문제링크
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/42577
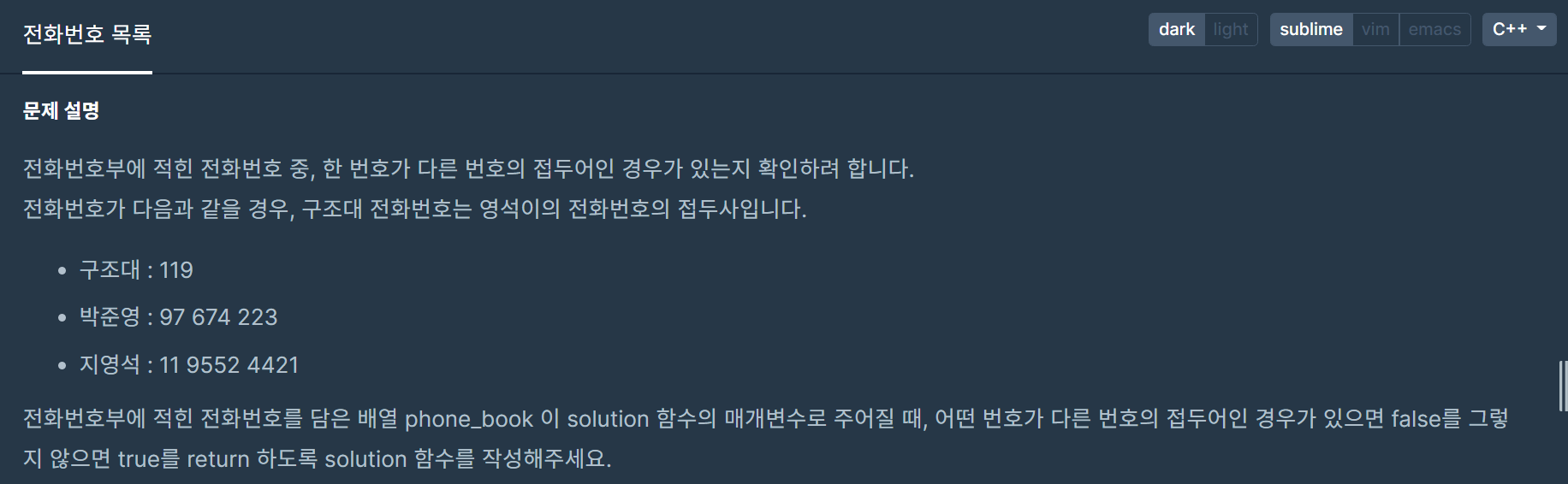
문제
풀이
-
해시를 이용한 풀이
1-1 phonebook을 정렬
1-2 단, 해시에 삽입하기 전에 문자를 하나씩 더해 문자열을 만들어가며 접두어가 존재하는지 확인
1-3 접두어가 존재하지 않으면 해시에 삽입간단하나 시간복잡도 측면에서 비효율적이다.
-
트라이 자료구조를 이용한 풀이
트라이 자료구조를 활용한 기본유형의 문제이다.
예전에 비슷한 유형의 문제를 풀어봐서 처음에 트라이 자료구조를 활용한 풀이를 생각했다.(*자세한 풀이는 코드를 확인)
시행착오
해시
풀이가 단순해 큰 어려움은 없었다.
트라이
처음에는 다음값이 존재하는지 확인하기 위한 방법으로 반복문을 이용해 체크하여 시간복잡도 측면에서 비효율적이었다.
좀 더 효율적인 방법을 고민하여 isnext변수를 두었고 훨씬 개선된 성능을 보였다.
코드
code1 해시 자료구조
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool solution(vector<string> phonebook) {
sort(phonebook.rbegin(), phonebook.rend());
unordered_map<string, int> m;
for (int i = 0; i < phonebook.size(); i++) {
string temp = "";
for (int j = 0; j < phonebook[i].size(); j++) {
temp += phonebook[i][j];
if (m[temp] != 0) return false;
}
m[temp]++;
}
return true;
}code2 트라이 자료구조
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
struct Trie {
bool finish;
bool isnext;
Trie* next[10];
Trie() : finish(false),isnext(false) {
memset(next, 0, sizeof(next));
}
~Trie() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
if (next[i]) delete next[i];
}
bool insert(const char* key) {
if (finish) {
return false;
}
if (*key == '\0') {
finish = true;
if (isnext) return false;
return true;
}
else {
int curr = *key - '0';
if (next[curr] == NULL) {
next[curr] = new Trie();
isnext = true;
}
return next[curr]->insert(key + 1);
}
}
};
bool solution(vector<string> phonebook) {
Trie* root = new Trie();
for (int i = 0; i < phonebook.size(); i++) {
char cstr[21];
strcpy(cstr, phonebook[i].c_str());
bool check = root->insert(cstr);
if (!check) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
후기
트라이 자료구조에 대한 복습기회였다.
https://eun-jeong.tistory.com/29
해당 링크에 트라이 자료구조에 관해 정리가 잘 되어있다.
