OOP (Object-Oriented Programming)
-
객체 지향 프로그래밍
-
객체의 관점에서 프로그래밍을 하는 것.
-
프로그래밍에서 필요한 데이터를 추상화시켜 객체를 만들고, 객체들 간의 상호작용을 통해 로직을 구성하는 프로그래밍 방법론
-
Java, C++, Python ...
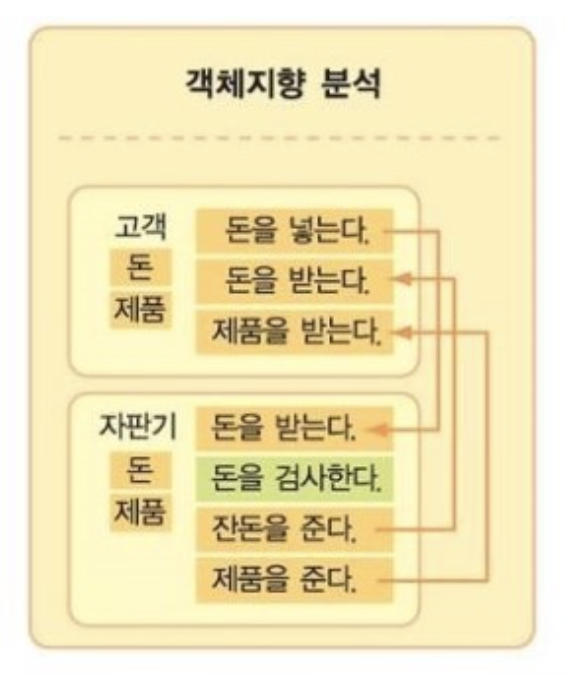
📌 절차적 프로그래밍 (Procedure Programming)
- 프로그램을 일련의 절차나 함수의 집합으로 보고, 이를 순차적으로 실행하여 문제를 해결하는 방식
- C언어

- 절차적 프로그래밍
1. 강일구라는 사람은 머리 2개, 다리 3개, 팔 4개를 가지고 있고, 경찰이다.
2. 강일구.소개함수()
3. 여진구라는 사람은 머리 2개, 다리 3개, 팔 4개를 가지고 있고, 의사이다.
4. 여진구.소개함수()- 객체 지향 프로그래밍
1. class 정의 (인간 데이터, 함수, 추가 변수)
2. 강일구 = class 객체(경찰)
3. 여진구 = class 객체(의사)
5. 강일구.소개함수()
6. 여진구.소개함수()💡 절차적 프로그래밍의 장단점
1. 장점
- 객체나 클래스를 만들 필요 없이 바로 프로그램을 코딩할 수 있다.
- 필요한 기능을 함수로 만들어 두기 때문에 같은 코드를 복사하지 않고 호출하여 사용할 수 있다.
- 프로그램의 흐름을 쉽게 추적할 수 있다.
2. 단점
- 각 코드가 매우 유기성이 높기 때문에 수정하기가 힘들다. (새로운 데이터나 기능을 추가하기가 어려움)
- 프로그램 전체에서 코드를 재사용할 수 없어 개발 비용과 시간이 늘어난다.
- 디버깅이 어렵다.
📌 OOP의 5대 원칙
1. 단일 책임 원칙 (Single Responsibility Principle)
- 모든 클래스는 각각 하나의 책임만 가져야 한다.
- 모듈이 변경되는 이유가 한 가지 여야 함을 뜻함.
- 한 클래스는 한 가지 책임에 관한 변경사항이 생겼을 때만 코드를 수정하게 되는 구조가 좋은 구조.
- 변경의 이유가 하나 여야 한다는 것이 이해가 가지 않았다.
- 그럼 클래스 하나당 메서드가 하나여야 한다는 건가 ? 그까지 분리를 하라는 건가 ? 했는데 . .
