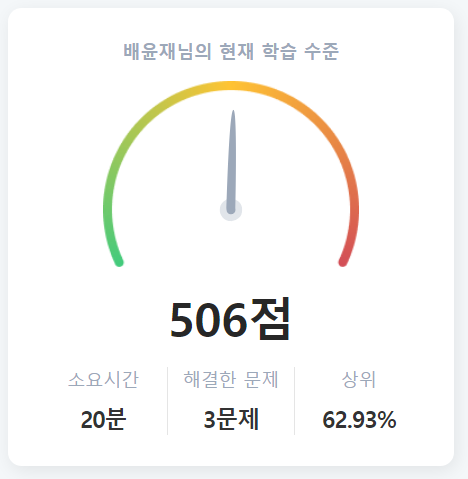
⭐실력진단 결과
객체를 정렬하는 방법에 대해 배우게 됩니다.
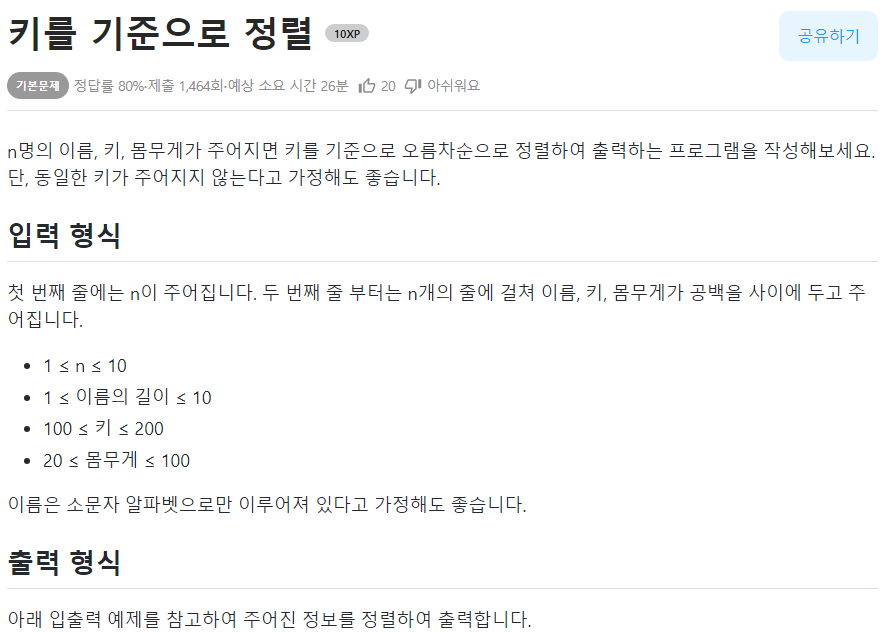
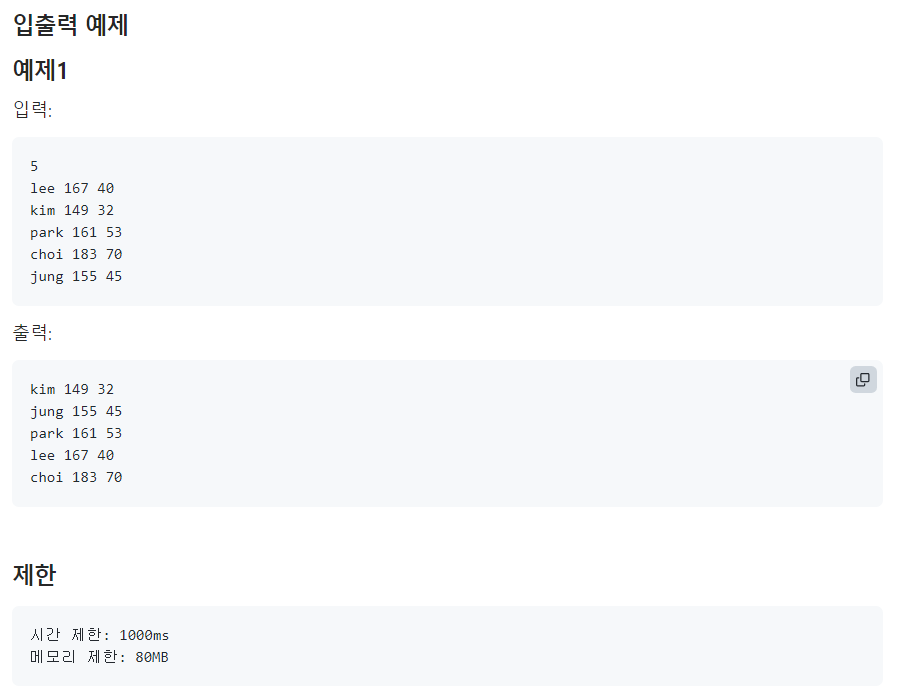
🟢키를 기준으로 정렬
✏️class를 이용한 객체 정렬
lambda는 이름 없이 사용하는 익명함수
f = lambda x: x * 2 # lambda 인자 : 반환값
print(f(3)) # 6- 객체 정렬에서는 lambda 함수의 반환값에 기준이 되기를 원하는 값을 적어준다.
