AWS Scalability & High Availability

Scalability
- An application or system can handle greater loads by adapting
- Vertical Scalability
- Horizontal Scalability (elasticity)
Vertical Scalability
- Increase or decrease the size of the instance
- Scale up or down
- For non distributed systems such as database (RDS, ElastiCache)
- ex) t2.micro -> t2.large
Horizontal Scalability
- Increase or decrease the number of instances or systems for application
- Scale out or in
- Auto Scaling Group and Load Balancer
- For distributed systems such as web applications
- Easy to horizontally scale due to EC2
High Availabilty
- Means running in at lease 2 data centers (Availabilty Zones)
- The goal is to survive a data center loss
- Auto Scaling Group with multi AZ
- Load Balancer with multi AZ
Load Balances
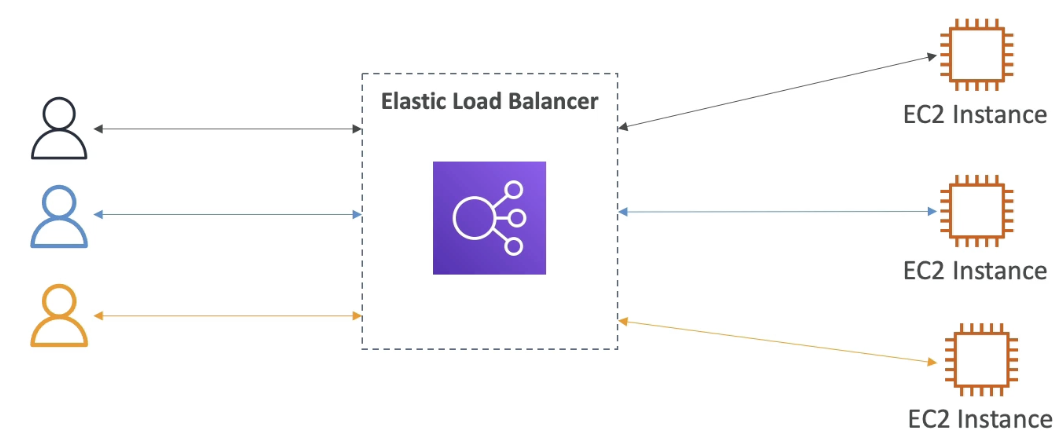
- Servers that forward traffic to multiple servers downstream
- Users only know that they have to connect to the load balancer