- 가장 이해가 쉬운 예시로 백엔드 개발을 할 때 Service와 Repository 를 구분해서 개발하는 것이라고 예를 들 수 있겠다.
- SRP 를 준수하지 않은 예제
// 커피를 만드는 책임, 커피 머신을 청소하는 책임, 사용자에게 알림을 보내는 책임을 모두 가지고 있음.
// 만약 커피 만드는 방법이 변경되거나 청소 방법이 변경된다면, CoffeeMachine 클래스는 여러 이유로 변경될 수 있음.
class CoffeeMachine {
public void brewCoffee() {
// 커피를 만드는 로직
System.out.println("Brewing coffee...");
}
public void cleanMachine() {
// 커피 머신을 청소하는 로직
System.out.println("Cleaning the machine...");
}
public void notifyUser() {
// 사용자에게 알림을 보내는 로직
System.out.println("Your coffee is ready!");
}
}- SRP를 준수한 예제
// 커피를 만드는 클래스
// 책임 : 커피를 만드는 모든 작업
// 변경의 이유 : 커피를 만드는 방법이나 종류, 커피의 양이나 농도를 조절하는 방법이 변경될 때
class CoffeeMachine {
public void brewEspresso() {
System.out.println("Brewing espresso...");
}
public void brewLatte() {
System.out.println("Brewing latte...");
}
public void setCoffeeStrength(int strength) {
System.out.println("Setting coffee strength to " + strength);
}
public void setCoffeeAmount(int amount) {
System.out.println("Setting coffee amount to " + amount + "ml");
}
}
// 청소를 담당하는 클래스
// 책임 : 커피 머신의 청소 작업
// 변경의 이유 : 청소 방법이나 청소 과정이 변경될 때
class CleaningService {
public void startCleaning() {
System.out.println("Starting cleaning process...");
}
public void cleanWaterTank() {
System.out.println("Cleaning water tank...");
}
public void cleanCoffeeGroundsContainer() {
System.out.println("Cleaning coffee grounds container...");
}
public void notifyCleaningRequired() {
System.out.println("Cleaning required soon.");
}
}
// 알림을 담당하는 클래스
// 책임 : 사용자에게 알림을 보내는 작업
// 변경의 이유 : 알림의 내용이나 알림 방법이 변경될 때
class UserNotifier {
public void notifyCoffeeReady() {
System.out.println("Your coffee is ready!");
}
public void notifyMaintenanceRequired() {
System.out.println("Maintenance required.");
}
public void notifyLowWaterLevel() {
System.out.println("Water level is low.");
}
}2. 개방-폐쇄 원칙 (Open Closed Principle)
-
확장에는 열려있고, 수정에는 닫혀있는. 기존의 코드를 변경하지 않으면서(Closed), 기능을 추가할 수 있도록(Open) 설계가 되어야 한다는 원칙.
-
기능 추가 요청이 오면 확장을 통해 손쉽게 구현하면서, 확장에 따른 클래스 수정은 최소화 하도록.
-
확장에 열려있다.
- 모듈의 확장성 보장.
- 새로운 변경 사항이 발생했을 때 유연하게 코드를 추가함으로써 어플리케이션의 기능을 큰 힘을 들이지 않고 확장
-
변경에 닫혀있다.
- 객체를 직접적으로 수정하는 것은 제한.
- 객체를 직접 수정하지 않고도 변경사항을 적용할 수 있도록 설계해야 함.
