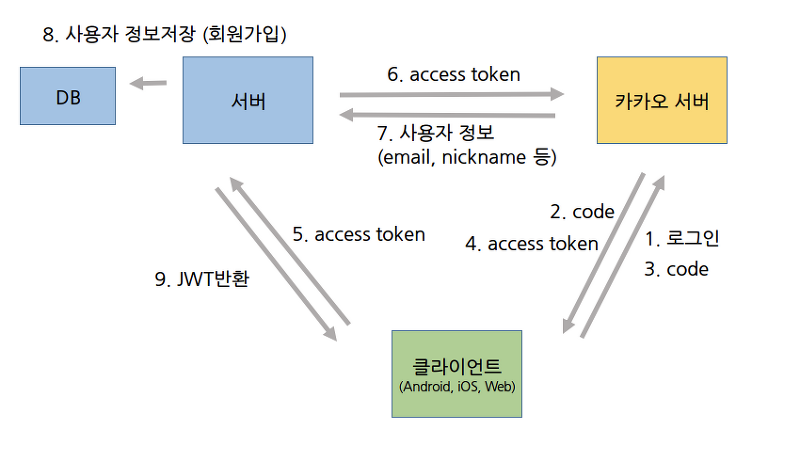
우리 프로젝트 로그인은 그림과 같이, 프론트로부터 token을 받아와서 카카오로 부터 정보를 받아와 저장하고, JWT를 프론트로 return 시켜주는 방법을 사용하기로 했다.
카카오톡 로그인 구현
Controller
@PostMapping("/kakao")
public void kakaoLogin(@RequestHeader(value = "Authorization") String token) throws Exception{
kakaoService.getUserInfoWithToken(token);@RestController
@RestController는 @Controller에 @ResponseBody가 추가된 것이다. 주용도는 Json 형태로 객체 데이터를 반환하는 것이다.
@RequiredArgsConstructor
클래스에 선언된 final 변수들, 필드들을 매개변수로 하는 생성자를 자동으로 생성해주는 어노테이션이다.
Service
public void getUserInfoWithToken(String accessToken) throws Exception {
//HttpHeader 생성
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("Authorization", accessToken);
headers.add("Content-type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8");
//HttpHeader 담기
RestTemplate rt = new RestTemplate();
HttpEntity<MultiValueMap<String, String>> httpEntity = new HttpEntity<>(headers);
ResponseEntity<String> response = rt.exchange(
KAKAO_API_URI + "/v1/user/access_token_info",
HttpMethod.GET,
httpEntity,
String.class
);
//Response 데이터 파싱
JSONParser jsonParser = new JSONParser();
JSONObject jsonObj = (JSONObject) jsonParser.parse(response.getBody());
long id = (long) jsonObj.get("id");
}@Service
해당 클래스를 루트 컨테이너에 빈(Bean) 객체로 생성해주는 어노테이션이다.