1. Combinational Logic Elements
1.1 Stateless logic
- no embedded state(memory)
- input에 의해서만 output이 결정됨
1.2 예시
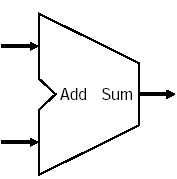
- Adder
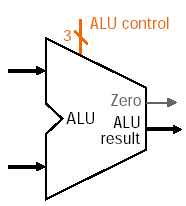
- ALU
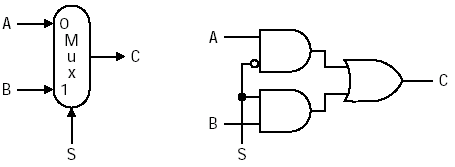
- two-input multiplexer
S의 값을 통해 A, B 중 하나를 선택
2. Storage Elements
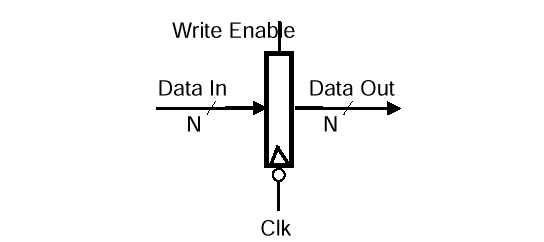
2.1 Register
- 다음 특성을 제외하고는 D flipflop과 유사함
- n bit의 input/output
- write enable input
- write enable
- 0 : data out 변하지 않음
- 1 : data out은 data in이 됨
- 저장된 데이터는 falling clock edge에서만 바뀐다
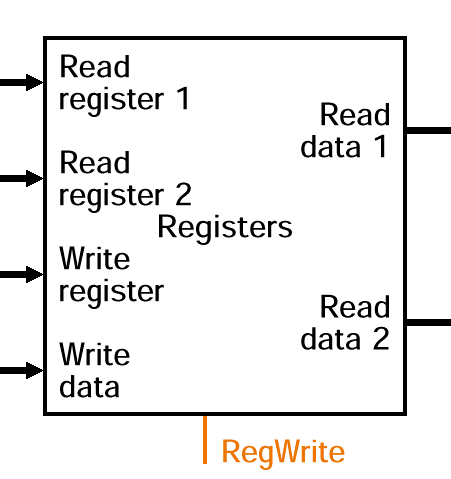
2.2 Register file
- 32개의 register로 구성됨
- 동작 방식
- Read register1은 Read data1에 들어갈 register 선택
- Read register2은 Read data2에 들어갈 register 선택
- RegWrite = 1일 때, Write register는 Write Data 값을 통해 쓰일 register 선택
- Clock input(CLK)
write operation만을 위한 요소
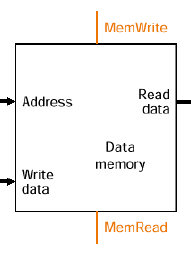
2.3 Memory
- 레지스터는 두 개의 레지스터를 읽으면서 하나의 레지스터를 쓰는 것이 가능하지만, 메모리는 한 순간에 읽기/쓰기 중 하나만 할 수 있음
- 동작 방식
- MemRead = 1일 때, Data Out에 데이터를 넣어서 읽기
- MemWrite = 1일 때, Data in에 값을 넣어서 데이터 쓰기
- Clock input(CLK)
write operation만을 위한 요소
3. Clocking
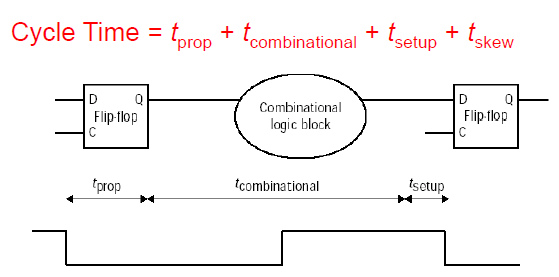
- t-combinational
storage element의 output이 combinational logic block을 거져 storage element의 input이 되는데, cycle time은 그동안 걸리는 시간의 최댓값을 고려해야 한다.
- t-skew
clock이 모든 storage element에게 가는데, 모두에게 동시에 도착하는 것이 아님. 가장 빠른 지점과 느린 지점의 차이를 구한 것
- t-prop & t-skew
clock의 falling edge이 되기 조금 전에는 storage element의 input 값을 유지해야 하고 이를 t-setup 타임이라고 하고, 반대로 falling edge 이후의 input 값을 유지해야 하는 시간을 t-hold이라고 한다. 또한 그 이후의 output값을 유지하는 시간을 t-prop이라고 하고, t-prop이 t-hold보다 크기 때문에 t-prop을 반영하는 것
참고
http://olc.kr/classroom/index.jsp?cuid=310525 16, 17강