- Users do not know which backend instance will respond
Benefits
- Spread load accross multiple downstream instances
- Expose a single point of access (DNS) to application
- Handles failures of downstream instances
- Regular health check to instances
- Provide SSL termination HTTPS
- Stickiness with cookies
- High availabilty across zones
- Seperate public traffic from private traffic
Elastic Load Balancer
- Managed load balancer
- AWS guarantees that it works
- AWS takes care of upgrades, maintenance, high availabilty
- AWS provides a few configuration knobs to tweak load blancer
- It costs less to setup own load balancer
- It is integrated with many AWS offerings
Health Checks
- Check if the instane is working
- Crutial for load balancers as it can know the instance is able to reply to requests

- Response is 200 if healthy
- Resposne is noy 200 if unhealthy and load balancer will not send traffics to the instance
Types of Load Balancer
- 4 types of managed Load Balancers
- Classic Load Balancer (HTTP,HTTPS,TCP,SSL)
- Application Load Balancer (HTTP,HTTPS,WebSocket)
- Network Load Balancer (TCP,TLS,UDP)
- Gateway Load Balancer (Operates at Network layer) - Some load balancers can be set up as private or public
Security Groups
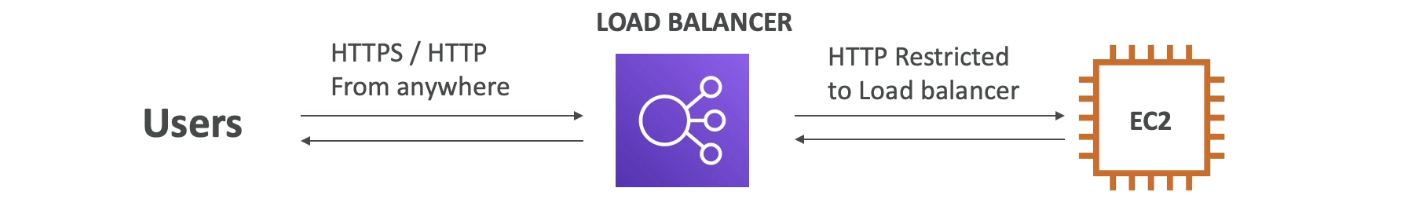
-
Enhanced security mechanism
-
Make instance only accessible through the ALB
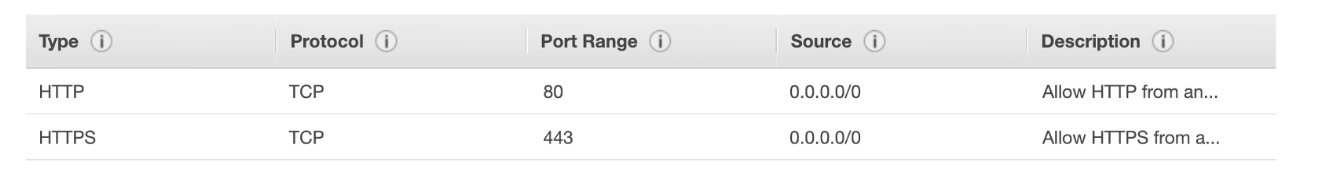
-
Load Balancer allows HTTPS (443) and HTTP (80) requests from anywhere (0.0.0.0/0)

- EC2 instance allows HTTP (80) requests from the Load Balancer
- Therefore, the source is the security group of the Load Balancer
Security group of EC2 and Load Balancer are linked, meaning EC2 only allows requests originated from Load Balancer
Application Load Balancer
- Layer 7 (HTTP)
- Load balances to multiple HTTP applications across machines (target groups)
- Load balances to multiple applications on the same machine (containers)
- Support for HTTP/2 and WebSocket
- Support redirects (from HTTP to HTTPS)