- sort 함수에서 key 인자로 lambda 함수를 작성하면, x인자에 들어오는 값은 하나의 객체
class Student:
def __init__(self, kor, eng, math):
self.kor = kor
self.eng = eng
self.math = math
students = [
Student(90, 80, 80),
...
Student(30, 40, 10),
]
students.sort(key=lambda x: x.kor) # 국어 점수 기준 오름차순 정렬
for student in students:
print(student.kor, student.eng, student.math)
- 내림차순 정렬은 x.kor 앞에 -를 붙여 해결
students.sort(key=lambda x: -x.kor) # 국어 점수 기준 내림차순 정렬✏️tuple를 이용한 객체 정렬
- x값이 하나의 tuple값
- 예를 듣어, 국어 점수에 해당하는 x[0]을 lambda 함수의 반환값을 적어준다.
students = [
(90, 80, 90),
...
(30, 40, 70),
]
students.sort(key=lambda x: x[0]) # 국어 점수 기준 오름차순 정렬- tuple 원소 리스트를 순회할 때 for loop와 동시에 unpacking을 진행하면 더 깔끔한 코드 작성 가능
for kor, eng, math in students:
print(kor, eng, math)📌문제
📌나의 코드
- class
class Student:
def __init__(self, name, height, weight):
self.n = name
self.h = height
self.w = weight
n = int(input())
students = []
for _ in range(n):
name, height, weight = input().split()
students.append(Student(name, int(height), int(weight)))
