✨ AOP
📌 AOP ( Aspect Oriented Programming )
-
관점 지향 프로그래밍
-
여러 오브젝트에 나타나는 공통적인 부가 기능을 모듈화하여 재사용하는 기법
📌 핵심기능과 부가기능
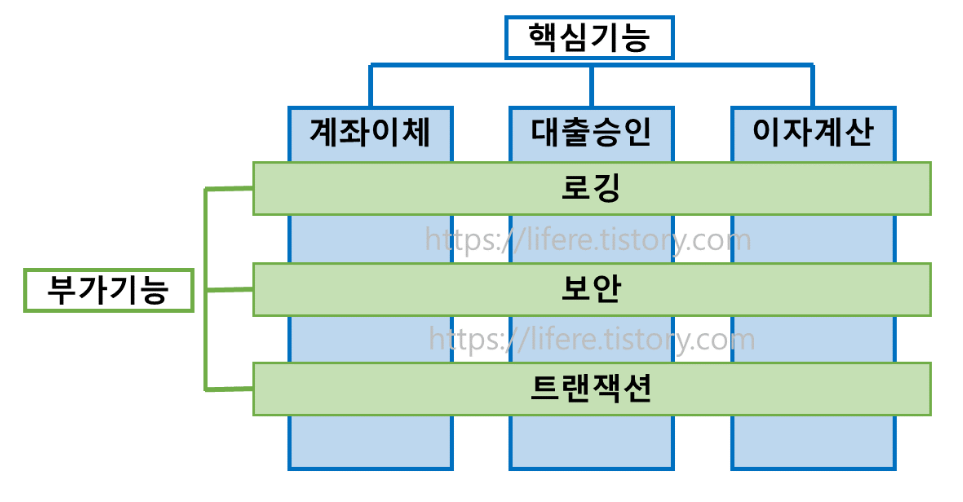
- 업무 로직을 포함하는 기능을 핵심 기능 (Core Concerns)
- 핵심기능을 도와주는 부가적인 기능 (주로 성능검사, 트랙잭션 처리, 로깅, 보안 등) (Cross-cutting Concerns)
- 이러한 공통적인 부가적인 기능들을 횡단 관심사라고 함
- 핵심기능에서 부가기능을 분리해서 모듈화하는 프로그래밍 기법 → AOP
로그를 남기거나, 핵심기능을 사용할 때 인증, 인가를 한다던가, 비즈니스 로직의 트랜잭션 처리를 하는 작업은 모든 핵심기능에 공통적으로 사용되는 기능이다. AOP는 비즈니스 로직을 나타내는 핵심기능을 작성할 때마다 공통적으로 작성하는 부가기능을 분리해서 프로그래밍하는 기법이다.📌 AOP 의 장점
- 핵심 기능 서비스를 제외한 횡단관심사항 서비스를 별도의 모듈에서 개발하여 적용하므로, 여러 서비스에 걸쳐있는 반복적 작업을 줄일 수 있어 생산성이 높아진다.
- 요구사항 변경 시에도 유연하게 대처할 수 있으므로, 유지보수성이 높아진다.
📌 AOP 주요 용어
-
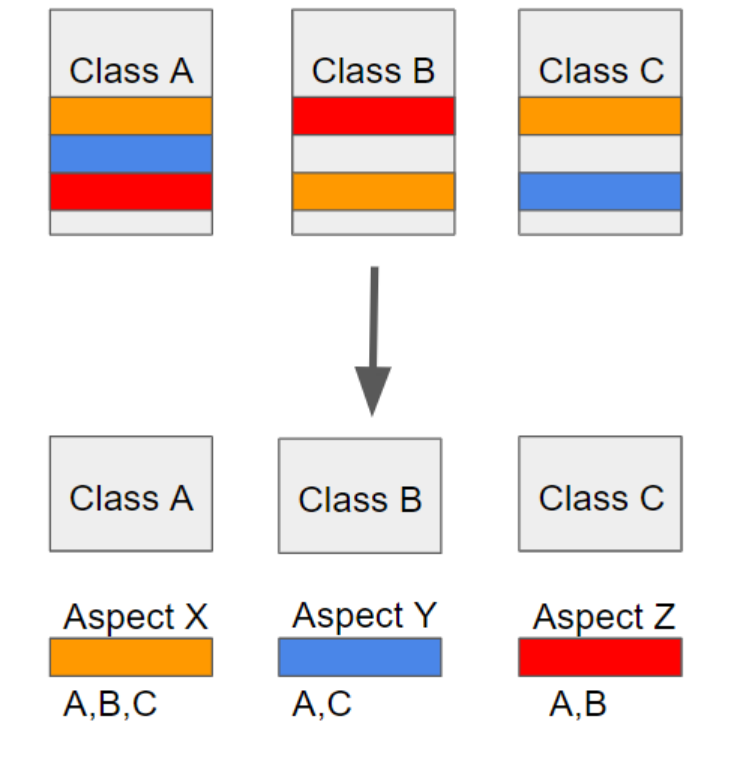
Aspect
- AOP 의 단위가 되는 횡단관심사를 의미 ex) 로깅, 트랙잭션관리 등
-
JoinPoint
- 횡단관심사가 실행될 지점
- 메서드를 호출할 때 (스프링 AOP에서)
-
Advice
- 횡단관심사를 처리하는 부분, 특정 JoinPoint에서 실행되는 코드
- 어떤 부가기능을, 언제 ?
