Proxy Pattern?
Proxy는 대리인이란 뜻으로 뭔가를 대신해서 처리하는 것이다.
Proxy Class를 통해서 대신 전달하는 형태로 설계되며, 실제 Client는 Proxy로 부터 결과를 받는다. cache의 기능으로 활용이 가능하다.

그냥 객체를 이용하면 되지, 이렇게 번거롭게 중계 대리자를 통해 이용하는 방식을 취하는 이유는, 대상 클래스가 민감한 정보를 가지고 있거나 인스턴스화 하기에 무겁거나 추가 기능을 가미하고 싶은데, 원본 객체를 수정할수 없는 상황일 때를 극복하기 위해서 이다. 대체적으로 정리하자면 다음과 같은 효과를 누릴수 있다고 보면 된다.
- 보안(Security) : 프록시는 클라이언트가 작업을 수행할 수 있는 권한이 있는지 확인하고 검사 결과가 긍정적인 경우에만 요청을 대상으로 전달한다.
- 캐싱(Caching) : 프록시가 내부 캐시를 유지하여 데이터가 캐시에 아직 존재하지 않는 경우에만 대상에서 작업이 실행되도록 한다.
- 데이터 유효성 검사(Data validation) : 프록시가 입력을 대상으로 전달하기 전에 유효성을 검사한다.
- 지연 초기화(Lazy initialization) : 대상의 생성 비용이 비싸다면 프록시는 그것을 필요로 할때까지 연기할 수 있다.
- 로깅(Logging) : 프록시는 메소드 호출과 상대 매개 변수를 인터셉트하고 이를 기록한다.
- 원격 객체(Remote objects) : 프록시는 원격 위치에 있는 객체를 가져와서 로컬처럼 보이게 할 수 있다.
구현 코드
// proxy.IBrowser
// subject
public interface IBrowser {
Html show();
}// proxy.Html
public class Html {
private String url;
public Html(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
}// proxy.Browser
public class Browser implements IBrowser{
private String url;
public Browser(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
@Override
public Html show() {
System.out.println("browser loading html from : " + url);
return new Html(url);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Browser browser = new Browser("www.naver.com");
browser.show();
browser.show();
browser.show();
browser.show();
}
}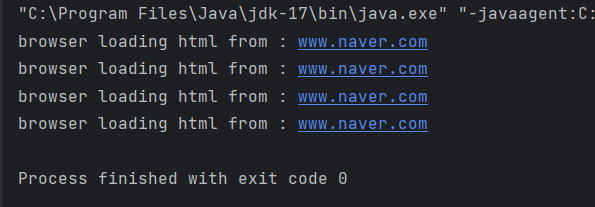
이렇게 실행하니 브라우저를 계속 로딩하고 있다. 실제라면 시간이 걸릴 것이다. 이를 해결하기 위해서 캐싱을 사용하는 예제를 만들어보자.
가상프록시
public class BrowserProxy implements IBrowser{
private String url;
private Html html;
public BrowserProxy(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
@Override
public Html show() {
// show()가 실행될때 실제 객채 생성
if(html == null) {
this.html = new Html(url);
System.out.println("BrowserProxy loading html from : " + url);
}
System.out.println("BrowserProxy use cache from : " + url);
return null;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IBrowser browser = new BrowserProxy("www.naver.com");
browser.show();
browser.show();
browser.show();
browser.show();
browser.show();
}
}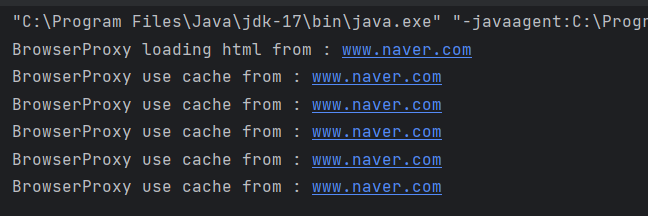
BrowserProxy 클래스는 IBrowser 인터페이스를 구현하여 실제 객체와 동일한 메서드를 제공하지만, 실제 객체를 생성 및 호출하는 시점을 제어하여 필요할 때만 실제 객체를 생성하고 반환한다. 이 코드에서는 show()가 처음 호출될 때에만 실제 객체를 생성하고, 이후 호출에서는 생성된 객체를 재사용할 수있음을 알수있다.
AOP 구현해보기
// aop.AopBrowser
public class AopBrowser implements IBrowser {
private String url;
private Html html;
private Runnable before;
private Runnable after;
public AopBrowser(String url, Runnable before, Runnable after) {
this.url = url;
this.before = before;
this.after = after;
}
@Override
public Html show() {
before.run();
if (html == null) {
this.html = new Html(url);
System.out.println("AopBrowser html loading from : " + url);
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
after.run();
System.out.println("AopBrowser html cache : " + url);
return html;
}
}AopBrowser는 IBrowser를 구현하여 AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming)를 구현해 보았다. 처음 브라우저를 로딩하는데 걸리는 시간을 확인하고 싶어하는 상황을 가정하고 말이다.
Runnable클래스의 before, after를 인자로 받아 로딩 전과 후에 실행할 동작을 설정한다.
최초 호출 시에만 URL을 로딩하고, 이후 호출에서는 캐시를 사용한다. Thread.sleep()을 사용하여 로딩하는데 걸리는 시간을 인위적으로 주어 로딩과 캐싱을 사용할때의 시간차이를 확인 해보겠다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicLong start = new AtomicLong();
AtomicLong end = new AtomicLong();
IBrowser aopBrowser = new AopBrowser("www.naver.com",
() -> {
System.out.println("before");
start.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
},
() -> {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
end.set(now - start.get());
}
);
aopBrowser.show();
System.out.println("loading time : " + end.get());
aopBrowser.show();
System.out.println("loading time : " + end.get());
}
}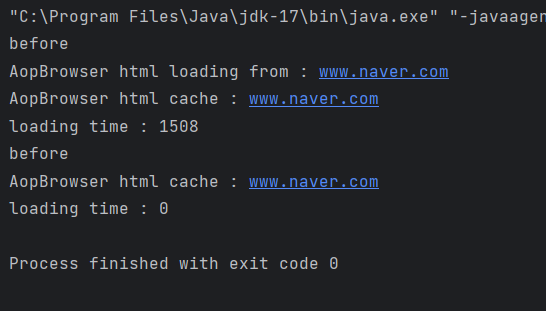
실행결과 처음 로딩할 때는 1508ms의 시간이 걸리지만 캐시에 저장되고 나서는 0으로 나옴을 알 수 있다.
참고자료
출처: https://inpa.tistory.com/entry/GOF-💠-프록시Proxy-패턴-제대로-배워보자#thankYou [Inpa Dev 👨💻:티스토리]
