PersistContext를 사용해야 하는 이유
EntityManager 에 @Autowired 를 사용하여 의존관계를 주입받을 경우 다른 스레드들끼리 같은 EntityManager 를 공유하여 동시성 문제가 생길 수 있다고 합니다.(EntityManager 는 thread-safe 하지 않다)
그래서 PersistContext 를 이용하여 EntityManager 를 주입받게 되면 컨테이너가 EntityManger 가 1개의 스레드에 할당되도록 제한해준다고 합니다.
EntityManager 동시성 문제 - 김영한님의 답변
EntityManager - Baeldung
동시성 문제가 왜 발생하는가?
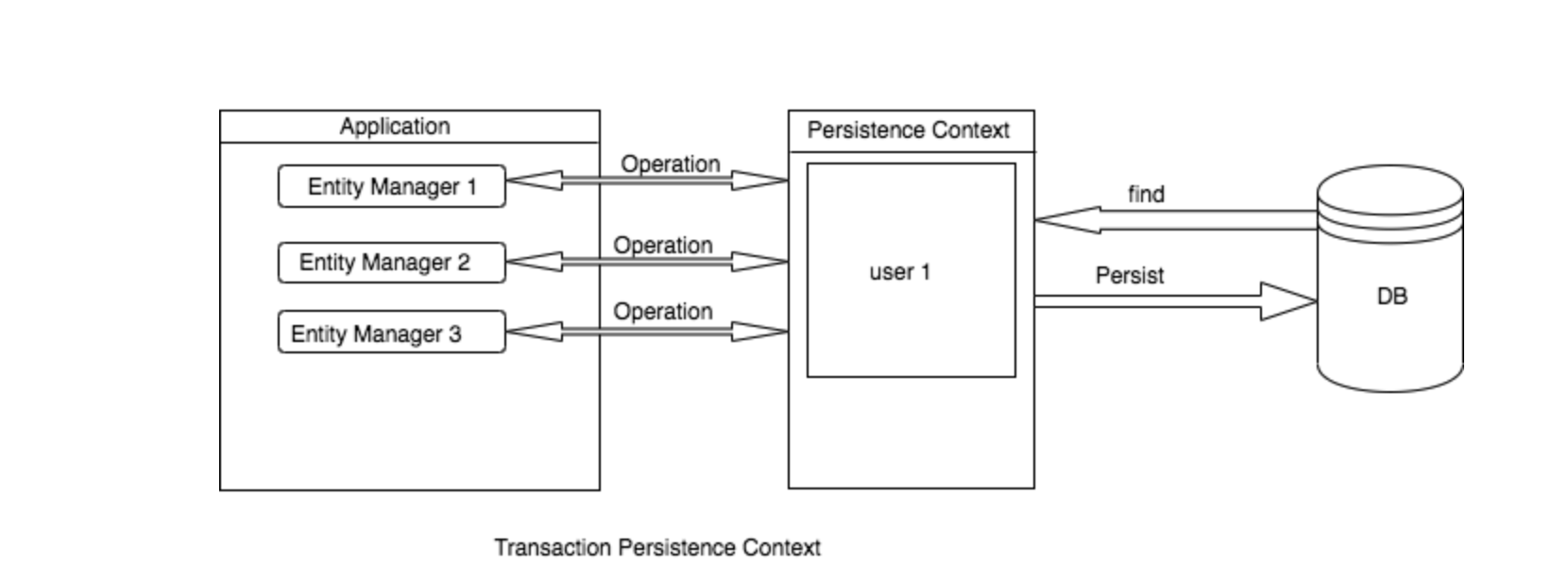
@Autowired 로 의존관계를 주입할 경우 싱글톤의 EntityManager 와 연결되어 위 그림과 같이 수행됩니다.
Persistence Context 영역을 공유하여 아직 반영되지 않은 값을 받을 수도 있고, 다른 스레드가 가져온 엔티티를 수정하는 경우가 생길 수 있습니다.
그래서 @PersistContext 을 이용하여 1개의 스레드마다 1개의 EntityManager 를 할당 받아 아래 그림과 같이 독립적으로 사용해야 합니다.
