HashSet 의 구현 / C++
구현 과정
Hash Table 의 구현을 통해 Key 와 Value 를 맵핑하는 방식
key를 index 로 변환시키는 Hash 함수 들이 존재하고, 함수의 성능에 따라 성능이 좌우된다.
-> 즉 변환된 index 값을 이용해 배열에 접근하고,
배열에 저장되어 있는 구조체에 접근해 Value 에 접근한다.
단점으로는 index 의 충돌을 막기 위해 데이터 갯수보다 더 큰 크기의 배열을 사용해야한다.
-> 메모리를 많이 사용
index의 충돌 과정
간단한 예로key가 정수형일때
key값을배열의 크기로 나눠index값으로 사용하는 해쉬함수의 경우
1) key = 8 , 배열의 크기 = 7 이면 / index = 1
2) key = 15 , 배열의 크기 = 7 이면 / index = 1
-> 동일한 인덱스에 접근해 충돌
위 상황을 막기 위한 방안으로는
1) 배열의 요소를 연결리스트 로 구성하여 해당 index 에 데이터를 계속 추가하는 방법 -> Separate Chaining
2) 비어있는 index 를 찾을때까지 index를 조정 하는 방법 -> Open Addressing
2번 방안에서도 문제되는 것은 요소를 삭제할때.
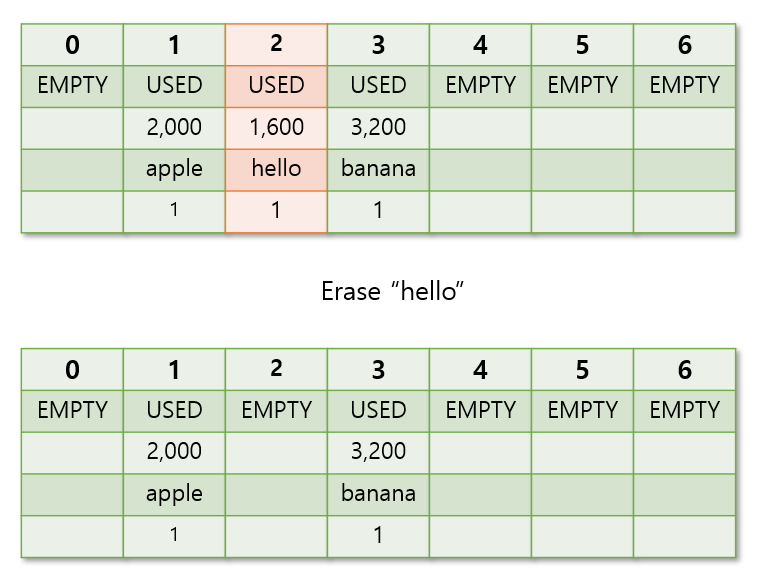
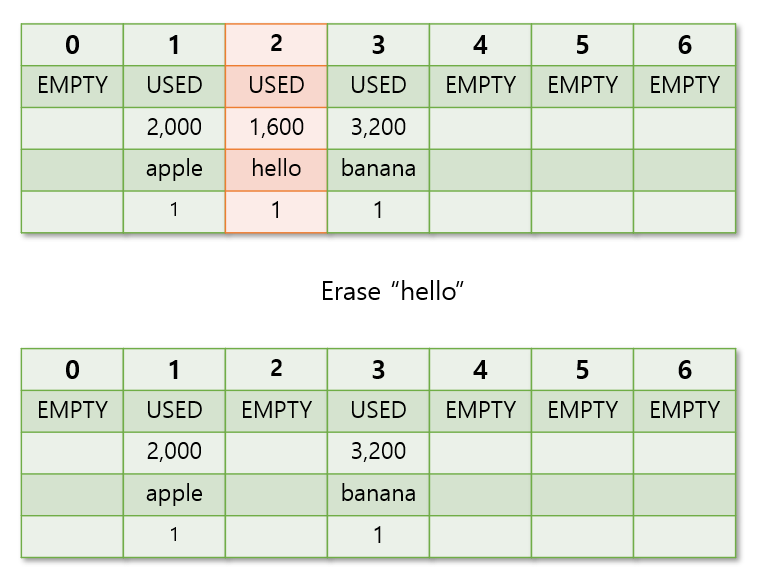
그림의 hello 와 banana 는 apple 과 hash 함수를 통해 도출된 index 값이 겹쳐, 비어있는 인덱스에 저장된 요소들이다.
