문제 출처는 제로베이스 데이터 스쿨
▶Ex01 함수
def add(a,b):
print(f'{a} + {b} = {a+b}')
def sub(a,b):
print(f'{a} - {b} = {a-b}')
def mul(a,b):
print(f'{a} * {b} = {a*b}')
def div(a,b):
print(f'{a} / {b} = {a/b}')
def mod(a,b):
print(f'{a} % {b} = {a%b}')
def flo(a,b):
print(f'{a} // {b} = {a//b}')
def exp(a,b):
print(f'{a} ** {b} = {a**b}')
while True:
print('-'*60)
choice = int(input('1.덧셈, 2.뺄셈, 3.곱셈, 4.나눗셈, 5.나머지, 6.몫, 7.제곱승, 8.종료'))
if choice ==8 :
print('Bye')
break
a = int(input('첫 번째 숫자 입력 : '))
b = int(input('두 번째 숫자 입력 : '))
if choice == 1:
add(a, b)
elif choice == 2:
sub(a, b)
elif choice == 3:
mul(a, b)
elif choice == 4:
div(a, b)
elif choice == 5:
mod(a, b)
elif choice == 6:
flo(a, b)
elif choice == 7:
exp(a, b)#출력
1.덧셈, 2.뺄셈, 3.곱셈, 4.나눗셈, 5.나머지, 6.몫, 7.제곱승, 8.종료4
첫 번째 숫자 입력 : 20
두 번째 숫자 입력 : 4
20 / 4 = 5.0
------------------------------------------------------------
1.덧셈, 2.뺄셈, 3.곱셈, 4.나눗셈, 5.나머지, 6.몫, 7.제곱승, 8.종료1
첫 번째 숫자 입력 : 5
두 번째 숫자 입력 : 10
5 + 10 = 15
------------------------------------------------------------
1.덧셈, 2.뺄셈, 3.곱셈, 4.나눗셈, 5.나머지, 6.몫, 7.제곱승, 8.종료2
첫 번째 숫자 입력 : 20
두 번째 숫자 입력 : 7
20 - 7 = 13
------------------------------------------------------------
1.덧셈, 2.뺄셈, 3.곱셈, 4.나눗셈, 5.나머지, 6.몫, 7.제곱승, 8.종료8
Bye💡8번의 종료를 else로 뺐었는데, 변수를 받는 부분보다 순서가 뒤라 어떻게 처리해야 할 지를 몰랐었다. 아주 간단하게 종료는 다자선택 코드보다 위에 두면 되는거였다..
▶Ex02 함수
def getDistance(s, h, m):
distance = s * (h + (m / 60))
return distance
def getTime(s, d):
t = d / s
h = int(t) # 시간 단위는 정수형만 하면 해결
m = (t-h)*100 * 60 / 100 # 분단위로 만들고 0.6(60분단위) 곱하기
return [h, m]
print('-' * 60)
s = float(input('속도(km/h) 입력 : '))
h = float(input('시간(h) 입력 : '))
m = float(input('시간(m) 입력 : '))
d = getDistance(s,h,m)
print(f'{s}(km/h)속도로 {h}시간 {m}분 동안 이동한 거리 {d:.2f}km')
print('-' * 60)
print('-' * 60)
s = float(input('속도(km/h) 입력 : '))
d = float(input('거리(km) 입력 : '))
t = getTime(s,d)
print(f'{s}(km/h)속도로 {d}km 이동한 시간 : {t[0]}시간 {t[1]:.2f}분 소요')
print('-' * 60)#출력
------------------------------------------------------------
속도(km/h) 입력 : 87
시간(h) 입력 : 4
시간(m) 입력 : 29
87.0(km/h)속도로 4.0시간 29.0분 동안 이동한 거리 390.05km
------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------
속도(km/h) 입력 : 49
거리(km) 입력 : 124
49.0(km/h)속도로 124.0km 이동한 시간 : 2시간 31.84분 소요
------------------------------------------------------------💡두번째 함수에서 return 타입, 시와 분 단위를 어떻게 떼어 반환할 것인가. 가 포인트 였던 것 같다.