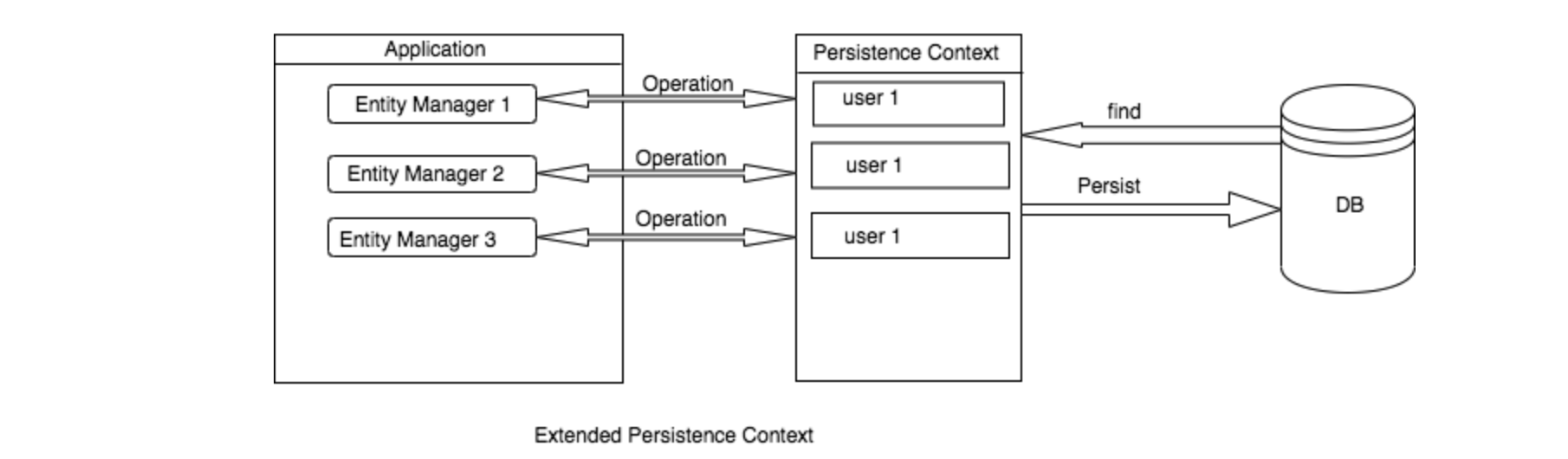
JPA/Hibernate Persistence Context - baeldung
@PersistContext는 어떻게 해결하는가?
@PersistContext 가 어떻게 해결하는지를 알아보기 위해 주입되는 코드를 살펴보겠습니다.
// AnnotationConfigUtils.java
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for Jakarta Annotations support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if ((jakartaAnnotationsPresent || jsr250Present) &&
!registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
}어노테이션 설정 처리를 해주는 메소드입니다. @autowired 설정과 JPA 어노테이션 설정도 해주는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
주석을 통해 JPA 설정은 PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 에서 해준다는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
코드를 계속 타고 가다보면 어노테이션이 있을 경우 메타정보로 PersistenceElement 클래스를 만들어 놓습니다.
// PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java
public PersistenceElement(Member member, AnnotatedElement ae, @Nullable PropertyDescriptor pd) {
super(member, pd);
PersistenceContext pc = ae.getAnnotation(PersistenceContext.class);
PersistenceUnit pu = ae.getAnnotation(PersistenceUnit.class);
Class<?> resourceType = EntityManager.class;
if (pc != null) {
if (pu != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Member may only be annotated with either " +
"@PersistenceContext or @PersistenceUnit, not both: " + member);
}
Properties properties = null;
PersistenceProperty[] pps = pc.properties();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(pps)) {
properties = new Properties();
for (PersistenceProperty pp : pps) {
properties.setProperty(pp.name(), pp.value());
}
}
this.unitName = pc.unitName();
this.type = pc.type();
this.synchronizedWithTransaction = SynchronizationType.SYNCHRONIZED.equals(pc.synchronization());
this.properties = properties;
}
else {
resourceType = EntityManagerFactory.class;
this.unitName = pu.unitName();
}
checkResourceType(resourceType);
}@PersistenceUnit 가 선언되어 있을 경우 EntityManagerFactory 를 넣어주고
@PersistenceContext 가 선언되어 있을 경우 EntityManager 를 만들어 줍니다.
// PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java
// 주입할 때 사용하는 메소드
@Override
protected Object getResourceToInject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName) {
// Resolves to EntityManagerFactory or EntityManager.
if (this.type != null) {
return (this.type == PersistenceContextType.EXTENDED ?
resolveExtendedEntityManager(target, requestingBeanName) :
resolveEntityManager(requestingBeanName));
}
else {
// OK, so we need an EntityManagerFactory...
return resolveEntityManagerFactory(requestingBeanName);
}
}// PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java
// 싱글톤 EntityManager를 찾거나 생성하여 반환하는 메소드
private EntityManager resolveEntityManager(@Nullable String requestingBeanName) {
// Obtain EntityManager reference from JNDI?