위에서key값이 hello 인 요소를 삭제했다.
-> 그럼index= 2 가empty상태가 되는데
->key값이 banana 인 요소를 찾으려할때, 요소가empty상태인 인덱스가 나올때까지 순회 해야하는데.. 중간에 비어있는 인덱스가 있어서 banana 를 못 찾는 상황이 발생할 수 도 있다.
-> 따라서deleted상태를 추가해서 테이블의 구조를 데이터 탐색에 방해되지 않도록 유지해줘야한다.
부하율 : 데이터의 갯수를 배열의 크기로 나눈 값
해쉬테이블을 구현할때는 특정 부하율을 넘어섰을때, 배열 크기를 재조정하는 작업을 해줘야한다.
-> 기존에 저장되어있던 값들의 hash 를 조정된 배열의 크기로 다시 연산해 기존 데이터들도 다시 배치해줘야한다
구현 코드
- hash.h
#ifndef HASH_H
#define HASH_h
//header 파일의 중복 include 를 막기위함
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "Pair.h"
#define MAX_LOAD_FACTOR 0.5
#define INITIAL_CAPACITY 7
typedef enum State{
EMPTY,
USED,
DELETED
};
typedef struct node{
Pair *data;
unsigned int hash_value;
State state;
};
typedef struct Hash{
node *bucket;
int size;
int capacity;
};
void initialize(Hash *hash);
void insert(Hash *hash, Pair *data);
void erase(Hash *hash, char *key);
Pair *find(Hash *hash, char *key);
#endif- hash.cpp
#include "Hash.h"
//소수 찾기
static int get_next_prime(int num){
while(true){
bool is_prime = true;
for (long long i=2; i*i<=num; ++i){
if (num%i==0){
is_prime = false;
break;
}
}
if (is_prime == true){
return (num);
}
++num;
}
}
static unsigned int hashing(unsigned char* str){
unsigned int hash = 5381;
while(*str != '\0'){
hash = hash*33 + *str;
++str;
}
return hash;
}
static int find_idx(Hash *hash, char *key){
unsigned int hash_value = hashing((unsigned char*)key);
unsigned int idx = hash_value;
for (int i=0; i<hash->capacity; ++i, ++idx){
if (hash->bucket[idx%hash->capacity].state==EMPTY){
break;
}
if (hash->bucket[idx%hash->capacity].state==DELETED){
continue;
}
if (strcmp(hash->bucket[idx%hash->capacity].data->key, key) ==0){
return idx%hash->capacity;
}
}
return -1;
}
void initialize(Hash *hash){
hash->bucket = NULL;
hash->size = 0;
hash->capacity = 0;
}
static void re_allocate(Hash *hash, int size){
// 재배치 해주는 과정에서 사용
int prev_capacity = hash->capacity;
if (size ==0){
hash->capacity = INITIAL_CAPACITY;
}
else{
hash->capacity = get_next_prime(size);
}
node* new_bucket = (node*)malloc(hash->capacity * sizeof(node));
for (int i=0; i<hash->capacity; i++){
new_bucket[i].state = EMPTY;
}
for (int i=0; i< prev_capacity; i++){
if (hash->bucket[i].state != USED){
continue;
}
unsigned int idx = hash->bucket[i].hash_value;
while(new_bucket[idx%hash->capacity].state==USED){
if (strcmp(new_bucket[idx%hash->capacity].data->key, hash->bucket[i].data->key)==0){
return;
}
++idx;
}
new_bucket[idx%hash->capacity]= (node){hash->bucket[i].data, hash->bucket[i].hash_value, USED};
}
free(hash->bucket);
hash->bucket = new_bucket;
}
void insert(Hash *hash, Pair *data){
if (hash->size==0 || (double)hash->size/hash->capacity > MAX_LOAD_FACTOR){
re_allocate(hash, hash->capacity*2);
}
unsigned int hash_value = hashing((unsigned char*)data->key);
unsigned int idx = hash_value;
while (hash->bucket[idx%hash->capacity].state == USED){
if (strcmp(hash->bucket[idx%hash->capacity].data->key, data->key)==0){
return;
}
++idx;
}
hash->bucket[idx%hash->capacity] = (node){data,hash_value,USED};
++hash->size;
}
void erase(Hash *hash, char *key){
int idx = find_idx(hash, key);
if (idx == -1){
return ;
}
free(hash->bucket[idx].data->key);
free(hash->bucket[idx].data);
hash->bucket[idx].state = DELETED;
--hash->size;
}
Pair *find(Hash *hash, char *key){
int idx = find_idx(hash, key);
if (idx == -1){
return NULL;
}
return hash->bucket[idx].data;
}- pair.h
#ifndef PAIR_H
#define PAIR_H
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
typedef struct Pair{
char *key;
int value;
};
Pair* make_pair(const char* key, int value);
#endif- pair.cpp
#include "Pair.h"
Pair* make_pair(const char* key, int value){
Pair* new_pair = (Pair*)malloc(sizeof(Pair));
