동시성 컬렉션과 Thread Safe
Thread Safe
Thread Safe 란?
멀티 스레드 환경에서, 여러 스레드가 동시에 접근해도 동시성 문제나, 특이 사항이 발생하지 않는. 즉, 안전한 경우를 Thread Safe 하다 라고 한다.
동시성 컬렉션
동시성 컬렉션의 필요성
- 멀티 스레드 환경에서는 Thread Safe 하도록 Lock 전락 혹은 CAS 연산등을 사용하는게 필수적이다.
- 이를 위해서 Java 에서는 Thread Safe 한 동시성 컬렉션을 제공한다.
- 예제를 통해, 동시성 컬렉션이 필요한 경우를 살펴 보자.
Bad Code
- ArrayList는 Thread Safe 하지 않은 컬렉션이다.
- 이를 확인해 보기 위해서 다음과 같은 코드를 실행 해 보겠다.
- 0부터 9999 까지 array list에 값을 추가하는 Runnable 객체이다.
- 이를 10개의 Thread에서 접근하여 실행 해 본다.
public class ArrayListMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> sharedList = new ArrayList<>();
Runnable task = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
// ArrayList에 값 추가
sharedList.add(i);
}
};
Thread[] threads = new Thread[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(task);
}
for (Thread thread : threads) {
thread.start();
}
// 모든 스레드가 종료될 때까지 대기
for (Thread thread : threads) {
try {
thread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("Expected size: " + (10 * 1000));
System.out.println("Actual size: " + sharedList.size());
}
}Expected size: 10000
Actual size: 7394- ArrayList는 중복을 허용하는 컬렉션으로, 멀티 스레드의 병렬 작업 특성 상, 저장되는 값은 순서대로 들어가지 않을 수 있어도, 0이 10개, 1이 10개... 999가 10개 저장되어 총, 10,000개의 자료가 들어가 있어야 한다.
- 실행 결과는 7394개의 자료만 들어가있다.
- 즉, 유실이 발생한 것이다.
Bad Code 원인 분석
- 원인은 ArrayList가 Thread Safe 하지 않기 때문이다.
- 정확하게는 ArrayList의 add(E e) 메서드가 원자적 연산이 아니기 때문이다.
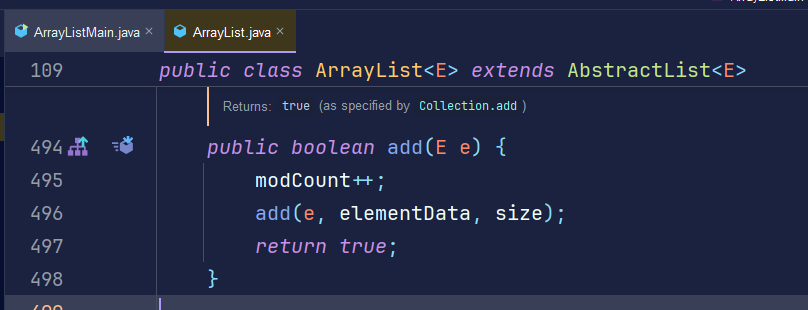
- 비 원자적 연산의 멀티 스레드 문제. (링크)
- 해당 ArrayList를 Thread Safe 하게 사용하기 위해서는, 프록시 객체를 생성하여 접근하여 해결 할 수 있다.
Bad Code 해결
- ArrayList의 프록시 객체를 생성하여, add를 사용할 경우,
syncronized키워드를 통해 lock을 획득 후, 접근 하도록 변경 해 보자.
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ArrayListProxy {
private final List<Integer> lists;
public ArrayListProxy(List<Integer> lists) {
this.lists = lists;
}
public synchronized boolean add(Integer data){
return lists.add(data);
}
}
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ArrayListMainV2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> sharedList = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayListProxy arrayListProxy = new ArrayListProxy(sharedList);
Runnable task = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
// ArrayList에 값 추가
arrayListProxy.add(i);
}
};
Thread[] threads = new Thread[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(task);
}
for (Thread thread : threads) {
thread.start();
}
// 모든 스레드가 종료될 때까지 대기
for (Thread thread : threads) {
try {
thread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("Expected size: " + (10 * 1000));
System.out.println("Actual size: " + sharedList.size());
}
}Expected size: 10000
Actual size: 10000- 기대하는 결과 대로
10000이 나온 모습을 확인 할 수 있다.
