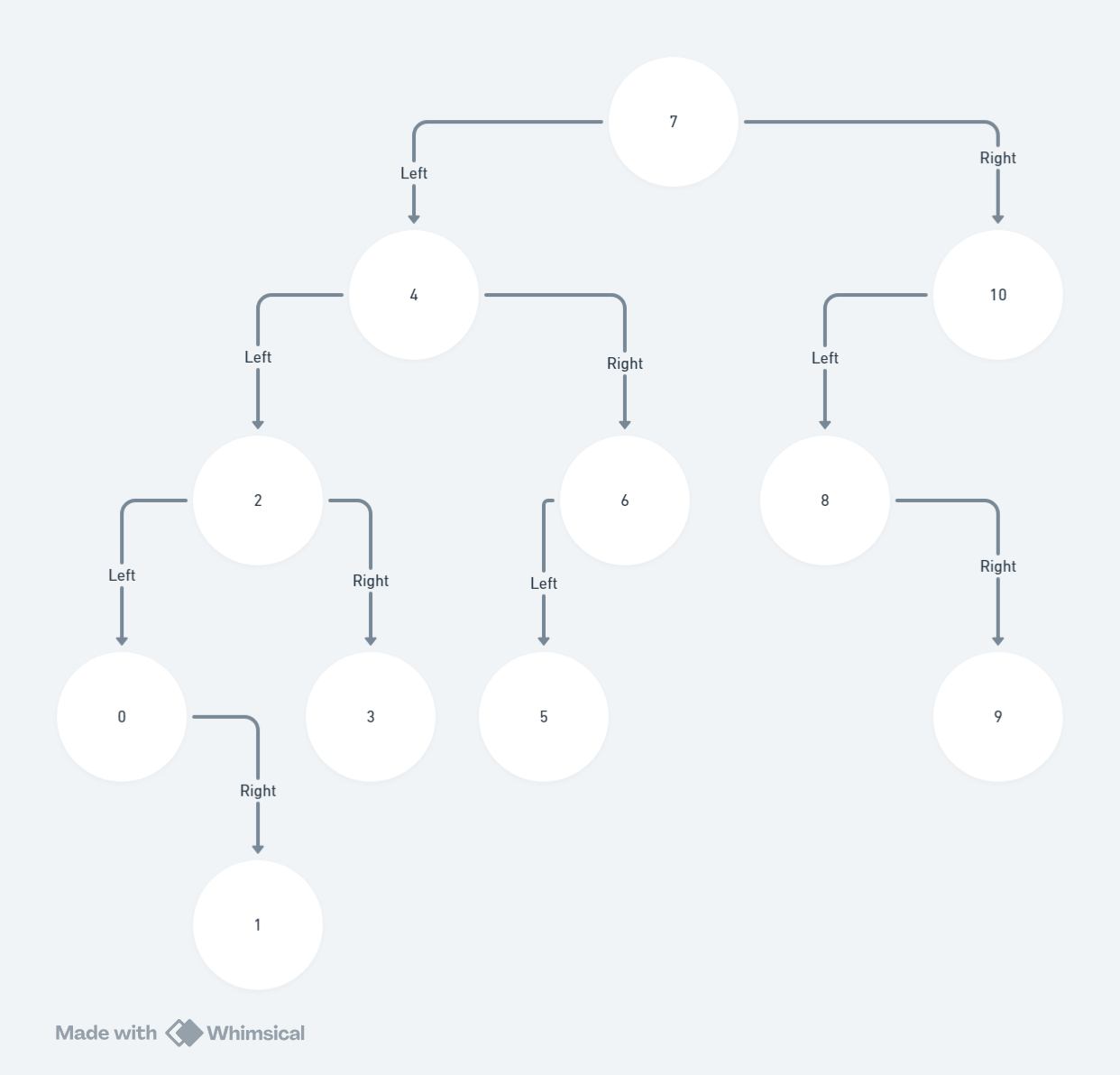
Problem: Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes' values.