students.sort(key = lambda x: x.h)
for student in students:
print(student.n, student.h, student.w)- tuple
n = int(input())
# 이름, 키, 몸무게
ls = [tuple(input().split()) for _ in range(n)]
ls.sort(key = lambda x: x[1])
for name, height, weight in ls:
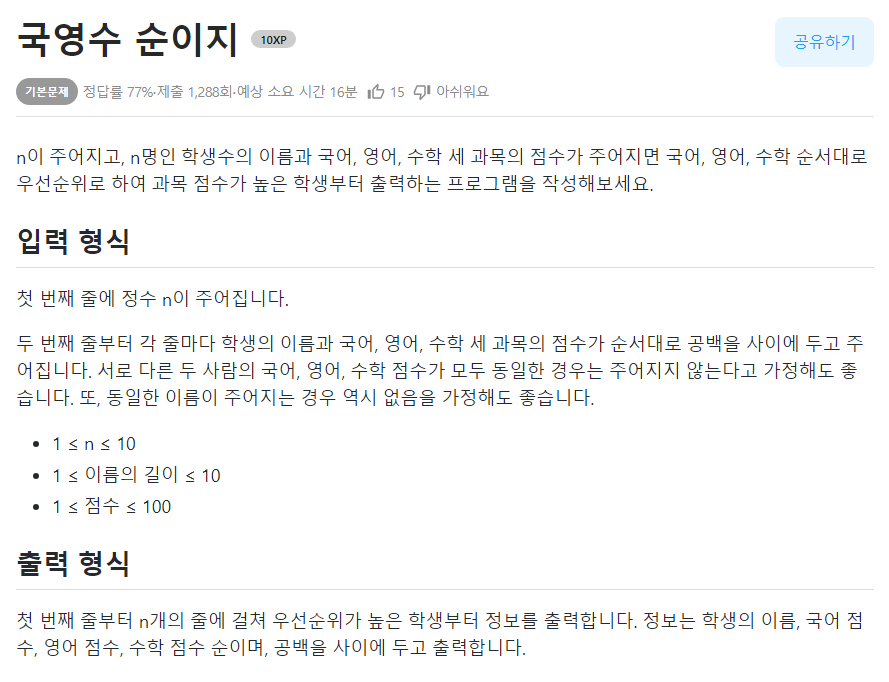
print(name, height, weight)🟢국영수 순이지
✏️여러 우선순위를 갖는 객체 정렬
-
여러 우선순위를 갖는 경우 lambda 함수의 반환값을 단일 값이 아닌, tuple값으로 정의
-
여러 개 (예: 2개) 의 원소로 이루어진 tuple끼리 비교 연산을 하는 경우
1.먼저 첫 번째 원소를 기준으로 비교
2.첫 번째 원소가 동일하다면 두 번째 원소를 기준으로 비교 -
위의 tuple 특성을 이용해 lambda 함수의 반환값에 우선순위대로 각 기준이 되는 값을 적어준다.
# 첫 번째 우선순위는 국어 점수 오름차순
# 국어 점수가 같다면 두 번째 우선순위는 영어 점수 오름차순
students.sort(key=lambda x: (x.kor, x.eng))
# 국어 점수 오름차순, 영어 점수 내림차순의 경우
students.sort(key=lambda x: (x.kor, -x.eng))- tuple을 이용한 객체 정렬도 마찬가지로 lambda 함수의 반환값으로 tuple 사용
# 첫 번째 우선순위 : 국어 점수 오름차순, 두 번째 우선순위 : 영어 점수 내림차순
students.sort(key=lambda x: (x[0], -x[1]))📌문제
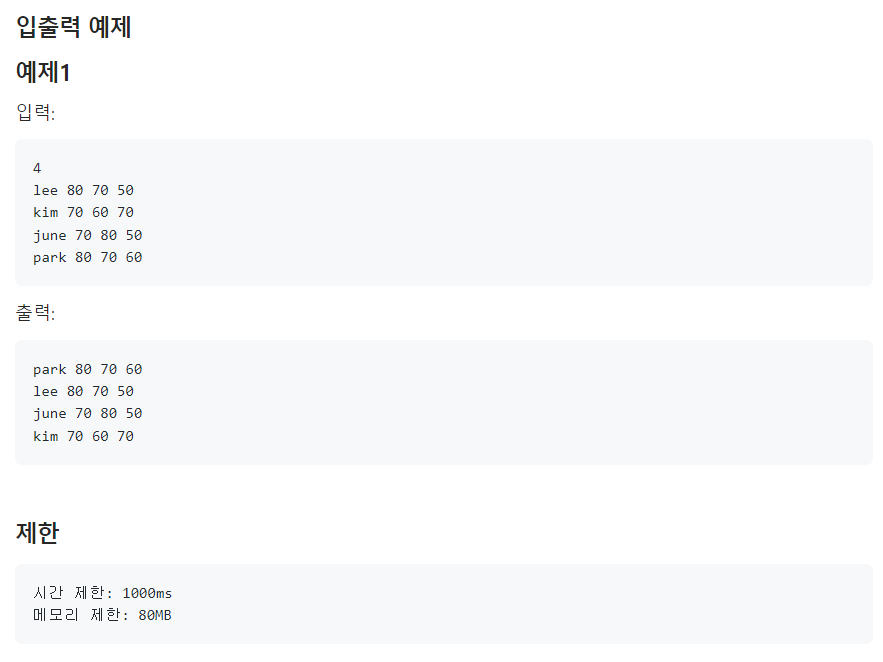
📌나의 코드
- class
class Student:
def __init__(self, name, kor, eng, math):