-
Pointcut
- 여러 JoinPoint 중 실제 Advice를 적용할 곳을 선별하기 위한 표현식
-
Weaving
- 어플리케이션의 적절한 지점에 aspect를 적용하는 것을 말함
-
Target
- Aspect가 적용된 객체를 말한다.
- ex) 클래스, 메서드 ..
📌 AOP Advice 유형
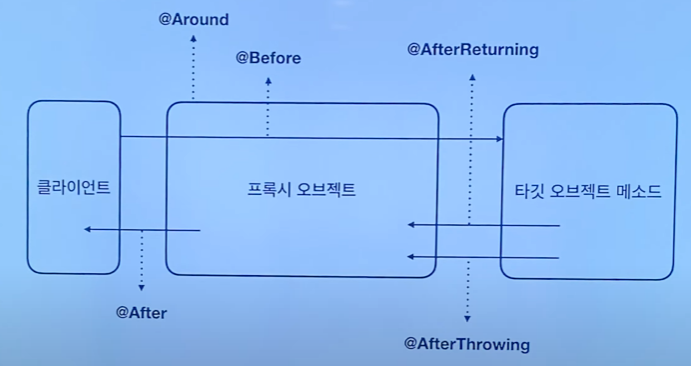
- Before
- 메서드 실행 전에 실행하는 Advice
- After Returning
- 메서드 정상 실행 후 실행하는 Advice
- After Throwing
- 메서드 실행시 예외 발생시 실행하는 Advice
- After
- 메서드 정상 실행 또는 예외 발생 상관없이 실행하는 Advice
- After Returning + After Throwing
- Around
- 위 네가지 Advice를 모두 포함, 모든 시점에서 실행할 수 있는 Advice
📌 AOP 구현 방법
- 컴파일 시점에 코드에 공통 기능을 삽입하는 방법
- 클래스 로딩 시점에 바이트 코드에 공통 기능을 삽입하는 방법
- 런타임에 프록시 객체를 생성해서 공통 기능을 삽입하는 방법
📌 스프링 AOP 특징
- 프록시 기반의 AOP 구현체
- 스프링 빈에만 AOP 를 적용할 수 있다.
- 동적 프록시 빈을 만들어 등록시켜준다.
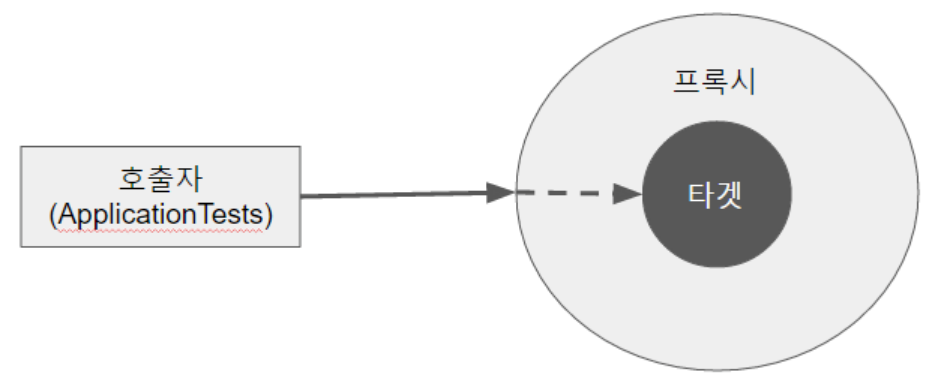
📌 프록시 패턴
- 실제 기능을 수행하는 객체 대신 가상의 객체(proxy object)를 사용해 로직의 흐름을 제어하는 디자인 패턴.