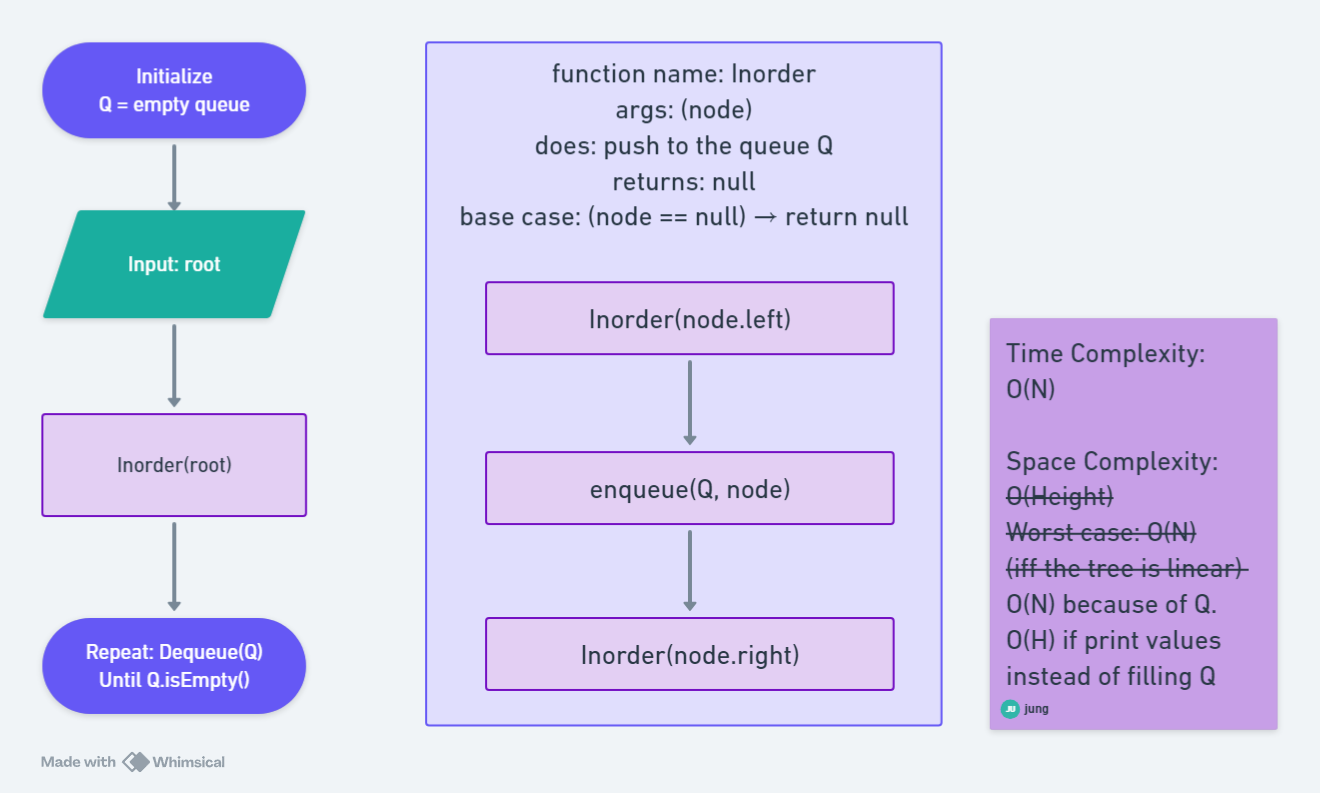
Method 1) Recursion
Method 2) Iteration - Use a stack
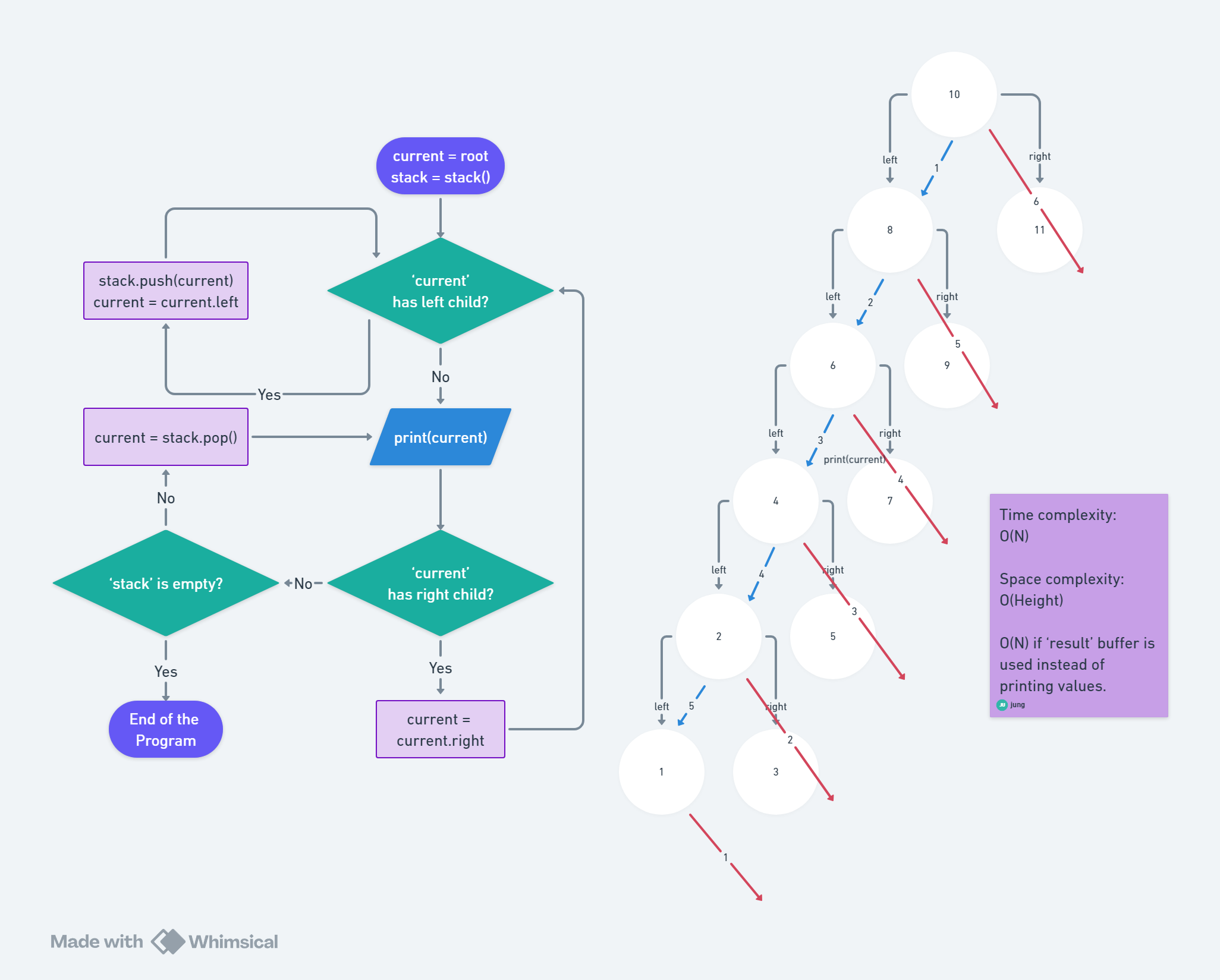
Brief explanation of method 2:
See the tree diagram.
In a high level description, what we need to do is:
First, go down the blue stream(left, downward). In this step we only store the visited nodes in a stack, sequentially. (Go all the way down, to the left)
Second, When we reach an end in the blue stream, we print out where we are at. (Printing current node)
Third, And then we go down in the red stream direction(right, downward). But we don't go all the way down. We only go down 1 level. And then, repeat all the previous steps starting from the First step.
(Going 1 Level down, to the right)
Fourth, Pop the last element from the stack we built in the First step. Do the Second step: "Printing current node", and then do the Third step: "Going 1 Level down, to the right". (Going 1 Level up)
Fifth, Repeat the Fourth step until the stack is empty.
Below is a Python3 code that is successfully submitted at
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/populate-inorder-successor-for-all-nodes/?ref=gcse
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.right = None
self.data = val
self.left = None
self.next = None
class Solution:
def populateNext(self, root):
current = root
stack = []
result = []
check_left = True
while True:
if check_left and current.left:
stack.append(current)
current = current.left
continue
result.append(current)
if current.right:
current = current.right
check_left = True
continue
if not stack:
for i, j in enumerate(result[:-1]):
j.next = result[i+1]
break
current = stack.pop()
check_left = FalseMethod 3: Morris Traversal - O(1) Auxiliary Space
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/populate-inorder-successor-for-all-nodes/?ref=gcse
Insight:
Consider this simple binary tree
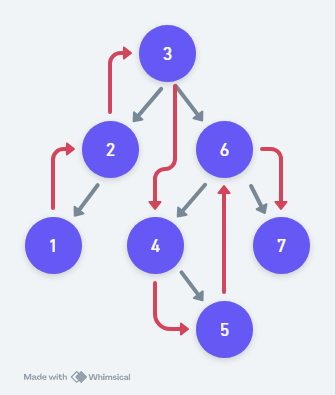
Grey arrows mean the parent-child relationships.
Red arrows mean the inorder traversal order.
Next node in inorder traversal can be summarized with this algorithm:
1) If a node A has a left child, go to its left child, and then keep going downstream to the right side as long as the node has a right child. Repeat until they don't have a right child. The node where you finally reached will be the inorder predecessor of node A.
Example of case 1) is node 5->6. (and also node 1->2, 2->3)
2) If a node B does not satisfy condition 1), (no left child) and is a right child of a parent node, go to its parent, and then keep going upstream to its parent as long as the child is the left child of the parent. If the child is the right child of the parent, then that parent is the inorder predecessor of node B.
Example of case 2) is node 3->4. (and also node
Implementation 1 of Morris Traversal (Divide and Conquer)