▶Ex03 함수
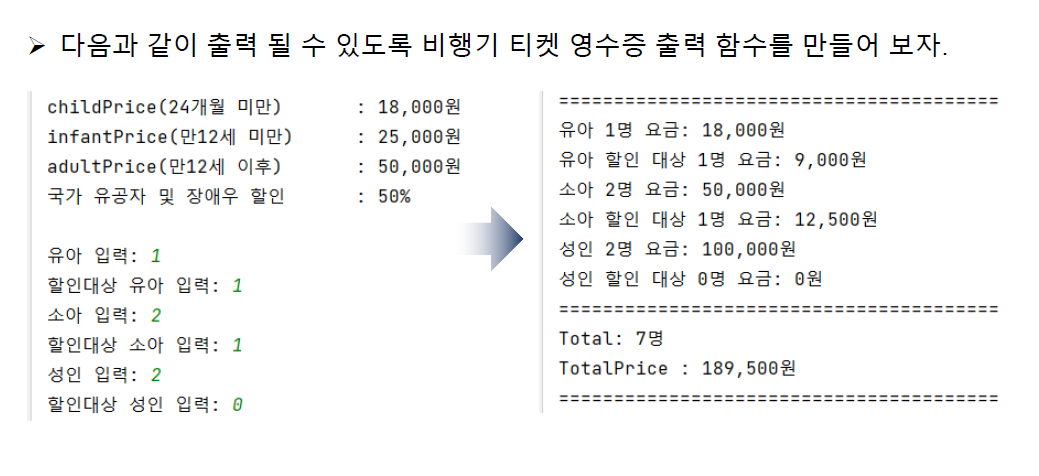
def babyFee(n,d):
result1 = 18000 * n
result2 = 18000 * d * 0.5
return [result1, result2]
def childFee(n,d):
result1 = 25000 * n
result2 = 25000 * d * 0.5
return [result1, result2]
def adultFee(n,d):
result1 = 50000 * n
result2 = 50000 * d * 0.5
return [result1, result2]
inputBaby = int(input('유아 입력 : '))
disBaby = int(input('할인대상 유아 입력 : '))
inputChild = int(input('소아 입력 : '))
disChild = int(input('할인대상 소아 입력 : '))
inputAdult = int(input('성인 입력 : '))
disAdult = int(input('할인대상 성인 입력 : '))
b = babyFee(inputBaby,disBaby)
c = childFee(inputChild,disChild)
a = adultFee(inputAdult,disAdult)
sumPeo = inputBaby + disBaby + inputChild + disChild + inputAdult + disAdult
list = babyFee(inputBaby,disBaby) + childFee(inputChild,disChild) + adultFee(inputAdult,disAdult)
sumPri = 0
for index in list:
sumPri += index
print('='*30)
print(f'유아 {inputBaby}명 요금 : {b[0]}원')
print(f'유아 할인대상 {disBaby}명 요금 : {b[1]}원')
print(f'소인 {inputChild}명 요금 : {c[0]}원')
print(f'소인 할인대상 {disChild}명 요금 : {c[1]}원')
print(f'성인 {inputAdult}명 요금 : {a[0]}원')
print(f'성인 할인대상 {disAdult}명 요금 : {a[1]}원')
print('='*30)
print(f'Total : {sumPeo}명')
print(f'TotalPrice : {sumPri}원')
print('='*30)#출력
유아 입력 : 1
할인대상 유아 입력 : 1
소아 입력 : 2
할인대상 소아 입력 : 1
성인 입력 : 2
할인대상 성인 입력 : 0
==============================
유아 1명 요금 : 18000원
유아 할인대상 1명 요금 : 9000.0원
소인 2명 요금 : 50000원
소인 할인대상 1명 요금 : 12500.0원
성인 2명 요금 : 100000원
성인 할인대상 0명 요금 : 0.0원
==============================
Total : 7명
TotalPrice : 189500.0원
==============================💡출력을 생각해서 반환을 어떤 식으로 할까?, 어디까지 변수가 필요할까? 아직 많이 버벅댄다.