self.name, self.kor, self.eng, self.math = name, kor, eng, math
n = int(input())
students = []
for _ in range(n):
name, k, e, m = input().split()
students.append(Student(name, int(k), int(e), int(m)))
# 점수가 높은 학생부터 출력하므로 내림차순 정렬
students.sort(key = lambda x : (-x.kor, -x.eng, -x.math))
for student in students:
print(student.name, student.kor, student.eng, student.math)- tuple
n = int(input())
students = []
for _ in range(n):
name, kor, eng, math = input().split()
students.append((name, int(kor), int(eng), int(math)))
# 점수가 높은 학생부터 출력하므로 내림차순 정렬
# tuple 0: 이름, 1: 국어, 2: 영어, 3: 수학
students.sort(key = lambda x : (-x[1], -x[2], -x[3]))
for name, kor, eng, math in students:
print(name, kor, eng, math)🔓풀이
- tuple을 이용할 시 내림차순으로 정렬할 때는 (-)연산을 위해서 원소가 정수여야 하므로 입력을 int형으로 바꿔주어야 한다.
- 오름차순으로 정렬할 때는 str형이어도 되기는 함
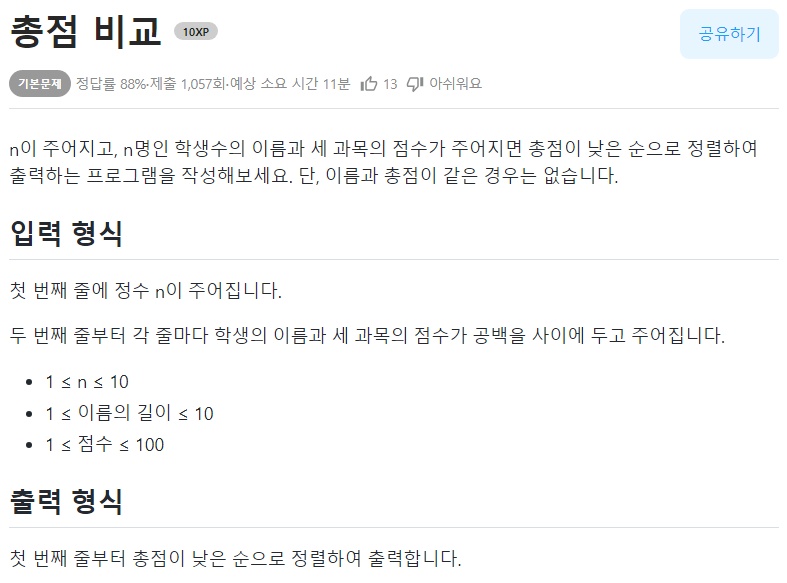
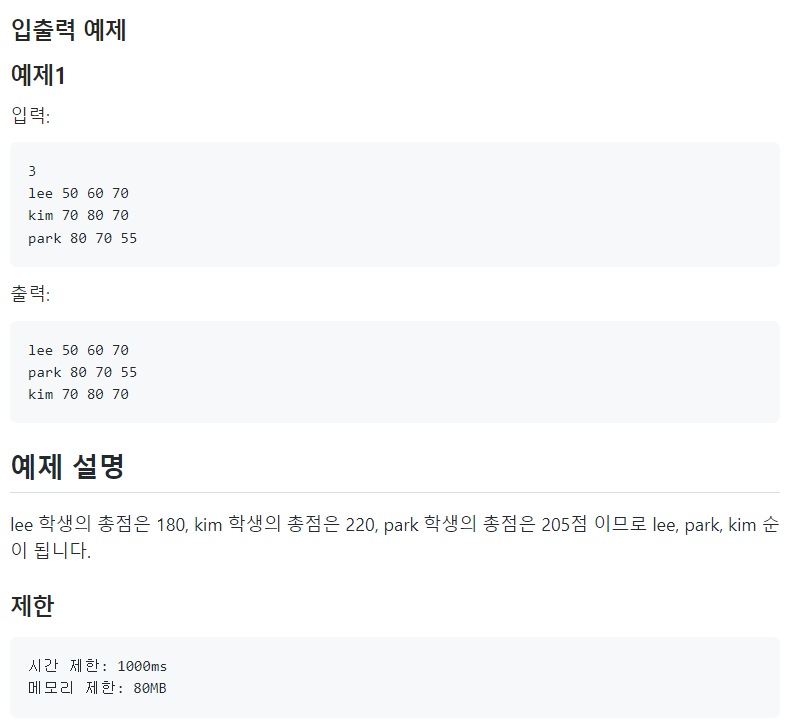
🟢총점 비교
✏️정렬 기준이 복잡한 객체 정렬
- 점수의 총합을 기준으로 정렬한다면 lambda 함수의 반환값을 합으로 설정해주면 된다.