-
OCP를 위반한 예시
class Animal {
String type;
Animal(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
}
// 동물 타입을 받아 각 동물에 맞춰 울음소리를 내게 하는 클래스 모듈
class HelloAnimal {
void hello(Animal animal) {
if(animal.type.equals("Cat")) {
System.out.println("냐옹");
} else if(animal.type.equals("Dog")) {
System.out.println("멍멍");
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloAnimal hello = new HelloAnimal();
Animal cat = new Animal("Cat");
Animal dog = new Animal("Dog");
hello.hello(cat); // 냐옹
hello.hello(dog); // 멍멍
}
}
// 새로운 동물을 추가하려면 ?
class HelloAnimal {
// 기능을 확장하기 위해서는 클래스 내부 구성을 일일히 수정해야 하는 번거로움이 생긴다.
void hello(Animal animal) {
if (animal.type.equals("Cat")) {
System.out.println("냐옹");
} else if (animal.type.equals("Dog")) {
System.out.println("멍멍");
} else if (animal.type.equals("Sheep")) {
System.out.println("메에에");
} else if (animal.type.equals("Lion")) {
System.out.println("어흥");
}
// ...
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloAnimal hello = new HelloAnimal();
Animal cat = new Animal("Cat");
Animal dog = new Animal("Dog");
Animal sheep = new Animal("Sheep");
Animal lion = new Animal("Lion");
hello.hello(cat); // 냐옹
hello.hello(dog); // 멍멍
hello.hello(sheep);
hello.hello(lion);
}
}- OCP 를 따른 예시
// 추상화
abstract class Animal {
abstract void speak();
}
class Cat extends Animal { // 상속
void speak() {
System.out.println("냐옹");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal { // 상속
void speak() {
System.out.println("멍멍");
}
}
class HelloAnimal {
void hello(Animal animal) {
animal.speak();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloAnimal hello = new HelloAnimal();
Animal cat = new Cat();
Animal dog = new Dog();
hello.hello(cat); // 냐옹
hello.hello(dog); // 멍멍
}
}
// 위와 같이 설계한다면
// 추상클래스를 상속만 하면 메소드 강제 구현 규칙으로 규격화만 하면 확장에 제한 없다 (opened)
class Sheep extends Animal {
void speak() {
System.out.println("매에에");
}
}
class Lion extends Animal {
void speak() {
System.out.println("어흥");
}
}
// 기능 확장으로 인한 클래스가 추가되어도, 더이상 수정할 필요가 없어진다 (closed)
class HelloAnimal {
void hello(Animal animal) {
animal.speak();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloAnimal hello = new HelloAnimal();
Animal cat = new Cat();
Animal dog = new Dog();
Animal sheep = new Sheep();
Animal lion = new Lion();
hello.hello(cat); // 냐옹
hello.hello(dog); // 멍멍
hello.hello(sheep); // 매에에
hello.hello(lion); // 어흥
}
}3. 리스코프 치환 원칙 (Liskov Substitution Principle)
- 자식 클래스는 언제나 자신의 부모 클래스를 대체할 수 있다는 원칙. 즉, 부모 클래스가 들어갈 자리에 자식 클래스를 넣어도 계획대로 잘 작동해야 한다.
- 자식클래스는 부모 클래스의 책임을 무시하거나 재정의하지 않고 확장만 수행하도록 해야 LSP를 만족한다.
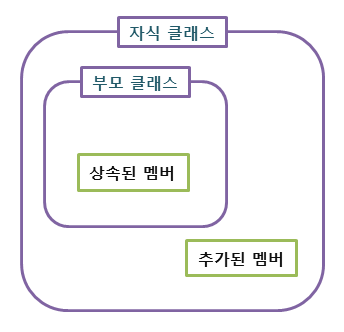
- LSP 를 위반한 예제
class Bird {
public void fly() {
System.out.println("Flying");
}
}
class Ostrich extends Bird {
@Override
public void fly() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Ostriches cannot fly");
}
}
// 타조는 날 수 없기 때문에 Bird를 상속받았을 때 fly 메서드를 오버라이드 하여 예외를 발생시킴.