new_pair->key = strdup(key);
new_pair->value = value;
return new_pair;
}- main.cpp
#include "Hash.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
void print_hash(Hash *hash){
cout<<"size: "<<hash->size<<" cap: "<<hash->capacity<<endl;
for (int i=0; i<hash->capacity; i++){
switch(hash->bucket[i].state){
case 0:
cout<<i<<" EMPTY , - : - [ - ]"<<endl;
break;
case 1:
cout<<i<<" USED , "<<hash->bucket[i].data->key<<" : "<<hash->bucket[i].data->value<< "[ "<<hash->bucket[i].hash_value%hash->capacity<<" ]"<<endl;
break;
case 2:
cout<<i<<" DELETED , - : - [ - ]"<<endl;
break;
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
void print_hash_find(Pair* result){
if (result == NULL){
cout<<"KEY NOT FOUND"<<endl;
}
else{
cout<<result->value<<endl;
}
}
int main(){
Hash hash;
printf("----- initialize -----\n");
initialize(&hash);
print_hash(&hash);
printf("----- insert -----\n");
insert(&hash, make_pair("hello", 1));
print_hash(&hash);
insert(&hash, make_pair("world", 2));
print_hash(&hash);
insert(&hash, make_pair("my name", 3));
print_hash(&hash);
insert(&hash, make_pair("is sikpang", 4));
print_hash(&hash);
insert(&hash, make_pair("nice", 5));
print_hash(&hash);
insert(&hash, make_pair("to meet you", 6));
print_hash(&hash);
insert(&hash, make_pair("this is", 7));
print_hash(&hash);
insert(&hash, make_pair("hash_table", 8));
print_hash(&hash);
insert(&hash, make_pair("thank you", 9));
print_hash(&hash);
printf("\n----- find -----\n");
print_hash_find(find(&hash, "hash_table"));
print_hash_find(find(&hash, "thank you!"));
print_hash_find(find(&hash, "thank you"));
print_hash_find(find(&hash, "hash_tablee"));
}- 출력 화면
----- initialize -----
size: 0 cap: 0
----- insert -----
size: 1 cap: 7
0 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
1 USED , hello : 1[ 1 ]
2 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
3 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
4 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
5 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
6 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
size: 2 cap: 7
0 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
1 USED , hello : 1[ 1 ]
2 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
3 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
4 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
5 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
6 USED , world : 2[ 6 ]
size: 3 cap: 7
0 USED , my name : 3[ 6 ]
1 USED , hello : 1[ 1 ]
2 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
3 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
4 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
5 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
6 USED , world : 2[ 6 ]
size: 4 cap: 7
0 USED , my name : 3[ 6 ]
1 USED , hello : 1[ 1 ]
2 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
3 USED , is sikpang : 4[ 3 ]
4 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
5 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
6 USED , world : 2[ 6 ]
size: 5 cap: 17
0 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
1 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
2 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
3 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
4 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
5 USED , hello : 1[ 5 ]
6 USED , world : 2[ 5 ]
7 USED , nice : 5[ 5 ]
8 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
9 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
10 USED , my name : 3[ 10 ]
11 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
12 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