Bad Code 해결의 문제점
- 프록시 객체를 사용하여 문제를 회피 했지만, 여전히 문제점은 존재한다.
- ArrayList의 모든 기능을 사용하려면, 모든 기능에 대한
syncronized동기화를 사용한 메서드를 만들어야 한다. syncronzied동기화를 사용하면, 모든 ArrayList에 접근하는 코드는 직렬적으로 접근하게 되어 성능이 나빠진다.
- 따라서, 프록시 객체로의 접근은 해결은 되었지만, 실용적이지 못하고, 성능적인 부분에서 문제점이 일부 발생한다.
- 이 문제에 따라 JAVA에서는 Thread Safe한,
동시성 컬렉션을 제공한다.
Bad Code 해결의 1번 문제점 해결
- Java 에서는 또다시, Java 개발자의 편의를 위해서
syncornized프록시 객체를 생성해주는키워드가 또 존재한다. Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());처럼 사용하면 Thread Safe 한 동기화 프록시 객체를 생성해 준다.
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class ArrayListMainV2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// List<Integer> sharedList = new ArrayList<>();
// ArrayListProxy arrayListProxy = new ArrayListProxy(sharedList);
List<Integer> arrayListProxy = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
Runnable task = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
// ArrayList에 값 추가
arrayListProxy.add(i);
}
};
Thread[] threads = new Thread[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(task);
}
for (Thread thread : threads) {
thread.start();
}
// 모든 스레드가 종료될 때까지 대기
for (Thread thread : threads) {
try {
thread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("Expected size: " + (10 * 1000));
System.out.println("Actual size: " + arrayListProxy.size());
}
}- Collections 의 기능을 사용하여, 간단하게 프록시 객체를 생성하여 해결 할 수 있었지만, 2번 문제인 성능 오버헤드 문제는 여전히 존재한다.
- 때문에, 동시성 컬렉션이 등장하게 되었다.
동시성 컬렉션 사용해보기
- 다양한 동시성 컬렉션이 있지만,
ArrayList의 동시성 컬렉션인CopyOnWriteArrayList를 사용해 보자.
package collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
public class ArrayListMainV3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> sharedList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
Runnable task = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
// ArrayList에 값 추가
sharedList.add(i);
}
};
Thread[] threads = new Thread[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(task);
}
for (Thread thread : threads) {
thread.start();
}
// 모든 스레드가 종료될 때까지 대기
for (Thread thread : threads) {
try {
thread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("Expected size: " + (10 * 1000));
System.out.println("Actual size: " + sharedList.size());
}
}Expected size: 10000
Actual size: 10000- 결과는 예상한 대로,
10000결과가 나왔다.
다양한 동시성 컬렉션의 종류
List계열CopyOnWriteArrayList:ArrayList의 대안
Set계열CopyOnWriteArraySet:HashSet의 대안ConcurrentSkipListSetTreeSet의 대안(정렬된 순서 유지,Comparator사용 가능)
Map계열ConcurrentHashMap:HashMap의 대안ConcurrentSkipListMap:TreeMap의 대안(정렬된 순서 유지,Comparator사용 가능)
Queue계열ConcurrentLinkedQueue: 동시성 큐, 비 차단(non-blocking) 큐이다.
Deque계열ConcurrentLinkedDeque: 동시성 데크, 비 차단(non-blocking) 큐이다.
또한, 스레드는 차단하는 블로킹 큐 또한 존재 한다.
BlockingQueueArrayBlockingQueue
크기가 고정된 블로킹 큐
공정(fair) 모드를 사용할 수 있다. 공정(fair) 모드를 사용하면 성능이 저하될 수 있다.LinkedBlockingQueue- 크기가 무한하거나 고정된 블로킹 큐
PriorityBlockingQueue- 우선순위가 높은 요소를 먼저 처리하는 블로킹 큐
SynchronousQueue- 데이터를 저장하지 않는 블로킹 큐로, 생산자가 데이터를 추가하면 소비자가 그 데이터를 받을 때까지 대기한다. 생산자-소비자 간의 직접적인 핸드오프(hand-off) 메커니즘을 제공한다. 쉽게 이야기해서 중간에 큐 없이 생산자, 소비자가 직접 거래한다.
DelayQueue- 지연된 요소를 처리하는 블로킹 큐로, 각 요소는 지정된 지연 시간이 지난 후에야 소비될 수 있다. 일정 시간이 지난 후 작업을 처리해야 하는 스케줄링 작업에 사용된다.