public void letBirdFly(Bird bird) {
bird.fly();
}
Bird sparrow = new Bird();
letBirdFly(sparrow); // 정상 작동
Bird ostrich = new Ostrich();
letBirdFly(ostrich); // 예외 발생: UnsupportedOperationException
// Bird 클래스로 대체되지 않아 LSP 를 위반함- LSP 를 준수하는 예제
// Bird 를 추상클래스로 만들고
abstract class Bird {
public abstract void makeSound();
}
// Flyable 인터페이스를 사용하여 날 수 있는 새들과 날 수 없는 새들 분리
interface Flyable {
void fly();
}
class Sparrow extends Bird implements Flyable {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Chirp chirp");
}
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("Flying");
}
}
class Ostrich extends Bird {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Boom boom");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void letBirdFly(Flyable bird) {
bird.fly();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sparrow sparrow = new Sparrow();
letBirdFly(sparrow); // 정상 작동: "Flying"
Ostrich ostrich = new Ostrich();
// letBirdFly(ostrich); // 컴파일 에러: Ostrich는 Flyable이 아님
Bird bird1 = new Sparrow();
bird1.makeSound(); // "Chirp chirp"
Bird bird2 = new Ostrich();
bird2.makeSound(); // "Boom boom"
}
}
4. 인터페이스 분리 원칙 (Interface Segregation Principle)
- 한 클래스는 자신이 사용하지 않는 인터페이스는 구현하지 말아야 한다.
- 인터페이스를 잘게 분리함으로써 클라이언트의 목적과 용도에 적합한 인터페이스만을 제공하는 것.
- 반드시 객체가 자신에게 필요한 기능만을 가지도록 제한하는 것.
- 불필요한 상속과 구현을 최대한 방지함으로써 객체의 불필요한 책임을 제거.

- User1, User2, User3 모두가 OPS를 상속받고 있지만 각각의 객체들은 오직 op1, op2, op3 메서드만 사용함. 그렇다면 다른 두 개의 메서드를 사용하지 않음에도 불구하고 사용하지 않는 메서드에 변경이 일어나면 영향을 받게됨.
- ISP 를 위반한 예시
// 스마트폰 인터페이스
interface ISmartPhone {
void call(String number); // 통화 기능
void message(String number, String text); // 문제 메세지 전송 기능
void wirelessCharge(); // 무선 충전 기능
void AR(); // 증강 현실(AR) 기능
void biometrics(); // 생체 인식 기능
}
// 최신 폰들은 가능
class S20 implements ISmartPhone {
public void call(String number) {
}
public void message(String number, String text) {
}
public void wirelessCharge() {
}
public void AR() {
}
public void biometrics() {
}
}
class S21 implements ISmartPhone {
public void call(String number) {
}
public void message(String number, String text) {
}
public void wirelessCharge() {
}
public void AR() {
}
public void biometrics() {
}
}
// 하지만 구식은 안됨. 쓸데 없는 메서드를 구현해야 함.
class S3 implements ISmartPhone {
public void call(String number) {
}
public void message(String number, String text) {
}
public void wirelessCharge() {
System.out.println("지원 하지 않는 기능 입니다.");
}
public void AR() {
System.out.println("지원 하지 않는 기능 입니다.");
}
public void biometrics() {
System.out.println("지원 하지 않는 기능 입니다.");
}
}- ISP 를 지킨 예시
// 기능별로 인터페이스 분리
interface IPhone {
void call(String number); // 통화 기능
void message(String number, String text); // 문제 메세지 전송 기능
}
interface WirelessChargable {
void wirelessCharge(); // 무선 충전 기능
}
interface ARable {
void AR(); // 증강 현실(AR) 기능
}
interface Biometricsable {
void biometrics(); // 생체 인식 기능
}
// 각각 필요한 기능만 implements 하면 됨
class S21 implements IPhone, WirelessChargable, ARable, Biometricsable {
public void call(String number) {
}
public void message(String number, String text) {
}
public void wirelessCharge() {
}
public void AR() {
}
public void biometrics() {
}
}
class S3 implements IPhone {
public void call(String number) {
}
public void message(String number, String text) {
}
}5. 의존 역전 원칙 (Dependency Inversion Principle)
- 의존 관계를 맺을 때 변화하기 쉬운 것 또는 자주 변화하는 것 보다는 변화하기 어려운 것, 거의 변화가 없는 것에 의존하라는 것.
