오늘의 코테문제
오늘은 bfs/dfs를 통한 탐색문제!
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
static int[] dx = {0,0,-1,1};
static int[] dy = {1,-1,0,0};
private static void bfs(int x,int y,int [][]computers, int[][]vis){
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(new int[]{x,y});
vis[x][y] =1;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int[] cur =q.poll();
for(int dir=0; dir<4; dir++){
int nx = cur[0] + dx[dir];
int ny = cur[1] + dy[dir];
if(nx <0 || ny <0|| nx>=vis.length|| ny>=vis.length){
continue;
}
if(vis[nx][ny] ==0&& computers[nx][ny] ==1){
q.add(new int[]{nx,ny});
vis[nx][ny] =1;
}
}
}
}
public int solution(int n, int[][] computers) {
int answer = 0;
int[][] vis = new int[n][n];
for(int x=0; x<n; x++){
for(int y=0; y<n; y++){
if(computers[x][y] ==1 && vis[x][y] ==0){
answer++;
bfs(x,y,computers,vis);
}
}
}
return answer;
}
}처음에 평번한 bfs로 풀었다가 낭패? 모든 테스트케이스가 통과하지 않는 끔찍한 상황 발생
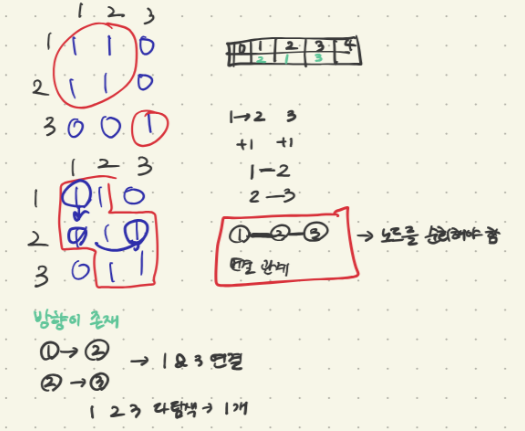
처음엔 그래프를 동서남북으로 쪼개서 확인했었다. 네트워크가 연결되있으려면 그래프가 어떤식으로든 연결이 되어 있어야 한다고 생각했다.
코드를 돌려보고 다 틀렸길래 다시 한번 문제를 생각해봤다.
결론은 그래프는 문제의 힌트?같은 것이고 결국에는 1,2,3번 네트워크가 연결이 되어있는지 확인하는 것이다.
computers로 주어진 그래프는 1번 2번 3번의 연결 여부를 노드들의 인접리스트로 표현한 것
노드를 탐색하는 방향으로 바꿔보자
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
private static void dfs2(int start, int[][]computers, boolean[]vis){
vis[start] =true;
for(int i=0; i<computers.length; i++){
if(computers[start][i] ==1 && !vis[i]){
dfs2(i, computers,vis);
}
}
}
private static void dfs1(int start ,int [][]computers, boolean[] vis){
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(start);
vis[start] =true;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
int cur = stack.pop();
for(int i=0; i< computers.length; i++){
if(computers[cur][i] ==1 && !vis[i]){
stack.push(i);
vis[i] =true;
}
}
}
}
private static void bfs(int start ,int[][] computers, boolean[] vis){
Queue<Integer> q= new LinkedList<>();
q.add(start);
vis[start] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int cur = q.poll();
for(int i=0; i<computers.length; i++){
if(computers[cur][i] ==1 &&!vis[i]){//노드와 연결된 곳 탐색, 노드가 방문하지 않은 곳
//q에 넣어주기
q.add(i);
vis[i] =true;
}
}
}
}
public int solution(int n, int[][] computers) {
int answer = 0;
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){//노드탐색
if(!vis[i]){
answer++;
// bfs(i, computers,vis);
// dfs1(i, computers,vis);
dfs2(i,computers,vis);
}
}
return answer;
}
}총 세 가지 방법을 통해서 탐색을 수행했다.
노드를 탐색하는 방법은 기존 bfs와 크게 다르지는 않다.
computers[cur][i] -> cur이 의미하는 것은 cur과 연결된 컴퓨터들을 찾겠다는 의미이다.
즉
for(int i=0; i<computers.length; i++){
if(computers[cur][i] ==1 &&!vis[i]){//노드와 연결된 곳 탐색, 노드가 방문하지 않은 곳
//q에 넣어주기
q.add(i);
vis[i] =true;
}
}각 탐색 방법의 for문 안에는 기준점 node와 이어진 노드들을 탐색한다.
탐색 후에는 vis에 true라고 표시해서 해당 노드를 지나갔다고 표시하면 된다.
\
총 세 가지 방법을 사용했는데
1. BFS
private static void bfs(int start ,int[][] computers, boolean[] vis){
Queue<Integer> q= new LinkedList<>();
q.add(start);
vis[start] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int cur = q.poll();
for(int i=0; i<computers.length; i++){
if(computers[cur][i] ==1 &&!vis[i]){//노드와 연결된 곳 탐색, 노드가 방문하지 않은 곳
//q에 넣어주기
q.add(i);
vis[i] =true;
}
}
}
}2. DFS (Stack을 사용함)
private static void dfs1(int start ,int [][]computers, boolean[] vis){
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(start);
vis[start] =true;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
int cur = stack.pop();
for(int i=0; i< computers.length; i++){
if(computers[cur][i] ==1 && !vis[i]){
stack.push(i);
vis[i] =true;
}
}
}
}3. 재귀를 활용한 DFS
private static void dfs2(int start, int[][]computers, boolean[]vis){
vis[start] =true;
for(int i=0; i<computers.length; i++){
if(computers[start][i] ==1 && !vis[i]){
dfs2(i, computers,vis);
}
}
}위의 경우로 풀었다.
첫 번째 BFS풀이의 반례
나는 동서남북 탐방을 하는 방식으로 처음에 풀었었다. 그 이유는 어짜피 노드들이 연결되어 있으면 1로 연결점이 있으니까 분명이 먹힐 것이라고 생각했다.
하지만 컴퓨터가 3대이고 1,3이 연결되어 있다고 가정해보자
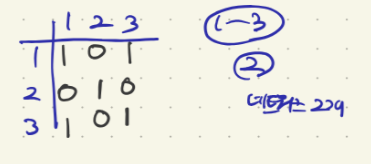
1, 3 번 노드가 연결되어 있는 경우이다.
여기서 리스트를 그리면 저렇게 되는데 처음에 내가 짠 방식으로 수행하면 네트워크가 5개가 나와버린다.
노드를 탐색하는 것이 아니라 그래프 자체를 탐색하는 방법을 택했기 때문이다. 참고로 그래프는 어떤 노드들이 연결되어 있는지 알려주는 '힌트' 같은 것이지 직접적으로 내가 탐색해야할 그래프를 의미하는 것이 아니다.
위의 그림에서는 (1,3) (2) 이렇게 연결돼있어서 답은 2가 나와야하는데 내가 풀이한 방식은 5가나온다.
REVIEW
쉬운 문제인줄 알았으나 의외로 복병이 있떤? 문제였다.
내가 그래프관련 문제를 잘 못풀어서 그런것도 있는 것 같다. 그래프를 더 열심히 공부해보쟈
#99클럽 #코딩테스트준비 #개발자취업 #항해99 #TIL