▶Ex04 함수
def factorial(n):
if n == 1:
return 1
return n * factorial(n-1)
res = factorial(20)
print('{:,}'.format(res))#출력
2,432,902,008,176,640,000💡return문에 다음으로 적은 값을 넣은 함수를 넣어 계산이 도미노처럼 되도록 하면 된다. if문을 일단 써놓고, n에 1을 넣고 break를 써야하나? 아니면 1을 바로 리턴하면 되나? 고민하다 1을 바로 return했다. 그리고 답이 나왔다. 'break'를 써보고도 싶었다. 그런데, 'break'는 쓸 수 없었다. break문은 반복문, loop를 빠져나오기 위한 목적으로 쓰는 것. 함수 내에서는 쓰지 않는다. 대신 함수는 'return'문을 쓰면 함수를 종료하고 값을 반환한다.
▶Ex05 함수
def ansn(a1, d, n):
for index in range(1,n+1):
an = int(a1 + (index - 1) * d)
sn = int((a1 + an) * index / 2)
print(f'{index}번째 항의 값 {an}')
print(f'{index}번째 항까지의 합 {sn}')
a1 = int(input('초항 입력 : '))
d = int(input('공차 입력 : '))
n = int(input('항 수 입력 : '))
ansn(a1, d, n)#출력
초항 입력 : 2
공차 입력 : 3
항 수 입력 : 7
1번째 항의 값 2
1번째 항까지의 합 2
2번째 항의 값 5
2번째 항까지의 합 7
3번째 항의 값 8
3번째 항까지의 합 15
4번째 항의 값 11
4번째 항까지의 합 26
5번째 항의 값 14
5번째 항까지의 합 40
6번째 항의 값 17
6번째 항까지의 합 57
7번째 항의 값 20
7번째 항까지의 합 77💡일반항과 n번째 까지의 합을 구하는 공식만 알면 그대로 대입하면 되었다.
▶Ex06 함수
def ansn(a1, r, n):
for index in range(1,n+1):
an = int(a1 * r ** (index-1))
sn = int(a1 * (1-r**index)/(1-r))
print(f'{index}번째 항의 값 {an}')
print(f'{index}번째 항까지의 합 {sn}')
a1 = int(input('초항 입력 : '))
r = int(input('공비 입력 : '))
n = int(input('항 수 입력 : '))
ansn(a1, r, n)#출력
초항 입력 : 2
공비 입력 : 3
항 수 입력 : 5
1번째 항의 값 2
1번째 항까지의 합 2
2번째 항의 값 6
2번째 항까지의 합 8
3번째 항의 값 18
3번째 항까지의 합 26
4번째 항의 값 54
4번째 항까지의 합 80
5번째 항의 값 162
5번째 항까지의 합 242💡일반항과 n번째 까지의 합을 구하는 공식만 알면 그대로 대입하면 되었다.
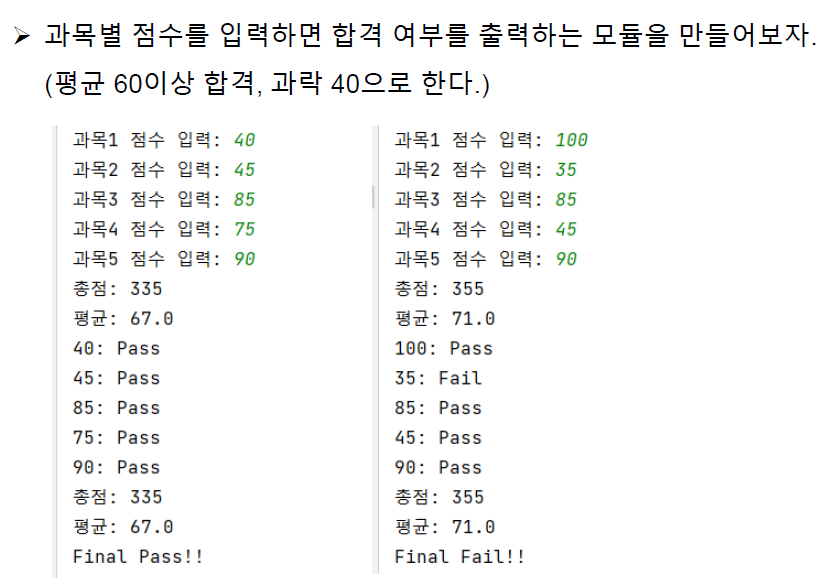
▶Ex07 모듈
first = int(input('1과목 점수 입력 : '))
second = int(input('2과목 점수 입력 : '))
third = int(input('3과목 점수 입력 : '))
fourth = int(input('4과목 점수 입력 : '))
fifth = int(input('5과목 점수 입력 : '))
total = first + second + third + fourth + fifth
avg = total / 5
if first >= 40 and second >= 40 and third >= 40 and fourth >= 40 and fifth >= 40 and avg >= 60 :
print(f'{first} : Pass')
print(f'{second} : Pass')
print(f'{third} : Pass')
print(f'{fourth} : Pass')
print(f'{fifth} : Pass')
print(f'총점 : {total}')
print(f'평균 : {avg}')
print('Final Pass!!')