- 구체적인 클래스보다 인터페이스나 추상 클래스와 관계를 맺으라는 것.
- 고수준 모듈은 저수준 모듈의 구현에 의존해서는 안된다. 대신 저수준 모듈이 고수준 모듈에서 정의한 추상 타입에 의존해야 한다.
고수준 모듈 : 어떤 의미 있는 단일 기능을 제공하는 모듈 (Interface, 추상 클래스)
저수준 모듈 : 고수준 모듈의 기능을 구현하기 위해 필요한 하위 기능의 실제 구현 (메인 클래스, 객체)
- 어떤 클래스를 참조해서 사용해야 하는 상황이 생긴다면, 그 클래스를 직접 참조하는 것이 아니라 그 대상의 상위 요소(추상 클래스 Or 인터페이스)로 참조하라는 원칙.
- DIP를 위반한 예시
public class Kid {
private Robot toy;
public void setToy(Robot toy) {
this.toy = toy;
}
public void play() {
System.out.println(toy.toString());
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Robot robot = new Robot();
Kid k = new Kid();
k.setToy(robot);
k.play();
}
}
// Kid는 robot 이라는 구체적인 객체에 의존하고 있음.
// 새로운 장난감이 추가되면 아래와 같이 Kid 클래스를 수정해야 함.
public class Kid {
private Robot toy;
private Lego toy; //레고 추가
// 아이가 가지고 노는 장난감의 종류만큼 Kid 클래스 내에 메서드가 존재해야함.
public void setToy(Robot toy) {
this.toy = toy;
}
public void setToy(Lego toy) {
this.toy = toy;
}
public void play() {
System.out.println(toy.toString());
}
}- DIP를 적용한 예시
// Toy 라는 추상클래스와 의존관계를 맺도록 설계
public class Kid {
private Toy toy;
public void setToy(Toy toy) {
this.toy = toy;
}
public void play() {
System.out.println(toy.toString());
}
}
public class Robot extends Toy {
public String toString() {
return "Robot";
}
}
// 새로운 장난감을 추가하고 싶다면 ?
public class Lego extends Toy {
public String toString() {
return "Lego";
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Toy lego = new Lego();
Kid k = new Kid();
k.setToy(lego);
k.play();
}
}* 정리
- SRP : 어떤 클래스를 변경해야 하는 이유는 오직 하나뿐이어야 한다.
- OCP : 자신의 확장에는 열려 있고, 주변의 변화에 대해서는 닫혀 있어야 한다.
- LSP : 서브 타입은 언제나 자신의 기반 타입으로 교체할 수 있어야 한다.
- ISP : 범용적인 인터페이스 하나보다 내가 쓸 인터페이스 따로 만들어라.
- DIP : 구현체에 의존하지 말고 인터페이스에 의존해라.
📌 OOP의 특징
1. 추상화 (Abstraction)
- 특정 개념이나 개체를 보았을 때 특정 관점에서 관심있거나 중요한 부분만 추려내는 작업.
- 어떤 대상/집단의 공통적이고 본질적인 특징을 추출하여 정의한 것.
- 어떤 대상을 구현할 때, 그 대상의 본질적인 특징을 정의하고, 이것에 기반하여 대상을 객체로 구현하는 것.
- 이 때, 본질적인 특징을 정의하는 데 활용되는 개념이 abstract class / interface
- 공통의 속성이나 기능을 묶어 이름을 붙이는 것
- 객체 지향 프로그래밍에서 클래스를 정의하는 것을 추상화라고 한다.