- 클라이언트에서 타겟을 호출하게 되면 타겟이 아닌 타겟을 감싸고 있는 프록시가 호출되어, 타겟 메소드 실행 전에 선처리, 타켓 메소드 실행 후 후처리를 실행시키도록 구성되어 있음.
- AOP에서 프록시는 호출을 가로챈 후, 어드바이스에 등록된 기능을 수행 후 타겟 메서드를 실행.
📌 AOP 구현 예제
🐥 준비
// 의존성 주입
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>// 간단한 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스 하나를 빈으로 정의
public interface EventService {
public void created();
public void operation();
public void deleted();
}
@Component
public class SimpleServiceEvent implements EventService {
@Override
public void created() {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("created");
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);
}
@Override
public void operation() {
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("operation");
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);
}
@Override
public void deleted() {
System.out.println("deleted");
}
}@Component
public class AppRuner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Autowired
EventService eventService;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
eventService.created();
eventService.operation();
eventService.deleted();
}
}🐥 실행결과
created
1011
operation
2004
deleted🐥 AOP 적용하기
// 위 코드에서는 수행 시간을 재는 아래 코드가 여러 곳에서 반복 사용되고 있음
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
... (수행) ...
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);// 위 코드를 하나로 묶기
// Aspect 정의
@Component
@Aspect
public class PerfAspect {
// Advice 정의 (Around 사용)
// Point Cut 표현식
// (com.example.demo 밑에 있는 모든 클래스 중 EventService 안에 들어있는 모든 메쏘드에 이 행위를 적용하라.)
@Around("execution(* com.example..*.EventService.*(..))")
public Object logPerf(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object retVal = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);
return retVal;
}
}// AOP를 위 코드에서 적용했으므로, 수행시간 출력 부분 코드 삭제
@Component
public class SimpleServiceEvent implements EventService {
@Override
public void created() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("created");
}
@Override
public void operation() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("operation");
}
@Override
public void deleted() {
System.out.println("deleted");
}
}🐥 실행결과
created
1011
operation
2004
deleted
3000🐥 Annotation 기반
- 나는
created()와operation()에만 적용하고 싶은데delete()에도 적용이 됐다 ! - 이를 Annotation 기반 Advice 정의로 해결하기
// Annotation 만들기
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
public @interface PerfLogging {
}// Aspect 클래스 수정
@Component
@Aspect
public class PerfAspect {
// PerfLogging 어노테이션이 달린 곳만 포인트컷 수정
@Around("@annotation(PerfLogging)")
public Object logPerf(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object retVal = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);
return retVal;
}
}// class method 수정
@Component
public class SimpleServiceEvent implements EventService {
@PerfLogging
@Override
public void created() {
...
}
@PerfLogging
@Override
public void operation() {
...
}
@Override
public void deleted() {
...
}
}🐥 출력 결과
created
1011
operation
2004
deleted📌 프록시 패턴 특징 예제
package org.springframework.samples.petclinic.proxy;
public interface Payment {
void pay(int amount);
}package org.springframework.samples.petclinic.proxy;
public class Cash implements Payment{
public void pay(int amount){
System.out.println(amount + " 현금 결제");
}
}package org.springframework.samples.petclinic.proxy;
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;
//프록시 클래스
public class CashPerf implements Payment{
Payment cash = new Cash();
@Override
public void pay(int amount) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
cash.pay(amount);
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println(stopWatch.prettyPrint());
}
}package org.springframework.samples.petclinic.proxy;
public class Store {
Payment payment;
public Store(Payment payment) {
this.payment = payment;
}
public void butSomething(int amount){
payment.pay(amount);
}
}package org.springframework.samples.petclinic.proxy;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class StoreTest {
//Cash 클래스와 Store클래스는 바뀌지 않았지만 이 코드 앞뒤로 성능 측정을 하도록 프록시 클래스를 이용함.
@Test
public void testPay(){
Payment cashPerf = new Cash();
Store store = new Store(cashPerf);
store.butSomething(100);
}
}📌 참고
https://dailyheumsi.tistory.com/202