else:
if first >= 40:
print(f'{first} : Pass')
else:
print(f'{first} : Fail')
if second >= 40:
print(f'{second} : Pass')
else:
print(f'{second} : Fail')
if third >= 40:
print(f'{third} : Pass')
else:
print(f'{third} : Fail')
if fourth >= 40:
print(f'{fourth} : Pass')
else:
print(f'{fourth} : Fail')
if fifth >= 40:
print(f'{fifth} : Pass')
else:
print(f'{fifth} : Fail')
print(f'총점 : {total}')
print(f'평균 : {avg}')
print('Final Pass!!')#Final Pass 출력
1과목 점수 입력 : 45
2과목 점수 입력 : 45
3과목 점수 입력 : 50
4과목 점수 입력 : 60
5과목 점수 입력 : 70
45 : Pass
45 : Pass
50 : Pass
60 : Pass
70 : Pass
총점 : 270
평균 : 54.0
Final Pass!!#Final Fail 출력
1과목 점수 입력 : 35
2과목 점수 입력 : 50
3과목 점수 입력 : 20
4과목 점수 입력 : 80
5과목 점수 입력 : 15
35 : Fail
50 : Pass
20 : Fail
80 : Pass
15 : Fail
총점 : 200
평균 : 40.0
Final Fail!!💡이것이 하드 코딩인가 싶었다..
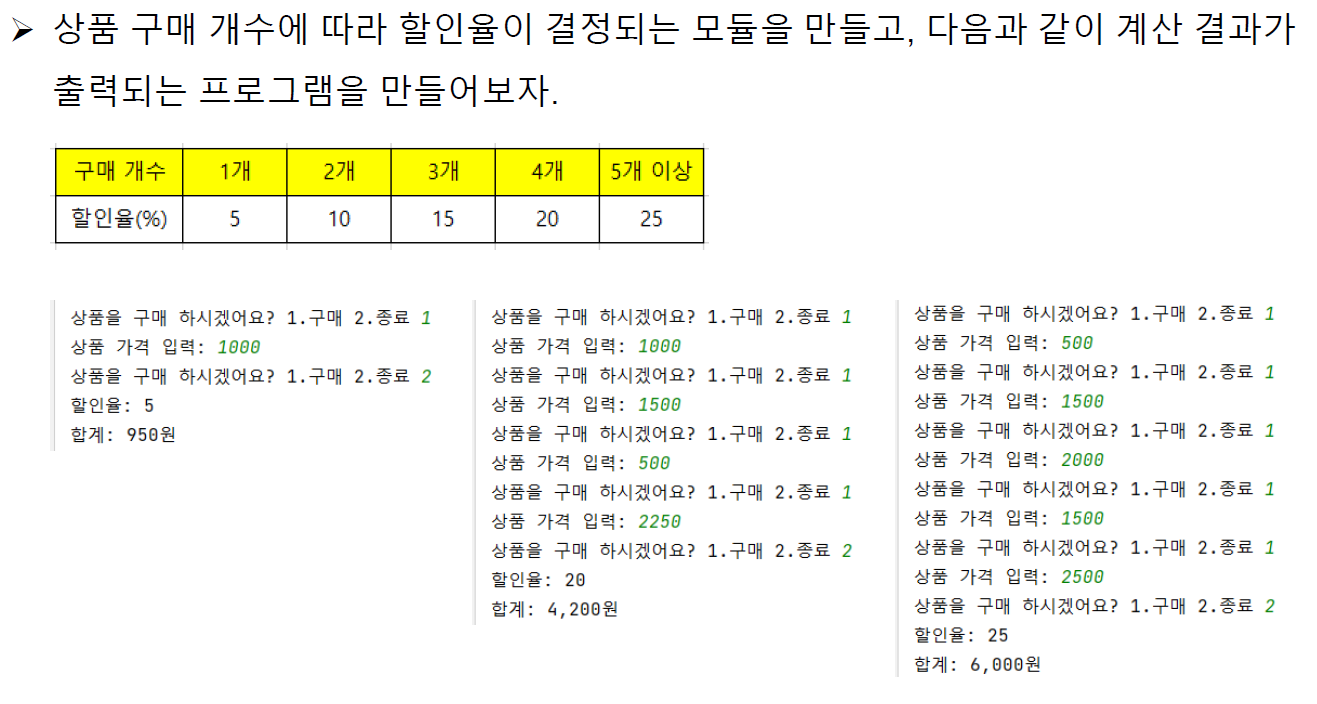
▶Ex08 모듈
disRate = 0
buyCnt = 0
costSum = 0
while True:
buyExit = int(input('상품을 구매하시겠어요? 1.구매 2.종료 : '))
if buyExit == 2:
break
if buyExit == 1:
cost = int(input('상품 가격 입력 : '))
costSum += cost
buyCnt += 1
if buyCnt == 1:
disRate = 5
costSum *= 0.95
elif buyCnt == 2:
disRate = 10
costSum *= 0.9
elif buyCnt == 3:
disRate = 15
costSum *= 0.85
elif buyCnt == 4:
disRate = 20
costSum *= 0.8
else:
disRate = 25
costSum *= 0.75
print(f'할인율 : {disRate}%')
print(f'합계 : {int(costSum)}원')#출력
상품을 구매하시겠어요? 1.구매 2.종료 : 1
상품 가격 입력 : 1000
상품을 구매하시겠어요? 1.구매 2.종료 : 1
상품 가격 입력 : 1500
상품을 구매하시겠어요? 1.구매 2.종료 : 1
상품 가격 입력 : 500
상품을 구매하시겠어요? 1.구매 2.종료 : 1
상품 가격 입력 : 2250
