{
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.springaop.member..*.*(..))")
private void allMember(){}
@Around("allMember()")
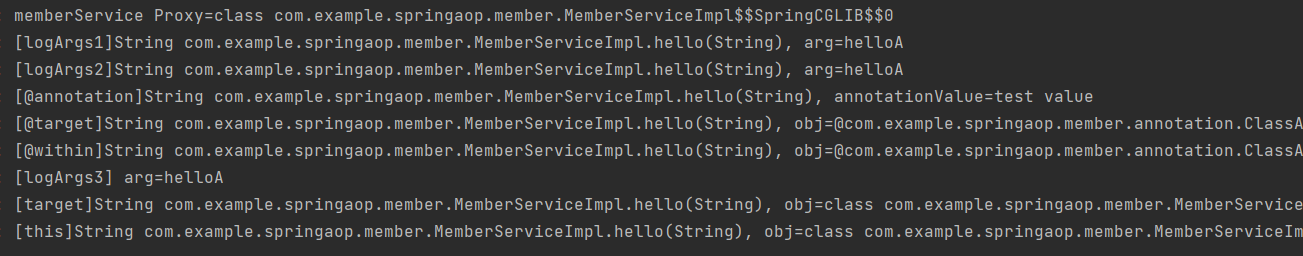
public Object logArg1(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
Object arg1 = joinPoint.getArgs()[0];
log.info("[logArgs1]{}, arg={}", joinPoint.getSignature(), arg1);
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
// args 사용
@Around("allMember() && args(arg,..)")
public Object logArgs2(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, Object arg) throws Throwable {
log.info("[logArgs2]{}, arg={}", joinPoint.getSignature(), arg);
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
// @Before 사용 축약 버전
@Before("allMember() && args(arg,..)")
public void logArgs3(String arg) {
log.info("[logArgs3] arg={}", arg);
}
// 프록시 객체를 전달 받음
@Before("allMember() && this(obj)")
public void thisArgs(JoinPoint joinPoint, MemberService obj) {
log.info("[this]{}, obj={}", joinPoint.getSignature(), obj.getClass());
}
// 실제 대상 객체를 전달 받음
@Before("allMember() && target(obj)")
public void targetArgs(JoinPoint joinPoint, MemberService obj) {
log.info("[target]{}, obj={}", joinPoint.getSignature(), obj.getClass());
}
// 타입의 애노테이션을 전달 받음
@Before("allMember() && @target(annotation)")
public void atTarget(JoinPoint joinPoint, ClassAop annotation) {
log.info("[@target]{}, obj={}", joinPoint.getSignature(), annotation);
}
// 타입의 애노테이션을 전달 받음
@Before("allMember() && @within(annotation)")
public void atWithin(JoinPoint joinPoint, ClassAop annotation) {
log.info("[@within]{}, obj={}", joinPoint.getSignature(), annotation);
}
// 메서드의 애노테이션을 전달 받음
@Before("allMember() && @annotation(annotation)")
public void atAnnotation(JoinPoint joinPoint, MethodAop annotation) {
log.info("[@annotation]{}, annotationValue={}", joinPoint.getSignature(), annotation.value());
}
}
}
logArgs1:joinPoint.getArgs()[0]와 같이 매개변수를 전달 받는다.logArgs2:args(arg,..)와 같이 매개변수를 전달 받는다.logArgs3:@Before를 사용한 축약 버전이다. 추가로 타입을 String`으로 제한했다.this: 프록시 객체를 전달 받는다.target: 실제 대상 객체를 전달 받는다.@target,@within: 타입의 애노테이션을 전달 받는다.@annotation: 메서드의 애노테이션을 전달 받는다. 여기서는annotation.value()로 해당 애노테이션의 값을 출력하는 모습을 확인할 수 있다.