- Routing tables to difference target groups
- Routing based on path in URL (ex.com/users & ex.com/posts)- Routing based on hostname in URL (one.com & two.com)
- Routing based on Query String, Headers (one.com/user?id=1&order=false)
Great for micro services and container based application such as Docker & Amazon ECS
- Has port mapping features to redirect
to dynamic port in ECS - We would need multiple Classic Load Balancer per application
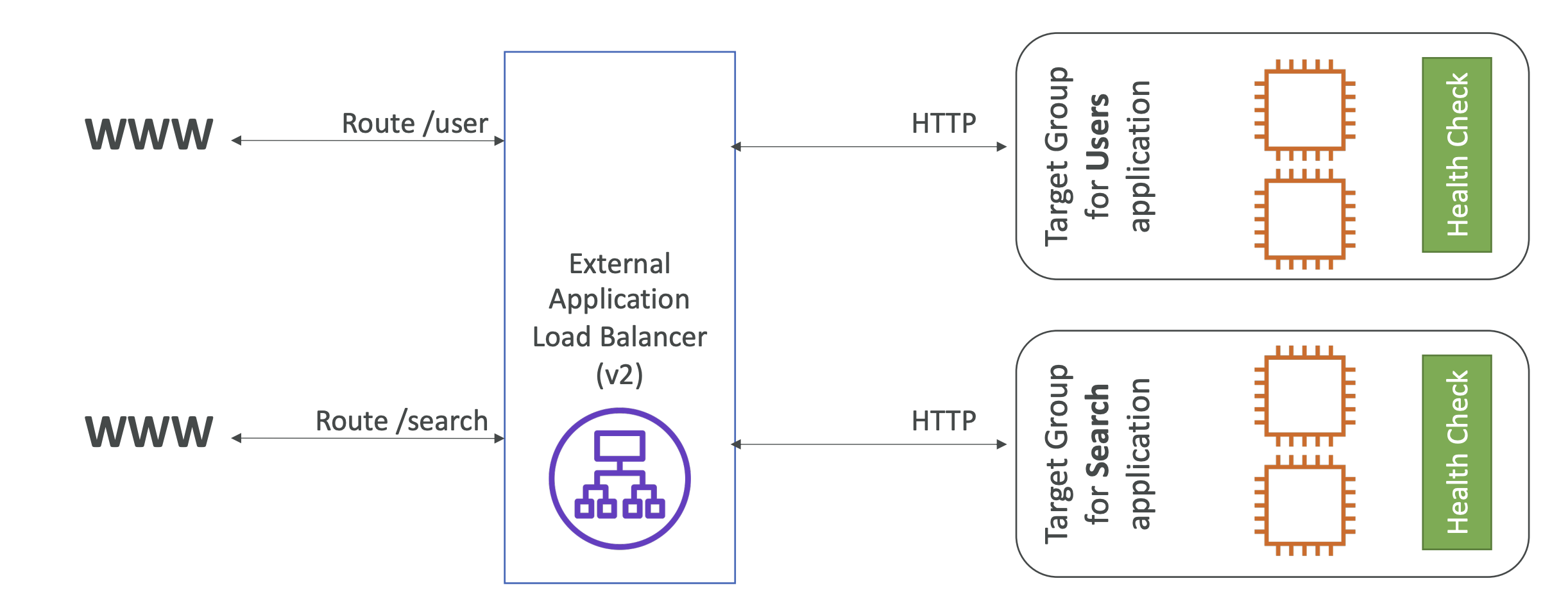
- Two target groups are behind the same ALB
- Traffics are routed based on path in URL
Target Groups
-
EC2 instances managed by an Auto Scaling Group
-
ECS tasks
-
Lambda functions
-
IP Addresses
-
ALB route to multiple target groups
-
Health checks are done at the target group level
X-Forwarded-Port/Porto
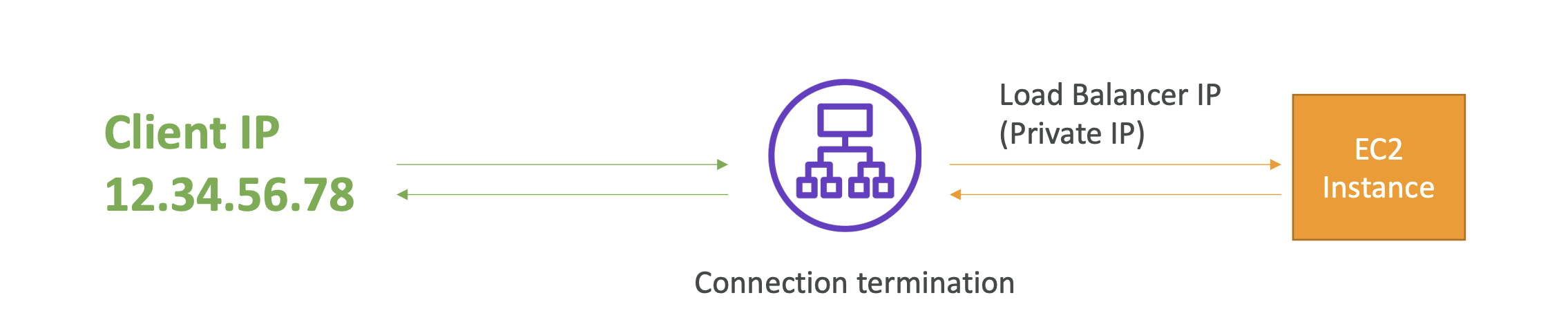
- Client communicates with Load Balancer using the public IP
- Load Balancer communicates with the instance using private IP
- For the Instance to know the client IP, it looks at the X-Forwarded-Port and Proto