상품을 구매하시겠어요? 1.구매 2.종료 : 2
할인율 : 20%
합계 : 4200원💡변수 설정을 해두고 실행되는 횟수와 가격값 누적만 잘 시키면 되었다.
▶Ex09 모듈
from random import randint
myList = []
for index in range(6):
num = int(input('번호(1~45) 입력 : '))
myList.append(num)
ranList = []
for index in range(6):
rNum = randint(1,45)
ranList.append(rNum)
matchList = []
for index1 in myList:
for index2 in ranList:
if index1 == index2:
matchList.append(index2)
if len(matchList) == 6:
print('당첨')
print(f'당첨 번호 : {matchList}')
else:
print('다음 기회에')
print(f'맞춘 번호 : {matchList}')#출력
번호(1~45) 입력 : 1
번호(1~45) 입력 : 7
번호(1~45) 입력 : 15
번호(1~45) 입력 : 24
번호(1~45) 입력 : 38
번호(1~45) 입력 : 44
다음 기회에
맞춘 번호 : [7, 15]💡내가 맞춘 숫자를 어떻게 출력해야할지만 고민하면 됐던 것 같다. matchList의 for문이다.
▶Ex10 모듈
#permutation.py 모듈
def permu(n, r, logPrint = True):
result = 1
for index in range(n, n-r, -1):
if logPrint : print(f'index : {index}')
result = result * index
return result
# python에 있는 'permutations()' 함수
from itertools import permutations
def getPermutations(ns, r):
# pList = list(permutations(ns, r)) #리스트화 해줌. '<class 'itertools.permutations'>' -> '<class 'list'>'
print(f'{len(ns)}P{r} 의 개수 : {len(list(permutations(ns, r)))}')
for index in permutations(ns, r):
print(index)
#실행파일
import permutation as pt
#개수만 출력하기
# n = int(input('n 입력 : '))
# r = int(input('r 입력 : '))
# print(f'{n}P{r} = {pt.permu(n,r,logPrint=False)}')
#경우의 수 모두 확인하기
plist = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
var = 3
pt.getPermutations(plist, var) #출력
8P3 의 개수 : 336
(1, 2, 3)
(1, 2, 4)
(1, 2, 5)
.