11. 포인트컷 - this, target
this: 스프링 빈 객체(스프링 AOP 프록시)를 대상으로 하는 조인 포인트target: Target 객체(스프링 AOP 프록시가 가르키는 실제 대상)를 대상으로 하는 조인 포인트
차이
this는 스프링 빈으로 등록되어 있는 프록시 객체를 대상으로 포인트컷을 매칭한다.target은 실제target객체를 대상으로 포인트컷을 매칭한다.
프록시 생성 방식에 따른 차이
- JDK 동적 프록시: 인터페이스가 필수이고, 인터페이스를 구현한 프록시 객체를 생성한다.
- CGLIB: 인터페이스가 있어도 구체 클래스를 상속 받아서 프록시 객체를 생성한다.
차이는 JDK 동적 프록시와 CGLIB 방식에서 MemberServiceImpl구체 클래스 지정 지정 할때 나타난다.
this(hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl): proxy 객체를 보고 판단한다. JDK 동적 프록시로 만들어진 proxy 객체는MemberService인터페이스를 기반으로 구현된 새로운 클래스다. 따라서MemberServiceImpl를 전혀 알지 못하므로 AOP 적용 대상이 아니다.this(hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl): proxy 객체를 보고 판단한다. CGLIB로 만들어진 proxy 객체는MemberServiceImpl를 상속 받아서 만들었기 때문에 AOP가 적용된다. this 가 부모 타입을 허용하기 때문에 포인트컷의 대상이 된다.
ThisTargetTest
package com.example.springaop.pointcut;
import com.example.springaop.member.MemberService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@Slf4j
@Import(ThisTargetTest.ThisTargetAspect.class)
@SpringBootTest(properties = "spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false") //JDK 동적 프록시
//@SpringBootTest(properties = "spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true") //CGLIB
public class ThisTargetTest {
@Autowired
MemberService memberService;
@Test
void success() {
log.info("memberService Proxy={}", memberService.getClass());
memberService.hello("helloA");
}
@Slf4j
@Aspect
static class ThisTargetAspect {
// 부모 타입 허용
@Around("this(com.example.springaop.member.MemberService)")
public Object doThisInterface(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("[this-interface] {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
// 부모 타입 허용
@Around("target(com.example.springaop.member.MemberService)")
public Object doTargetInterface(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("[target-interface] {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
// this: 스프링 AOP 프록시 객체 대상
// JDK 동적 프록시는 인터페이스를 기반으로 생성되므로 구현 클래스를 알 수 없음
// CGLIB 프록시는 구현 클래스를 기반으로 생성되므로 구현 클래스를 알 수 있음
@Around("this(com.example.springaop.member.MemberServiceImpl)")
public Object doThis(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("[this-impl] {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
// target: 실제 target 객체 대상
@Around("target(com.example.springaop.member.MemberServiceImpl)")
public Object doTarget(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable
{
log.info("[target-impl] {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
}
테스트 결과
JDK 동적 프록시 사용
spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false
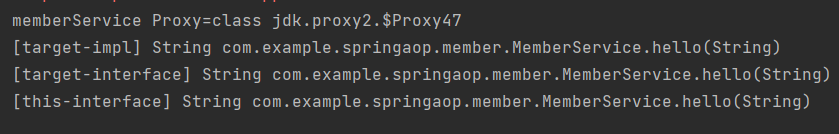
- JDK 동적 프록시를 사용하면
this(hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl)로 지정한[this-impl]부분이 출력되지 않는 것을 확인할 수 있다
CGLIB 사용
spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true, 또는 생략(스프링 부트 기본 옵션)
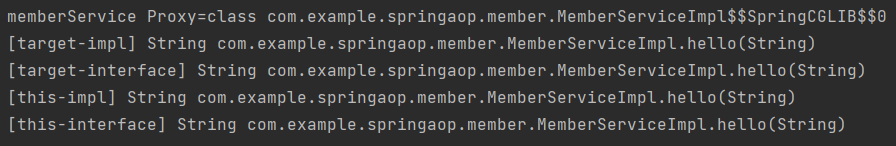
참고
김영한: 스프링 핵심 원리 - 고급편(인프런)
Github - https://github.com/b2b2004/Spring_ex
