문제링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1071
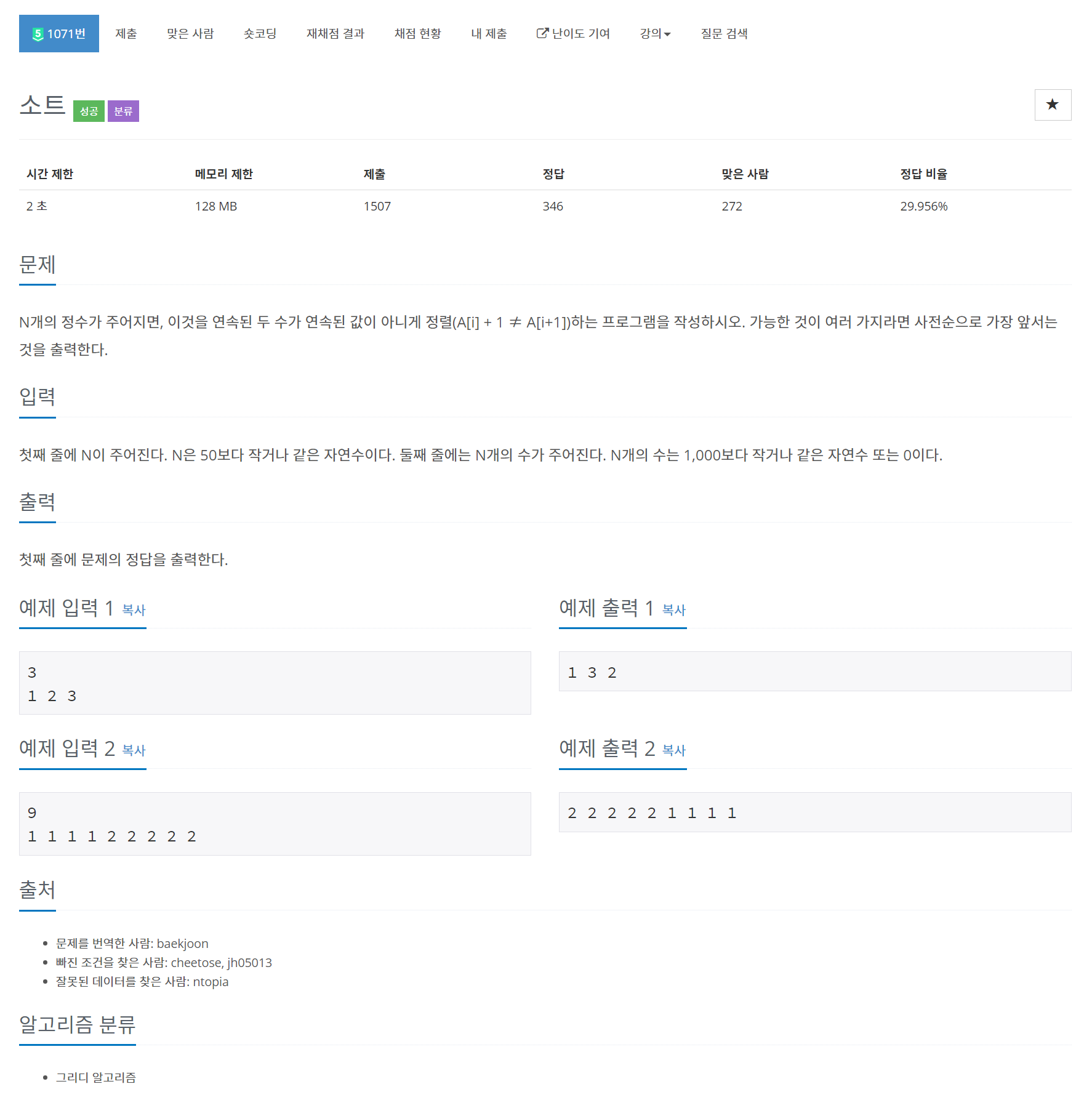
문제
풀이
-
배열을 오름차순으로 정렬시켜준다.
-
v[i]+1 == v[i+1] 인 경우 auto it = lower_bound로 v[i]+2가 존재한다면 위치를 찾아준다.
-
v[i]+2가 존재한다면 v[i]와 v[i+2] 의 위치를 바꿔준다.
-
it가 v.end()라면 v[i]+2가 존재하지 않는다는 것이므로 이때 배열의 상태는 이미 정렬이 완성된 상태이거나 ... 333 4444 처럼 연속된 숫자가 마지막에 묶음으로 존재하는 경우이다. (앞부분은 정렬이 완료 되었고 마지막 부분만 잘 정리하면 된다!)
lower_bound(v.begin()+i-cnt,v.end(),v[i])
uppwer_bound(v.begin()+i+1,v.end(),v[i])
를 통해 4의 시작위치에서 배열의 끝까지 가며 3의 위치와 단체 swap을 시켜주면 정답이 된다.
(cnt는 3의 시작위치를 알아내기 위해 앞에서 3이 몇번이나 연속으로 반복되었나 체크하는 변수)
코드
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> v;
int n; cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int t;
cin >> t;
v.push_back(t);
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < v.size() - 1; i++) {
if (v[i + 1] == v[i] + 1) {
auto it = lower_bound(v.begin() + i, v.end(), v[i] + 2);
if (it != v.end()) swap(*it, v[i + 1]);
else {
auto ub = upper_bound(v.begin() + i + 1, v.end(), v[i]);
auto lb = lower_bound(v.begin() + i-cnt, v.end(), v[i]);
while (ub != v.end()) {
swap(*lb, *ub);
lb++; ub++;
}
}
cnt = 0;
}
else if (v[i + 1] == v[i]) cnt++;
}
for (auto i : v) cout << i << ' ';
}후기
쉬운듯 잘 안풀린다.
