
class Solution {
List<TreeNode> answer = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
void func(int curDepth, int usedN, int n, TreeNode root, int depth, int count){
if(usedN == 0){
answer.add(root);
return;
}
if(count ==5)return;
//왼오 추가 후 계속 진행
root.left = new TreeNode(0);
root.right = new TreeNode(0);
usedN = usedN-2;
curDepth +=1;
count++;
func(curDepth, usedN, n, root.left, depth, count);
func(curDepth, usedN, n, root.right, depth, count);
}
public List<TreeNode> allPossibleFBT(int n) {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(0);
int depth = n/2;
int usedN = n-1; // 시작 노드는 하나 썻으니까
func(1, usedN, n, root, depth,0);
return answer;
}
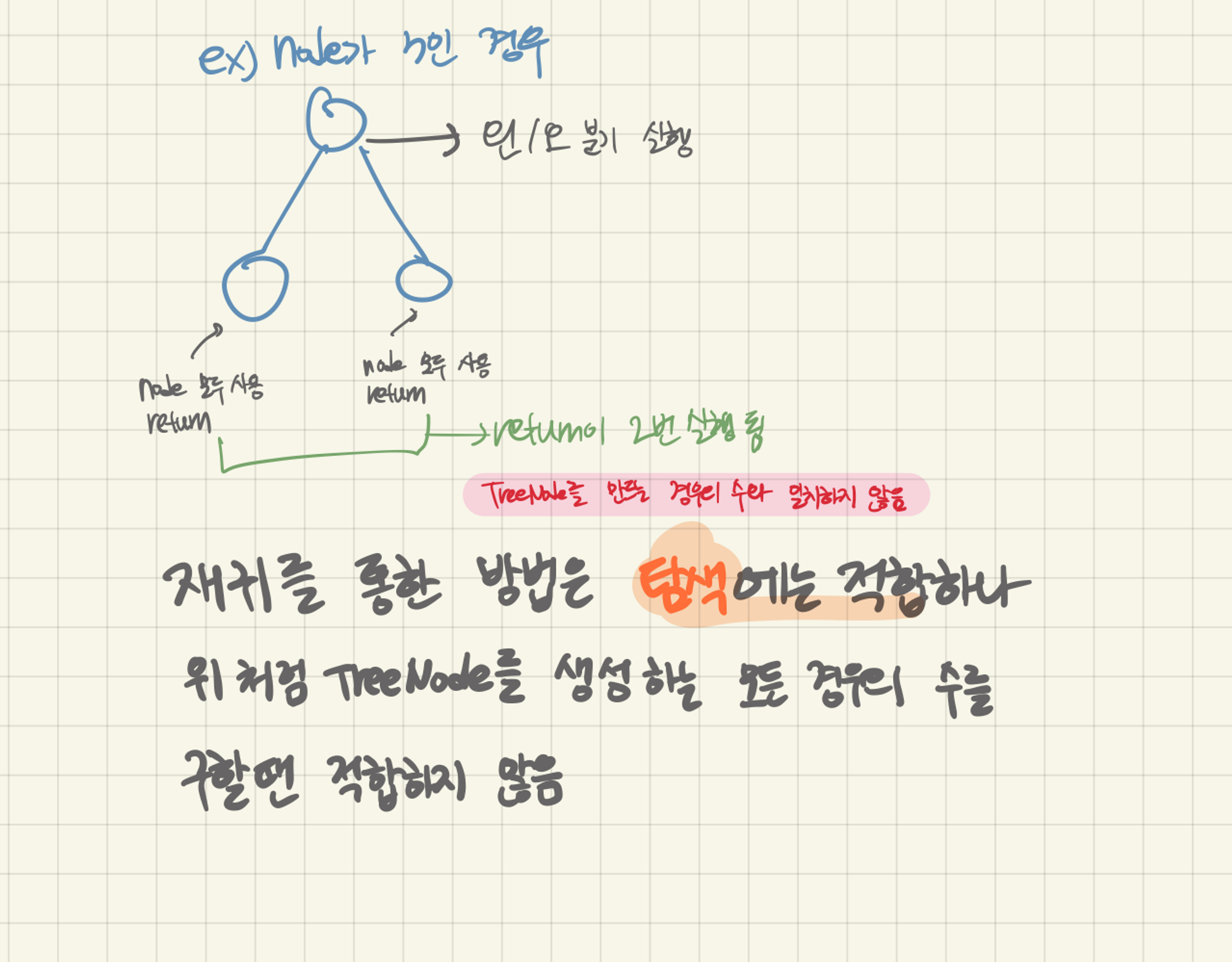
}현 코드의 문제점
트리노드의 전체 값을 저장하지 못한다.