## Class ##
students.sort(key=lambda x: x.kor + x.eng + x.math)
## Tuple ##
students.sort(key=lambda x: x[0] + x[1] + x[2])➕comparator 함수
- lambda 함수로 처리하기 어려운 경우, lambda 함수 대신 직접 기준을 정해주는 comparator 함수 생성
- comparator 함수를 sort 함수의 key 인자로 넘길 때, 반드시 functools 내 cmp_to_key 함수를 import하여 cmp_to_key(compare) 식으로 감싸줘야 한다.
예) 국어 점수 기준인데, 국어 점수가 30의 배수인 경우 먼저 나오도록 하는 정렬
## custom comparator 정의 ##
# x가 앞에 있는 학생, y가 뒤에 있는 학생이라 가정
# 이 순서가 원하는 순서면 0보다 작은 값 (-1),
# 반대라면 0보다 큰 값 (1),
# 둘의 우선순위가 동일하다면 0 반환
def compare(x, y):
# x만 국어 점수가 30의 배수라면 x가 더 앞에 있어야 함
# 현재 순서가 True
if x.kor % 30 == 0 and y.kor % 30 != 0:
return -1
# y만 국어 점수가 30의 배수라면 y가 더 앞에 있어야 함
# 현재 순서가 False
if x.kor % 30 != 0 and y.kor % 30 == 0:
return 1
# 우선 순위가 동일한 경우
# 즉, 국어 점수가 둘 다 30의 배수이거나 둘 다 30의 배수가 아닌 경우
return 0
students.sort(key = cmp_to_key(compare))📌문제
📌나의 코드
- class
class Student:
def __init__(self, name, s1, s2, s3):
self.name, self.s1, self.s2, self.s3 = name, s1, s2, s3
n = int(input())
students = []
for _ in range(n):
name, s1, s2, s3 = input().split()
students.append(Student(name, int(s1), int(s2), int(s3)))
students.sort(key = lambda x : x.s1 + x.s2 + x.s3)
for student in students:
print(student.name, student.s1, student.s2, student.s3)- tuple
n = int(input())
students = []
for _ in range(n):
name, s1, s2, s3 = input().split()
students.append((name, int(s1), int(s2), int(s3)))
students.sort(key = lambda x : x[1] + x[2] + x[3])
for name, s1, s2, s3 in students:
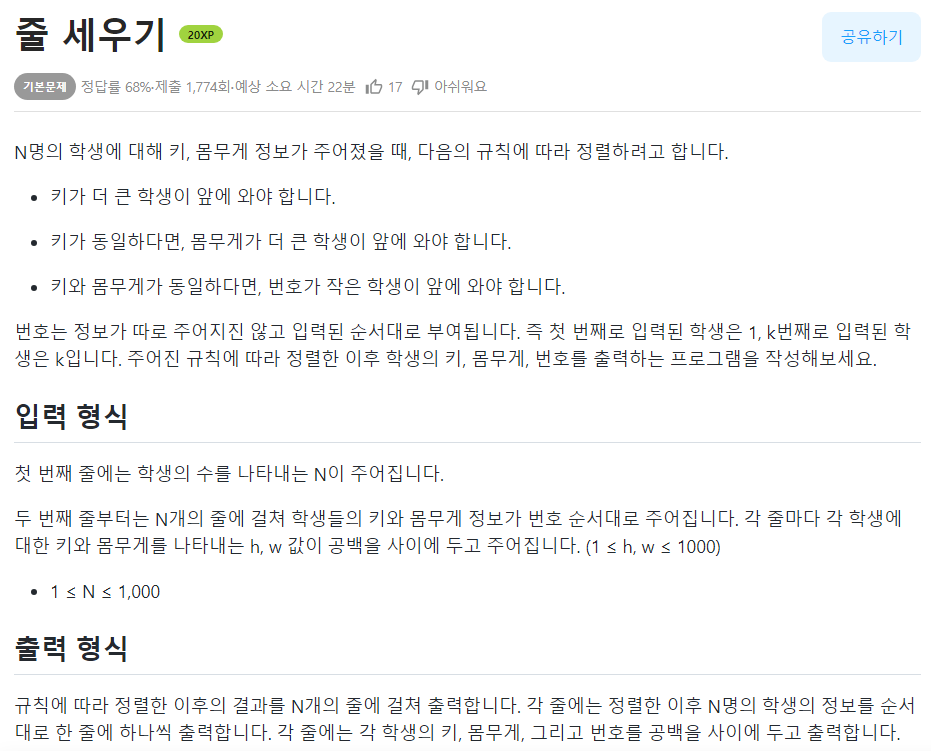
print(name, s1, s2, s3)🟢줄 세우기