.
.
.
.
(8, 7, 4)
(8, 7, 5)
(8, 7, 6)💡permutation의 원리를 이해하고 range의 범위를 거꾸로 주는 것을 알면 쉽게 풀 수 있었다. range에 값을 다양하게 줄 수 있다는 것이 떠오르지 않았었다. logPrint를 써서 조건에 맞는 출력 결과를 낼 수 있다는 것을 배웠다.
▶Ex11 모듈
#combination.py 모듈
def getCombinationCnt(n, r, logPrint = True):
resP = 1
resR = 1
resC = 1
for index in range(n, (n-r), -1):
resP *= index
if logPrint : print(f'result P : {resP}')
for index in range(r, 0, -1):
resR *= index
if logPrint : print(f'result R : {resR}')
resC = int(resP / resR)
if logPrint : print(f'result C : {resC}') #logPrint의 T/F로 중간 값들을 확인해 볼 수도 있다.
return resC
# itertools 모듈 사용
from itertools import combinations
def getCombinations(ns, r):
cList = list(combinations(ns, r))
print(f'{len(ns)}C{r}의 값 : {len(cList)}') # nCr 값만 확인
for index in cList:
print(f'{index}')#실행파일
import combination as cb
# n = int(input('n입력 : '))
# r = int(input('r입력 : '))
# res = cb.getCombinationCnt(n, r, logPrint=False)
# print(f'{n}C{r}의 값 : {res}')
list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
var = 4
cb.getCombinations(list, var)
#출력
8C4의 값 : 70
(1, 2, 3, 4)
(1, 2, 3, 5)
(1, 2, 3, 6)
(1, 2, 3, 7)
.
.
.
.
.
(4, 5, 6, 7)
(4, 5, 6, 8)
(4, 5, 7, 8)
(4, 6, 7, 8)
(5, 6, 7, 8)
💡조합은 순열에서 r의 팩토리얼을 나눠준다는 사실만 알면 풀 수 있었다.
▶Ex12 모듈
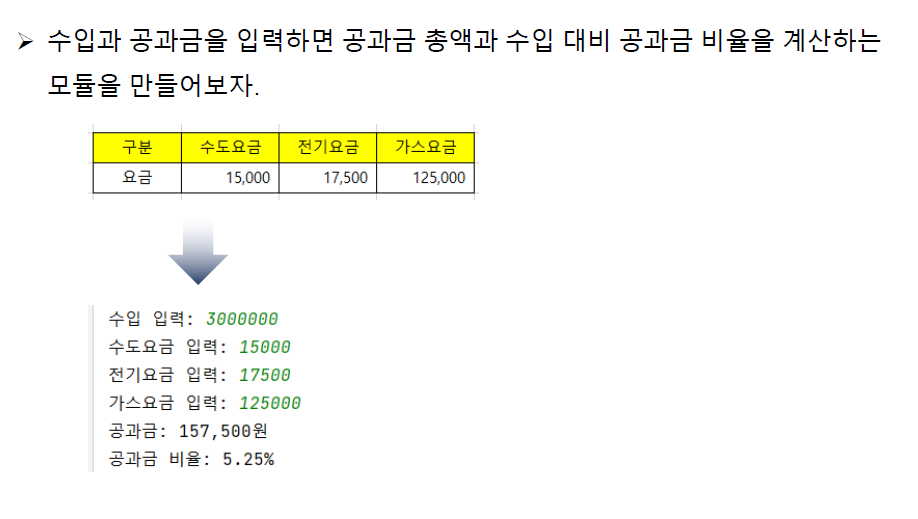
#utilityBill.py파일
income = 0; waterPrice = 0; electricPrice = 0; gasPrice = 0
def setIncome(ic):
global income
income = ic
def getIncome():
return income
def setWaterPrice(wp):
global waterPrice
waterPrice = wp
def getWaterPrice():
return waterPrice
def setEletricPrice(ep):
global electricPrice
electricPrice = ep
def getEletricPrice():
return electricPrice
def setGasPrice(gp):
global gasPrice
gasPrice = gp
def getGasPrice():
return gasPrice
def getUtilityBill():
result = waterPrice + gasPrice + electricPrice
return result
def getUtilityBillRate():
#result = getUtilityBill() / getIncome() * 100
return getUtilityBill() / getIncome() * 100#실행파일
import utilityBill as ub
inputIncome = int(input('수입입력 : '))
ub.setIncome(inputIncome)
inputWaterPrice = int(input('수도입력 : '))
ub.setWaterPrice(inputWaterPrice)
inputEletricPrice = int(input('전기입력 : '))