트리노드를 새로 만들면서 탐색할 수는 있지만 반대로 전체의 트리노드의 구성은 저장할 수 없는 구조이다.
종료되는 시점이 명확하지 않다.
노드를 다 사용하면 종료가 되게 설정했지만 이때 문제가 발생한다.
문제를 잘 풀은 누군가의 풀이
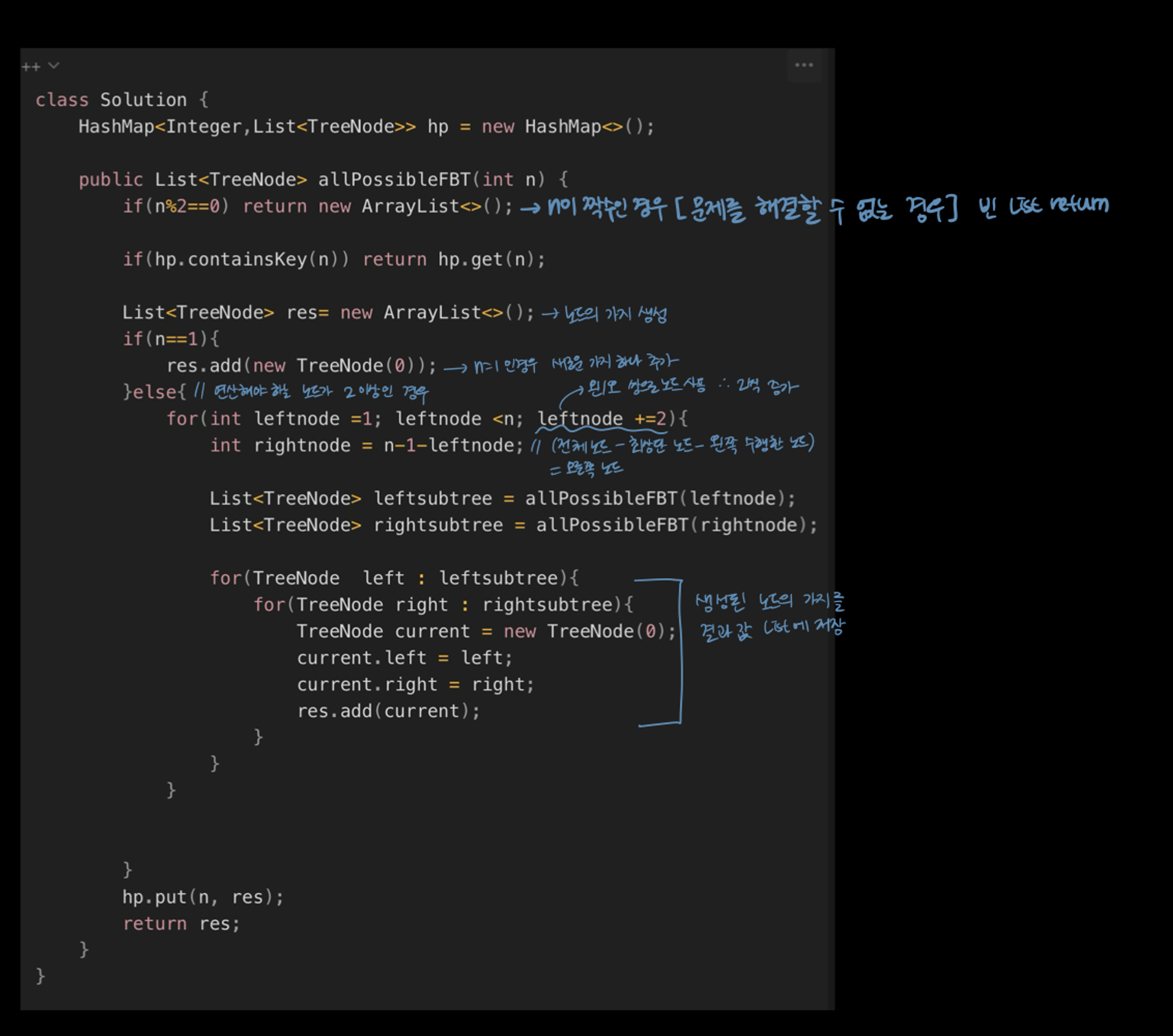
class Solution {
HashMap<Integer,List<TreeNode>> hp = new HashMap<>();
public List<TreeNode> allPossibleFBT(int n) {
if(n%2==0) return new ArrayList<>();
if(hp.containsKey(n)) return hp.get(n);
List<TreeNode> res= new ArrayList<>();
if(n==1){
res.add(new TreeNode(0));
}else{
for(int leftnode =1; leftnode <n; leftnode +=2){
int rightnode = n-1-leftnode;
List<TreeNode> leftsubtree = allPossibleFBT(leftnode);
List<TreeNode> rightsubtree = allPossibleFBT(rightnode);
for(TreeNode left : leftsubtree){
for(TreeNode right : rightsubtree){
TreeNode current = new TreeNode(0);
current.left = left;
current.right = right;
res.add(current);
}
}
}
}
hp.put(n, res);
return res;
}
}그리고 그 분의 설명
Approach
Base Cases:
If n is even, there are no possible full binary trees, so we return an empty list.
If n is 1, we return a list containing a single node with value 0, as it represents the base case of a full binary tree.
Memoization:
We utilize a memoization map (hp) to store previously computed results for different n values. This helps in avoiding redundant computations and improving the efficiency of the algorithm.
- 중복을 제거해줘서 불필요한 연산을 줄여준다는 뜻 여기에 HashMap을 사용한다.
Recursive Approach: 반복 접근에 관한 내용
