메소드로 각 자료형을 다루는 방법
문자열 접근
str[index]
💡read-only
index를 통해 문자열에 접근 가능하지만 쓸 수는 없다
var str = 'Happy Birthday';
console.log(str[0]); //'H'
console.log(str[5]); //' '
console.log(str[25]); //undefined
str[0] = 'G';
str; //'Happy Birthday
// 💡 not 'Gappy Birthday'!!💡배열의 경우 arr[3] = 'sth'했을 시 해당 인덱스의 값을 변경한다.
하지만 문자열의 경우 변경하려면 값을 새로 할당해야한다.
str[index]로는 조회만 가능하고 값을 쓸 수는없다.
문자열은 항상 READ-ONLY
문자열에는 ➕ 연산자 사용가능 ( ➖ 는 안됨)
string타입 + 다른타입
⇨ string타입으로 강제변환된 값 출력
see more: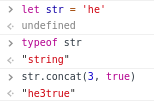
typeof str1; // "string"
str1.concat(str2, str3);
// + 연산자가 있으므로 굳이 .concat()을 안써도 되지만
// 결과값은 문자열이 나옴length PROPERTY
문자열의 길이
str.length; //14str.indexOf(찾고자하는 문자열)
returnvalue
- 찾고자 하는 문자열이 있으면 처음으로 일치하는 index를 출력한다
- 찾고자 하는 문자열이 없으면 -1 출력
- IMMUTABLE _기존string유지
see more:
str.lastIndexOf()는 문자열 뒤에서부터 찾아서 index출력
str.includes()는 boolean값을 출력
str.split(분리의 기준이 될 문자열)
returnvalue
- 분리된 문자열이 포함된 배열을 출력한다
IMMUTABLE _기존 string유지 - 줄바꿈으로 분리하고싶다면? str.split( '\n' )
str.substring(start index, end index)
str.substring(end index, start index) 로 순서를 바꿔써도 무방하다
returnvalue
- 시작과 끝 index사이의 문자열을 출력한다
IMMUTABLE _기존 string유지 - string의 일부만 똑 떼서 그 부분만 가져오고 싶을 때
var str = 'abcdefghijk';
str.substring(0,4); //'abc'
str.substring(3,0); //'abc', 순서를 바꿔써도 무방하다
str.substring(1,4); //'bcd'
str.substring(-1,4); //'abcd',음수는 0으로 취급
str.substring(0,20); //'abcdefghijk'see more:
str.substring(start, end) vs str.slice(start, end)
공통점
- 둘의 목적
- 출력값으로 string을 출력, 실행 후에도 기존 string유지 IMMUTABLE
차이점
- substring()은 start가 end보다 크면 자리를 바꾸기 때문에 순서가 상관없다
slice()는 empty string을 반환한다 - substring()은 start나 stop이 음수이거나 NaN이면 0을 사용한다
slice()는 string의 맨 뒤에서 음수만큼 내려온 index로 취급한다
String.slice() vs Array.slice()
차이점
- Array.slice()에서 start index는 생략하거나 undefined를 넣으면 자동으로 0에서 시작 ->배열복제 메소드로 활용
- String.slice()에서는 index를 생략할 수 없다
str.toLowerCase() / str.toUpperCase()
문자열을 소문자/ 대문자로 변경해서 출력해야할 때 사용
return value
- IMMUTABLE : 원본 유지
모든 STRING method는 IMMUTABLE
즉, 원본이 변하지 않는다
원본에 변화를 주고싶다면?
var str = 'Hello world';
str.substring(0,4); //'Hell'
str.toUpperCase(); //'HELLO WORLD'
str; //'Hello world'
str = str.substring(0,4); //'Hell'
str;
//'Hell' 원본에 할당을 해주면 된다배열 접근
Array.isArray ( 배열인지 확인하고 싶은 argument )
typeof로 배열/객체의 타입을 검사하면 모두 object 가 나온다.