ub.setEletricPrice(inputEletricPrice)
inputGasPrice = int(input('가스입력 : '))
ub.setGasPrice(inputGasPrice)
print(f'공과금 Total : {ub.getUtilityBill():,}원')
print(f'수입대비 공과금률 : {ub.getUtilityBillRate()}%')#출력
수입입력 : 3000000
수도입력 : 15000
전기입력 : 17500
가스입력 : 125000
공과금 Total : 157,500원
수입대비 공과금률 : 5.25%💡getter, setter라는 함수도 배웠다. 아직 함수를 호출할 때의 방식, 함수를 호출할 떄 반환값이 있는 건지, 아니면 또 다른 내부함수를 실행하는 함수인지.. 빠릿하게 구분이 안되고 멈칫한다.
▶Ex13 모듈
#basic_operator.py 모듈
def add(a, b):
return a + b
def sub(a, b):
return a - b
def mul(a, b):
return a * b
def div(a, b):
return a / b#developer_operator.py 모듈
def div2(a, b):
return a % b
def mod(a, b):
return a // b
def jegob(a, b):
return a ** b#실행파일
from arithmetic import basic_operator
from arithmetic import developer_operator
from shape import triangle_square_area
from shape import circle_area
n1 = float(input('숫자 1 입력 : '))
n2 = float(input('숫자 2 입력 : '))
print(f'{n1} + {n2} = {basic_operator.add(n1,n2)}')
print(f'{n1} - {n2} = {basic_operator.sub(n1,n2)}')
print(f'{n1} * {n2} = {basic_operator.mul(n1,n2)}')
print(f'{n1} / {n2} = {basic_operator.div(n1,n2)}')
print(f'{n1} % {n2} = {developer_operator.div2(n1,n2)}')
print(f'{n1} // {n2} = {developer_operator.mod(n1,n2)}')
print(f'{n1} ** {n2} = {developer_operator.jegob(n1,n2)}')#출력
숫자 1 입력 : 10.5
숫자 2 입력 : 2
10.5 + 2.0 = 12.5
10.5 - 2.0 = 8.5
10.5 * 2.0 = 21.0
10.5 / 2.0 = 5.25
10.5 % 2.0 = 0.5
10.5 // 2.0 = 5.0
10.5 ** 2.0 = 110.25#triangle_square_area.py 모듈
def triArea(a, b):
area = a * b / 2
return area
def squArea(a, b):
area = a * b
return area#circle_area.py 모듈
def cirArea(r):
area = (r ** 2) * 3.14
return area#실행파일
from shape import triangle_square_area
from shape import circle_area
width = float(input('가로 길이 입력 : '))
height = float(input('세로 길이 입력 : '))
radius = float(input('반지름 입력 : '))
print(f'삼각형 넓이 : {triangle_square_area.triArea(width, height)}')
print(f'사각형 넓이 : {triangle_square_area.squArea(width, height)}')
print(f'원 넓이 : {circle_area.cirArea(radius):.2f}')#출력
가로 길이 입력 : 11.5
세로 길이 입력 : 8
반지름 입력 : 6.5
삼각형 넓이 : 46.0
사각형 넓이 : 92.0
원 넓이 : 132.66💡다른 건 문제없었지만, 같은 폴더에 있는 모듈이 아니라 하위에 있는 모듈이라 'from 폴더명'을 붙여주어야 했다.