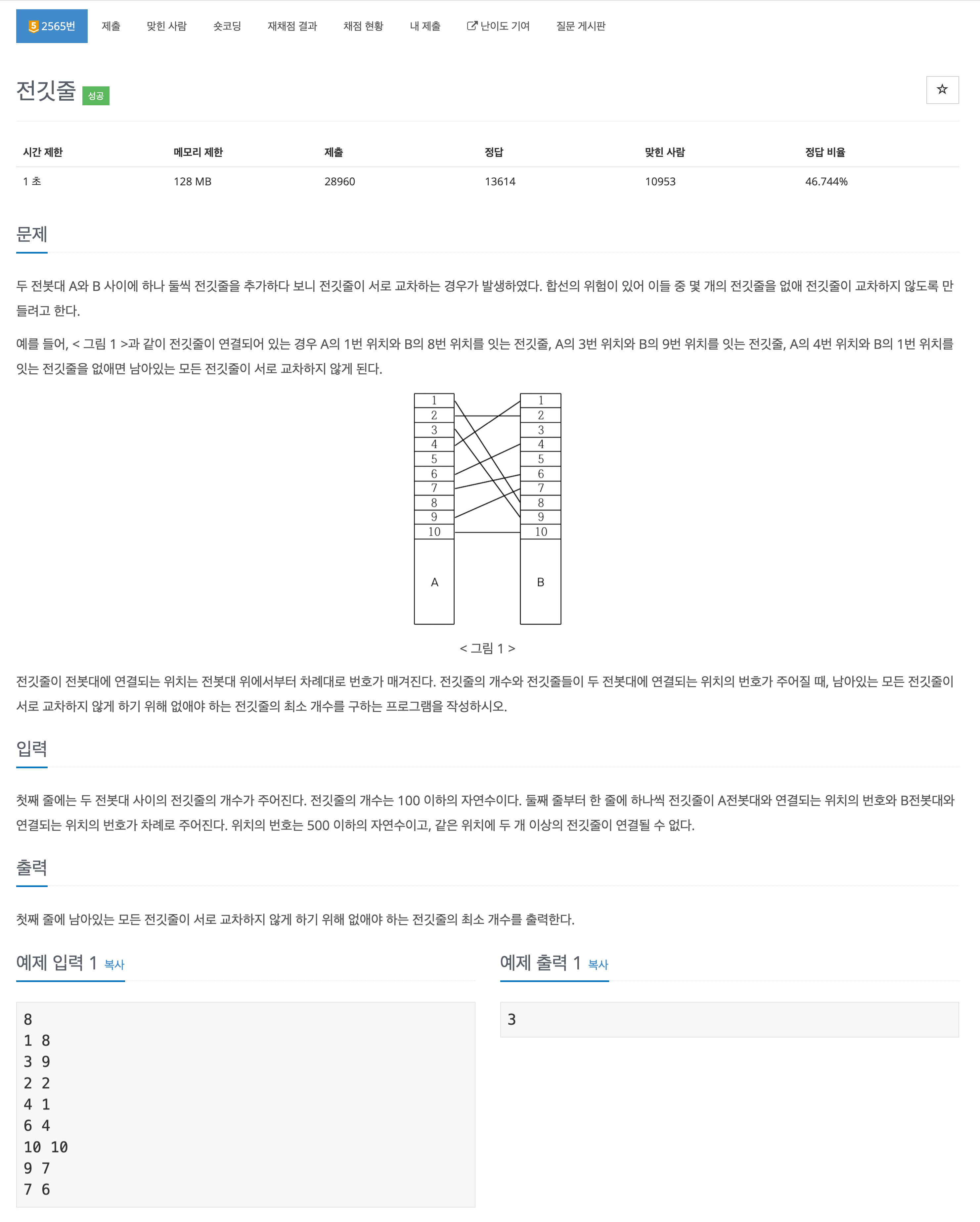
풀이 요약
완전 탐색 문제. 이론만 알고 있다면 쉽게 풀 수 있는 문제이다.
풀이 상세
- 델타를 활용하여 현재 맵의
X가 아니면서, 아직 방문하지 않은 곳이라면, 완전 탐색을 실행하여 인근 값을 더한 값을 구한다. 탐색은BFS로 하였다. - 예외 상황으로, 무인도가 하나도 없는 경우가 나타날 수 있다. 이 값은 탐색을 모두 끝냈는데도
answer.size()가 일 경우 을 넣어주는 것으로 했다. - 정렬하여 해당
answer를 반환하면 된다
코드
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pi;
vector<string> arr;
bool visited[104][104];
int dr[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dc[4] = {0, -1, 0, 1};
int rLen, cLen;
int bfs(int i, int j) {
queue<pi> q;
int cnt = arr[i][j] - '0';
q.push({i,j});
visited[i][j] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
pi curr = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int nr = curr.first + dr[d];
int nc = curr.second + dc[d];
if (nr < 0 || nc < 0 || nr >= rLen || nc >= cLen)
continue;
if (visited[nr][nc])
continue;
if (arr[nr][nc] == 'X')
continue;
visited[nr][nc] = true;
cnt += arr[nr][nc] - '0';
q.push({nr,nc});
}
}
return cnt;
}
vector<int> solution(vector<string> maps) {
vector<int> answer;
arr = maps;
rLen = maps.size();
cLen = maps[0].size();
for (int i = 0; i < rLen; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cLen; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] != 'X' && !visited[i][j])
answer.push_back(bfs(i, j));
}
}
sort(answer.begin(), answer.end());
if (answer.size() == 0)
answer.push_back(-1);
return answer;
}
int main() {
solution({"X591X", "X1X5X", "X231X", "1XXX1"});
return 0;
}