배열과 객체를 구분하려면?
Array.isArray ( 구분하려는 object );- Return value는 Boolean 값이다.
배열이면 true, 빈배열이어도 true, 배열이 아니면 false
.indexOf( 찾고자 하는 element )
-
Return value는 해당 element의 index
-
배열에 존재하지 않는 element를 넣으면 -1이 출력된다.(str.indexOf와 같다)
-
배열 안에 특정 단어의 존재여부를 파악하고 싶다면?
-1만 아니면 존재한다는 것이므로
배열이름.indexOf('특정 단어') !== -1
특정단어가 있으면 true
배열이름.indexOf('없는 단어') !== -1
없는 단어일 때는 false, 반대로 ===이면 true.
see more:
includes()도 같은 기능을 하지만 Boolean값만 출력하기 때문에 indexOf의 활용도가 더 높다
.push( 새로운 element )
배열의 맨 뒤에 새로운 element 추가
let 변수 = ['aa', 3, 's', 'a'];
변수.push( '이거추가' );
변수; //(5) ["aa", 3, "s", "a", "이거추가"]
// 📌 Mutable
// .push()는 기존배열을 변경한다.
see more: 기존배열을 바꾸지 않으려면 .concat()을 사용하자
let array = ['dfs' , 'fdas', 'sadf'];
array.concat(333, 666) //(5) ["dfs", "fdas", "sadf", 333, 666]
array; //(3) ["dfs", "fdas", "sadf"]
// 📌 Immutable
// .concat()은 기존배열을 보존, 변경하지 않는다..pop( )
배열 맨 뒤의 element 삭제
📌 Mutable
.pop()은 기존배열을 변경
.unshift( 새로운 element )
배열 맨 앞에 새로운 element 추가
📌 Mutable
.shift( )
배열 맨 앞의 element 삭제
📌 Mutable
배열의 메소드로 새로운 배열 만들기
let arr = ['Hello', 'World'];arr를 유지하면서 배열에 'Welcome','!','a','b','c' 5개의element를 추가하려면??
🚨 .push()를 사용하되 원본 배열은 변하면 안된다.
방법 1: For-Loop
- 원본배열을 복제할 빈배열만들기 ex)
newArr - 원본배열의 elements를
newArray에 모두 담아준다 - 복제완료 - 복제한
newArray에 새로 추가하고 싶은 element 1~5 추가
let newArray = [];
//newArray에 push(원본배열의 elements)
for (let i=0; i <arr.length; i++){
newArr.push(arr[i]);
}
newArray; //(2) ["Hello", "World"]
//newArray에 새로운elements추가
newArray.push('Welcome','!','a','b','c');
newArray; //(7) ["Hello", "World", "Welcome", "!", "a", "b", "c"]방법 2: slice method
- 원본배열arr를 복제하는 method
.slice()⇨newArray - 복제한
newArray에 추가할 elements.push()
let newArray = arr.slice();
newArray.push('Welcome','!','a','b','c');
newArray; //(7) ["Hello", "World", "Welcome", "!", "a", "b", "c"]
arr === newArray //false.slice()
지정한 인덱스 범위사이의 elements 추출
.slice (시작index, 끝index)
.slice(0) 배열의 처음 (0번째index)부터 끝까지 추출 = 복제
.splice()
배열.splice(a,b,c);
a: 배열의 변경을 시작할 인덱스
음수(-)일경우 배열의 끝에서 센다.b: 배열에서 제거할 요소의 수c: 배열에 추가할 요소- 아무 요소도 지정하지 않으면 .splice()는 요소를 제거하기만 한다.
- 반환값은 삭제된 요소를 담은 배열
- 원래의 배열은 변경된 값으로 저장된다. 📌 Mutable
str.split(
구분할 글자)
String 객체를 지정한 구분자를 이용하여 여러 개의 문자열로 나눈다 .