✏️객체 정렬시 index 멤버 변수의 필요성
- 정렬 이후 각 등수에 해당하는 학생의 번호를 출력할 수 있도록 객체에 학생 번호에 해당하는 멤버 변수 추가
- 등수별 학생의 번호를 출력할 때 for loop 진행 시 각 원소와 index를 뽑아주는 enumerate 함수 사용
start값을 인자로 넘기면 시작 index값을 설정할 수 있다.
# 정렬 이후 등수별 학생 번호 출력, 1등부터 시작 (start = 1)
for idx, student in enumerate(students, start=1):
print(f'{idx}등: {student.number}번')
>> 1등: 1번
2등: 3번
3등: 5번
4등: 4번
5등: 2번- tuple의 경우 enumerate로부터 뽑아낸 tuple 값에서 4번째 값인 number 값만 필요하므로 나머지는 _로 처리
for idx, (_, _, _, number) in enumerate(students, start=1):
print(f'{idx}등: {student.number}번')- 각 학생별 등수를 출력하고 싶은 경우
즉, 등수별 학생 번호가 주어졌을 때, 각 학생별 등수 구하는 방법
⇒ 어느 학생이 어떤 등수를 받았는지를 나타내는 배열을 새로 생성
등수별 학생 번호를 순회하면서, 각 학생 번호의 index에 해당 rank를 넣어주는 식으로 코드 작성 가능
num_to_rank = [0] * 6 # 5명이므로 1번부터 시작
nums = [1, 3, 5, 4, 2] # 학생 번호
# (등수, 번호)
# (1, 1), (2, 3), (3, 5), (4, 4), (5, 2)
for rank, num in enumerate(nums, start=1):
num_to_rank[num] = rank
print(num_to_rank) # [0, 1, 5, 2, 4, 3]📌문제


📌나의 코드
- class
class Student:
def __init__(self, height, weight, number):
self.height, self.weight, self.number = height, weight, number
n = int(input())
students = []
for i in range(1, n + 1):
h, w = map(int, input().split())
students.append(Student(h, w, i))
students.sort(key = lambda x : (-x.height, -x.weight, x.number))
for student in students:
print(student.height, student.weight, student.number)- tuple
n = int(input())
students = []
for i in range(1, n + 1):
h, w = map(int, input().split())
students.append((h, w, i))
students.sort(key = lambda x : (-x[0], -x[1], x[2]))
for h, w, num in students:
print(h, w, num)
