문제링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7576
문제
풀이
유명한 bfs 알고리즘 문제인 토마토 이다.
문제가 워낙 유명하기에 깔끔하게 코딩하는것에만 신경써서 풀었다.
코딩하는 과정에서 핵심은
-
days count 를 위한 방법
( sz 변수를 이용해 특정 시점의 큐의 크기를 저장) -
dx[4],dy[4] , 반복문을 이용한 상하좌우 탐색
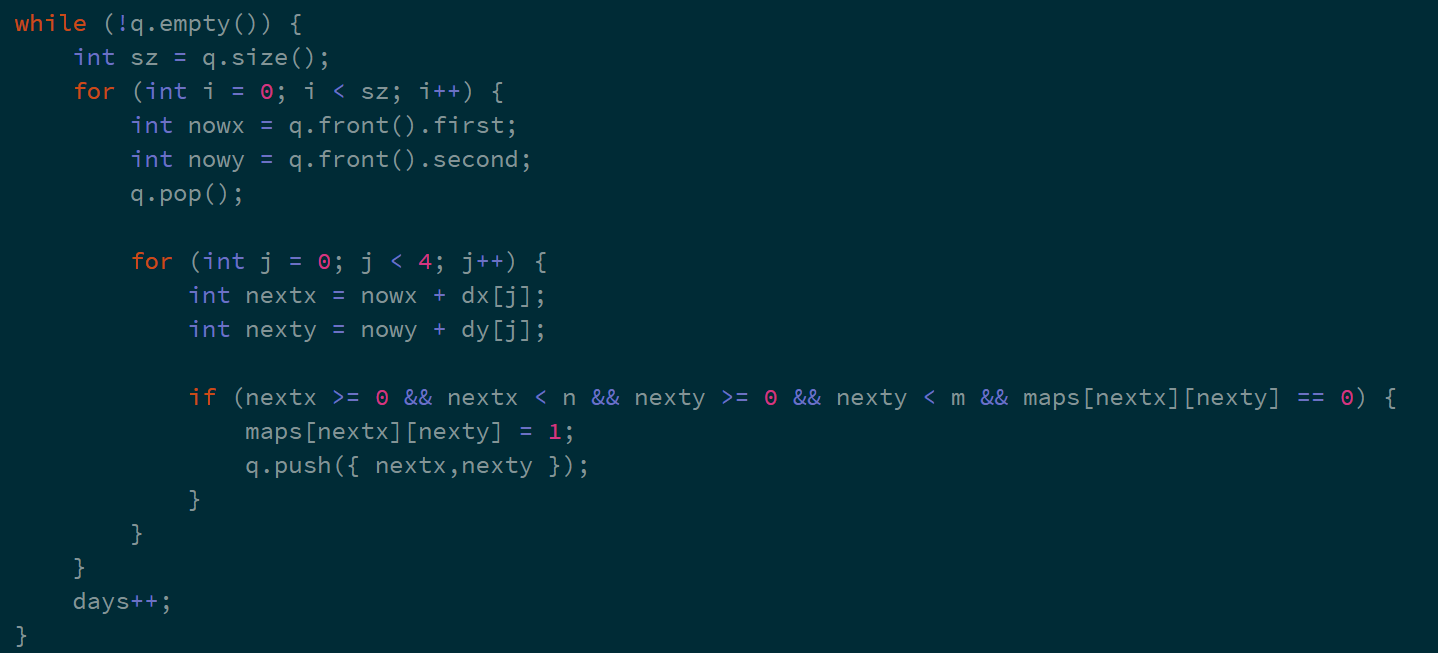 이다.
이다.
익은 토마토가 하나도 주어지지 않는 경우는 입력으로 주어지지 않기에 따로 처리해주지 않았다.
코드
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int n, m, days;
int maps[1001][1001];
int dx[4]{ 0,0,1,-1 };
int dy[4]{ 1,-1,0,0 };
queue<pii> q;
bool is_ripe() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (maps[i][j] == 0) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int bfs() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (maps[i][j] == 1) q.push({ i,j });
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int sz = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
int nowx = q.front().first;
int nowy = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
int nextx = nowx + dx[j];
int nexty = nowy + dy[j];
if (nextx >= 0 && nextx < n && nexty >= 0 && nexty < m && maps[nextx][nexty] == 0) {
maps[nextx][nexty] = 1;
q.push({ nextx,nexty });
}
}
}
days++;
}
if (is_ripe()) return days - 1;
else return -1;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cin >> maps[i][j];
}
}
cout << bfs();
}=======================
7576 토마토 문제에서 변형된 7569 토마토 문제 도 같이 풀어보았다.
문제링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7569
문제
풀이
7576 토마토 문제의 변형이다.
기존의 7576 토마토 문제는 앞뒤와 좌우만 탐색하면 되었기에 dx[4],dy[4] 배열을 사용했다.
하지만 7579 토마토 문제는 위 아래까지 모두 탐색해야 하기 때문에 dx[6],dy[6],dz[6] 배열을 사용했고 이에맞게 나머지 코드들도 조금씩 변경했다.
7576 토마토 문제와 코드를 비교하면서 보면 좋을듯 하다.
코드
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef struct pos {
int x, y, z;
};
int n, m, h, days;
int maps[101][101][101];
int dx[6]{ 0,0,0,0,1,-1 };
int dy[6]{ 0,0,1,-1,0,0 };
int dz[6]{ 1,-1,0,0,0,0 };
queue<pos> q;
bool is_ripe() {
for (int k = 0; k < h; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (maps[k][i][j] == 0) return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
int bfs() {
for (int k = 0; k < h; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (maps[k][i][j] == 1) q.push({ i,j,k });
}
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int sz = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
int nowx = q.front().x;
int nowy = q.front().y;
int nowz = q.front().z;
q.pop();
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
int nextx = nowx + dx[j];
int nexty = nowy + dy[j];
int nextz = nowz + dz[j];
if ( nextx >= 0 && nextx < n && nexty >= 0 && nexty < m && nextz >= 0 && nextz < h && maps[nextz][nextx][nexty] == 0) {
maps[nextz][nextx][nexty] = 1;
q.push({ nextx,nexty,nextz });
}
}
}
days++;
}
if (is_ripe()) return days - 1;
else return -1;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> m >> n >> h;
for (int k = 0; k < h; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cin >> maps[k][i][j];
}
}
}
cout << bfs();
}