13 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
14 USED , is sikpang : 4[ 14 ]
15 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
16 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
size: 6 cap: 17
0 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
1 USED , to meet you : 6[ 1 ]
2 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
3 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
4 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
5 USED , hello : 1[ 5 ]
6 USED , world : 2[ 5 ]
7 USED , nice : 5[ 5 ]
8 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
9 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
10 USED , my name : 3[ 10 ]
11 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
12 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
13 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
14 USED , is sikpang : 4[ 14 ]
15 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
16 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
size: 7 cap: 17
0 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
1 USED , to meet you : 6[ 1 ]
2 USED , this is : 7[ 2 ]
3 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
4 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
5 USED , hello : 1[ 5 ]
6 USED , world : 2[ 5 ]
7 USED , nice : 5[ 5 ]
8 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
9 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
10 USED , my name : 3[ 10 ]
11 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
12 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
13 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
14 USED , is sikpang : 4[ 14 ]
15 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
16 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
size: 8 cap: 17
0 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
1 USED , to meet you : 6[ 1 ]
2 USED , this is : 7[ 2 ]
3 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
4 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
5 USED , hello : 1[ 5 ]
6 USED , world : 2[ 5 ]
7 USED , nice : 5[ 5 ]
8 USED , hash_table : 8[ 8 ]
9 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
10 USED , my name : 3[ 10 ]
11 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
12 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
13 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
14 USED , is sikpang : 4[ 14 ]
15 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
16 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
size: 9 cap: 17
0 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
1 USED , to meet you : 6[ 1 ]
2 USED , this is : 7[ 2 ]
3 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
4 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
5 USED , hello : 1[ 5 ]
6 USED , world : 2[ 5 ]
7 USED , nice : 5[ 5 ]
8 USED , hash_table : 8[ 8 ]
9 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
10 USED , my name : 3[ 10 ]
11 USED , thank you : 9[ 11 ]
12 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
13 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
14 USED , is sikpang : 4[ 14 ]
15 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
16 EMPTY , - : - [ - ]
----- find -----
8
KEY NOT FOUND
9
KEY NOT FOUND
느낀 점
어렵다..
배열을 통해 구현되는 hashtable 특성 상
배열의 크기가 꽉 차면 크기를 재조정하는 과정이 필요하고,
이 과정에서 해싱과정과 일련의 알고리즘을 통해 도출되는 데이터의 index가 변화해, 기존 데이터의 위치를 새로 조정한 배열에 맞춰 넣는 과정이 인상 깊었다.
-> 데이터 마다 hashing 과정을 통해 도출되는 hash_value 변수를 저장해두고,
-> 배열 크기 재조정 과정을 거치면서 반복문을 이용해 hash_value 변수 값을 참조해 재배치
-> re_allocate 함수
또 부호를 신경쓰지않는 unsigned 자료형을 사용해 메모리의 효율을 높인 것도 기억해두어야겠다.
-> 키, 몸무게, 나이 등과같이 양수의 값만 가지는 데이터들을 다룰때 사용하기..