// Dog 추상클래스 생성
public abstract class Dog {
private String name;
private String type;
public Dog(String name, String type) {
this.name = name;
this.type = type;
}
abstract void howl();
abstract void walk();
public void smell() {
System.out.println(name + "이 냄새를 맡습니다.");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
}
public class WelshCorgi extends Dog {
public WelshCorgi(String name) {
super(name, "웰시코기");
}
@Override
void howl() {
System.out.println("왈왈! 나는야 " + getName() + ", " + getType());
}
@Override
void walk() {
System.out.println("터벅터벅");
}
@Override
public void smell() {
super.smell();
System.out.println("킁킁");
}
}
public class Maltese extends Dog {
public Maltese(String name) {
super(name, "말티즈");
}
@Override
void howl() {
System.out.println("멍멍! 나는야 " + getName() + ", " + getType());
}
@Override
void walk() {
System.out.println("총총");
}
@Override
public void smell() {
super.smell();
System.out.println("스읍스읍");
}
}
- 웰시코기와 말티즈는 모두 "Dog" 개다.
- 모든 개들은 이름이 있고, 종이 있고, 짖고 , 걷고, 냄새를 맡을 수 있다. -> 공통적인 특징. "개" 크래스로 추상화
2. 캡슐화 (Encapsulation)
- 데이터와 프로세스를 하나의 객체에 위치하도록 만드는 것.
- 클래스 내의 연관된 속성(property)이나 함수(method)를 하나의 캡슐로 묶어 외부로부터 클래스로의 접근을 최소화하는 것.
- 하나의 목적을 위해 필요한 데이터나 메소드를 하나로 묶는 것.
- 데이터는 외부에서 해당 객체에 접근 시 직접 접근이 아닌 함수를 통해서만 접근하여야 한다.
- 은닉화 : 객체의 세부 내용이 외부에 드러나지 않아 외부에서 데이터를 직접 접근하는 것을 방지한다.
- 장점
- 외부로부터 클래스의 변수, 함수를 보호
- 외부에는 필요한 요소만 노출하고, 내부의 상세한 동작은 은닉
- 접근제한자
public: 하위 클래스와 인스턴스에서 접근 가능static: 클래스와 외부에서 접근 가능. 인스턴스에서는 접근 불가private: 클래스 본인만 접근 가능, 하위클래스, 인스턴스 접근 불가protected: 클래스 본인, 하위 클래스에서 접근 가능, 인스턴스 접근 불가
- 유지보수가 용이하다.
- 캡슐화를 지키지 않은 코드 예제
class Person {
public String name;
public int age;
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
// 필드에 직접 접근하여 값을 설정
person.name = "Alice";
person.age = 25;
// 필드에 직접 접근하여 값을 출력
System.out.println("Name: " + person.name);
System.out.println("Age: " + person.age);
// 유효하지 않은 값도 직접 설정 가능
person.age = -5;
System.out.println("Invalid Age: " + person.age);
}
}
- 캡슐화를 지킨 코드 예시
// Person 클래스에 이름, 나이와 같은 속성과 get, set 메서드를 묶어 캡슐화
class Person {
// 접근 제한자를 통해 은닉화
private String name;
private int age;
// 이름을 가져오는 메서드
public String getName() {
return name;
}
// 이름을 설정하는 메서드
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 나이를 가져오는 메서드
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
// 나이를 설정하는 메서드
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age > 0) {
this.age = age;
} else {
System.out.println("유효하지 않은 나이입니다.");
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
// 메서드를 통해 값을 설정
person.setName("Alice");
person.setAge(25);
// 메서드를 통해 값을 출력
System.out.println("Name: " + person.getName());
System.out.println("Age: " + person.getAge());
// 유효하지 않은 값 설정 시도
person.setAge(-5); // "유효하지 않은 나이입니다." 메시지 출력
System.out.println("Age after invalid attempt: " + person.getAge());
}
}
3. 상속 (Inheritance)
- 부모 객체의 특징을 그대로 물려받는 것, 자바에서는 인터페이스 상속과 클래스 상속으로 나뉨.