For each n greater than 1, we iterate over all possible numbers of left nodes from 1 to n-1, incrementing by 2 to ensure that we only consider odd numbers (as full binary trees have an odd number of nodes). 2개씩 더해서 홀수 숫자만 체킹할 수 있도록
For each possible number of left nodes, we calculate the corresponding number of right nodes. 왼쪽 노드 탐색이 끝나면 right노드 탐색을 수행할 것임
We recursively call the allPossibleFBT function to compute all possible left subtrees and right subtrees for the current number of left and right nodes. // allPossibleFBT를 통해서 모든 leftsubtree, rightsubtree를 생성한다.
Combination of Subtrees:
Once we have lists of all possible left subtrees and right subtrees for the current number of left and right nodes, we generate all possible combinations of left and right subtrees.
For each combination of left and right subtrees, we create a new tree with value 0 as the root and the current left and right subtrees as its children.
Memoization of Results:
We memoize the result for the current n by storing the list of generated trees in the hp map.
Return Result:
Finally, we return the list of all possible full binary trees for the given n.
Complexity
- Time complexity: Exponential Time complexity
- Space complexity: Since we are using a map, the space is proportional to the number of unique inputs to the recursive function, which is O(n)
아직 완벽하게는 이해가 가지 않아서 몇 번 풀이가 더 필요할 것 같다!