Listener Rules
- Add rules to the Load Balancer
- Condition == Filtering requests
- Path, Query, Request method, IP- There can be multiple conditions
- Action types == What to do with the condition
- Forward to target groups- Redirect to URL
- Return fixd response
Network Load Balancers
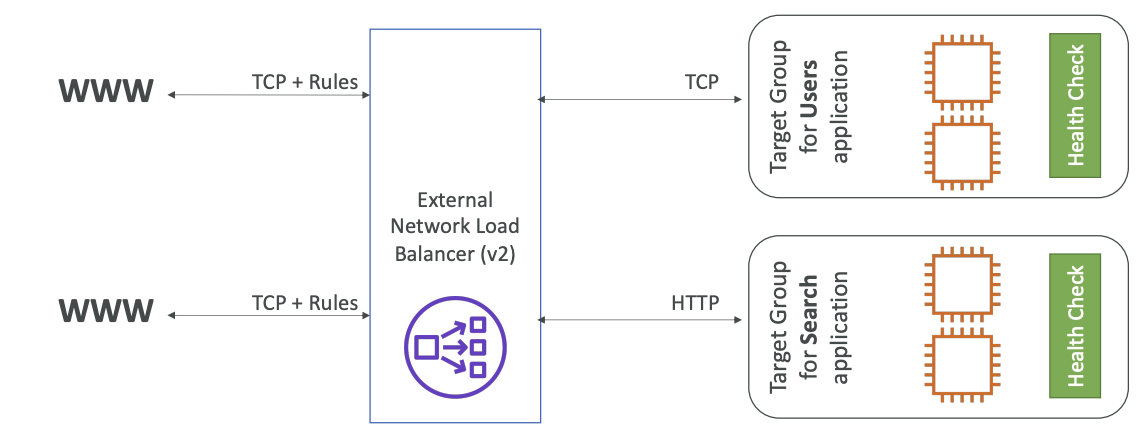
- Layer 4 TCP & UDP traffic to instances
- Handle millions of request per seconds
- Less latency ~100ms (400ms for ALB)
- One static iP per AZ and support assiging Elastic IP
- Helpful for whitelisting IPs
- Not AWS free tier
Target Groups
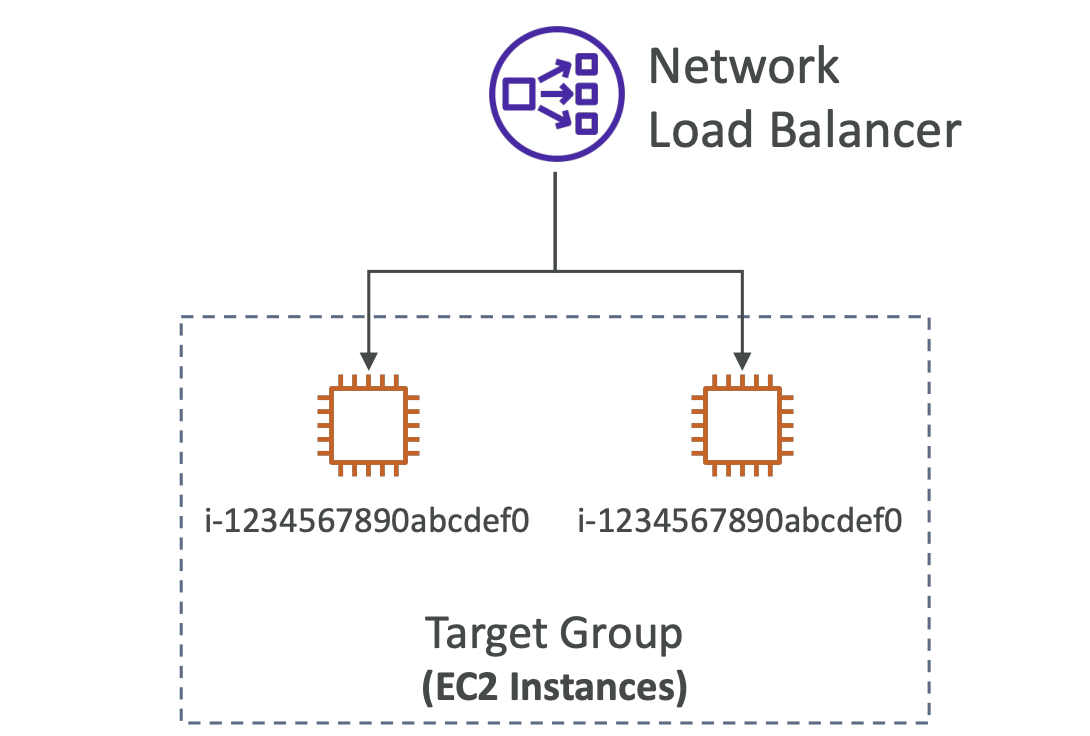
- Redirect to EC2 instances
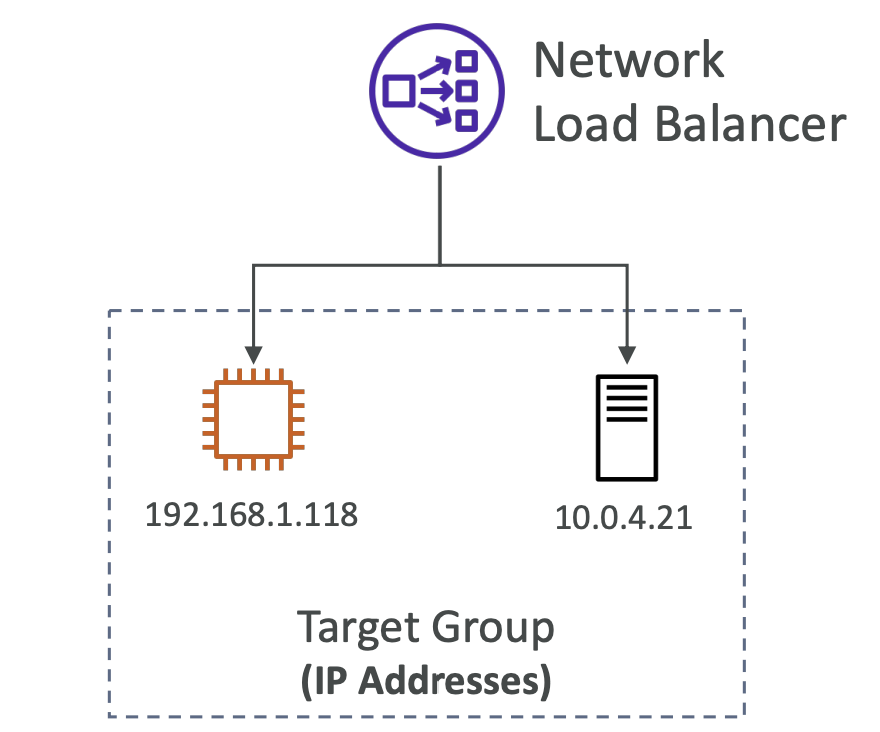
- IP Addresses (must be private IPs)
- Send requests to a server with private IP
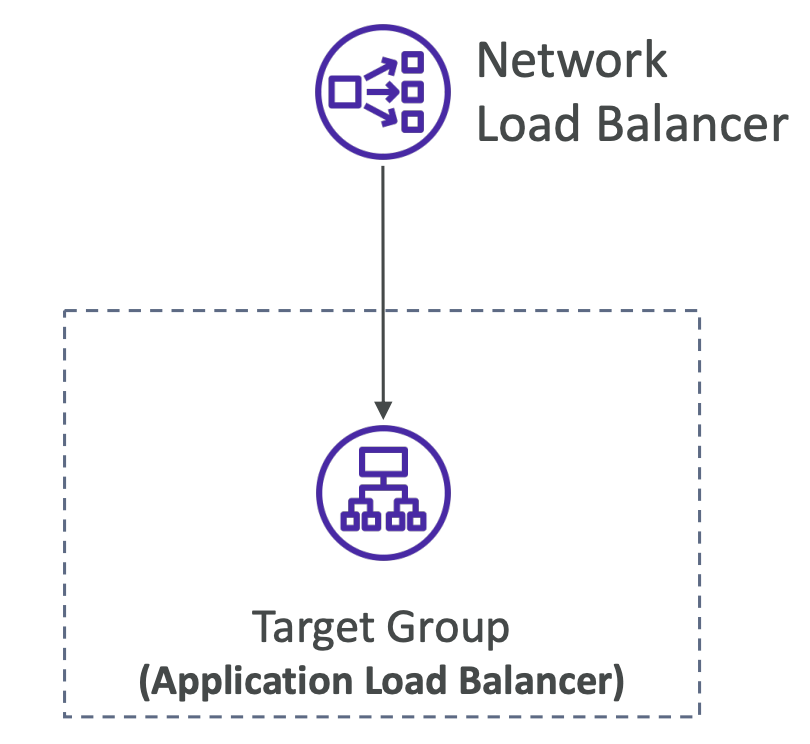
- Application Load Balancer
- NLB gets you a fixed IP address
- ALB handles HTTP requests based on rules
Health Check
- supports TCP, HTTP, HTTPS Protocols