- 대상을 객체로 추상화/구현할 때, 기존에 구현한 클래스를 재활용하여 구현할 수 있는 것.
- 기존 메서드와 변수를 물려받되, 필요한 기능을 더 추가하거나 자식클래에 맞게 재정의하는 방법
class Animal {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public abstract void cry(){
System.out.println("ㅜㅜㅜ");
}
}
// Cat 클래스는 Animal 클래스를 상속받았음.
// 따라서 모든 코드를 물려 받아 중복코드를 줄이고 수정하고 싶은 cry 메서드만 재정의하였다.
class Cat extends Animal {
public void cry() {
System.out.println("냐옹냐옹!");
}
}4. 다형성 (Polymorphism)
-
같은 요청으로부터 응답이 객체의 타입에 따라 나르게 나타나는 것.
-
어떤 객체의 속성이나 기능이 상황에 따라 여러 형태로 변할 수 있다는 것.
-
메서드 오버라이딩/오버로딩
- 오버라이딩 : 부모 클래스의 메서드를 자식 클래스에서 재정의하는 것.
- 메소드의 이름이 일치해야 함
- 메소드 매개변수의 개수, 순서 그리고 데이터 타입 일치해야 함
- 메소드의 return 타입이 일치해야 함
class Parent { void display() { System.out.println("부모 클래스의 display() 메소드입니다."); } } class Child extends Parent { void display() { System.out.println("자식 클래스의 display() 메소드입니다."); } }- 오버로딩 : 한 클래스에서 메소드 이름은 같지만 파라미터 개수나 자료형을 다르게 하여 서로 다르게 동작하게 하는 것
- 메소드의 이름이 일치해야 함
- 메소드 매개변수의 개수 또는 타입이 달라야 함 (개수가 같다면 타입, 타입이 같다면 개수를 다르게 해야함)
- 메소드의 return 타입이 달라야 함
void display(int num1){System.out.println(num1)} void display(int num1, int num2){System.out.println(num1+num2)} void display(int num1, double num2){System.out.println(num1+num2)} - 오버라이딩 : 부모 클래스의 메서드를 자식 클래스에서 재정의하는 것.
-
개발 유연성, 코드 재사용성을 제고시킬 수 있음.
-
상위 객체의 타입으로 하위 객체를 참조할 수 있음.
📌 OOP의 장점과 단점
1. 장점
- 코드 재사용성 증가
- 클래스를 가져와서 사용할 수 있고 상속을 통해 확장해서 사용할 수 있음
- 생산성 향상 및 대형 프로젝트에 적합
- 클래스 단위로 모듈화 시켜서 개발할 수 있으므로 대형 프로젝트에 적합
- 유지보수가 용이하다
- 캡슐화를 통해 주변에 영향을 거의 미치지 않기 때문에 문제가 생기는 클래스만 고치면 됨
2. 단점
- 설계 시 많은 시간과 노력이 필요
- 다양한 객체들의 상호작용을 통해 프로그램이 구성되므로 설계에 많은 시간과 노력이 필요
- 실행 속도가 상대적으로 느리다
- 클래스로 정의하고 그 안에서 또 변수와 함수를 만들 경우에 이들을 메모리에 저장해야 함. 객체가 호출 받으면
객체 호출 - 스택 저장 - 지역 변수 저장 - 코드 실행 - 반환 값 return - 호출 정보 제거과정을 거쳐야하기 때문에 절차지향보다 느림
- 클래스로 정의하고 그 안에서 또 변수와 함수를 만들 경우에 이들을 메모리에 저장해야 함. 객체가 호출 받으면
응집도와 결합도
응집도는 모듈에 포함된 내부 요소들이 연관되어 있는 정도를 나타낸다.
결합도는 의존성의 정도를 나타내며 다른 모듈에 대해 얼마나 많은 정보를 갖고 있는지 나타내는 정도다.