EntityManager em = getPersistenceContext(this.unitName, false);
if (em == null) {
// No pre-built EntityManager found -> build one based on factory.
// Obtain EntityManagerFactory from JNDI?
EntityManagerFactory emf = getPersistenceUnit(this.unitName);
if (emf == null) {
// Need to search for EntityManagerFactory beans.
emf = findEntityManagerFactory(this.unitName, requestingBeanName);
}
// Inject a shared transactional EntityManager proxy.
if (emf instanceof EntityManagerFactoryInfo emfInfo && emfInfo.getEntityManagerInterface() != null) {
// Create EntityManager based on the info's vendor-specific type
// (which might be more specific than the field's type).
em = SharedEntityManagerCreator.createSharedEntityManager(
emf, this.properties, this.synchronizedWithTransaction);
}
else {
// Create EntityManager based on the field's type.
em = SharedEntityManagerCreator.createSharedEntityManager(
emf, this.properties, this.synchronizedWithTransaction, getResourceType());
}
}
return em;
}// SharedEntityManagerCreator.java
// 메소드를 생성할 떄 사용하는 메소드, 프록시 인스턴스를 생성함
public static EntityManager createSharedEntityManager(EntityManagerFactory emf, @Nullable Map<?, ?> properties,
boolean synchronizedWithTransaction, Class<?>... entityManagerInterfaces) {
ClassLoader cl = null;
if (emf instanceof EntityManagerFactoryInfo emfInfo) {
cl = emfInfo.getBeanClassLoader();
}
Class<?>[] ifcs = new Class<?>[entityManagerInterfaces.length + 1];
System.arraycopy(entityManagerInterfaces, 0, ifcs, 0, entityManagerInterfaces.length);
ifcs[entityManagerInterfaces.length] = EntityManagerProxy.class;
return (EntityManager) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
(cl != null ? cl : SharedEntityManagerCreator.class.getClassLoader()),
ifcs, new SharedEntityManagerInvocationHandler(emf, properties, synchronizedWithTransaction));
}// EntityManagerFactoryUtils.java
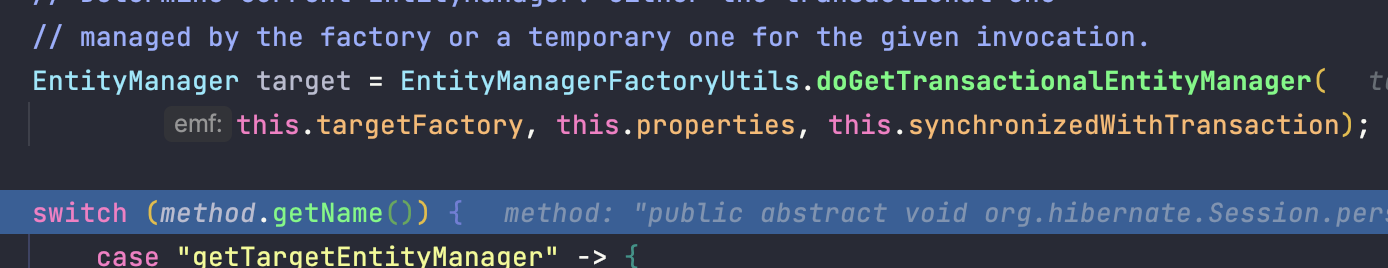
// 싱글톤 프록시 인스턴스의 invoke 메소드에서 트랜잭션에 연결된 실제 EntityManager를 얻을 떄 사용하는 메소드
@Nullable
public static EntityManager doGetTransactionalEntityManager(
EntityManagerFactory emf, @Nullable Map<?, ?> properties, boolean synchronizedWithTransaction)
throws PersistenceException {
Assert.notNull(emf, "No EntityManagerFactory specified");
EntityManagerHolder emHolder =
(EntityManagerHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(emf);
if (emHolder != null) {
if (synchronizedWithTransaction) {
if (!emHolder.isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive()) {
// Try to explicitly synchronize the EntityManager itself
// with an ongoing JTA transaction, if any.
try {
emHolder.getEntityManager().joinTransaction();
}
catch (TransactionRequiredException ex) {
logger.debug("Could not join transaction because none was actually active", ex);
}
}
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
Object transactionData = prepareTransaction(emHolder.getEntityManager(), emf);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(
new TransactionalEntityManagerSynchronization(emHolder, emf, transactionData, false));
emHolder.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
}
}
// Use holder's reference count to track synchronizedWithTransaction access.
// isOpen() check used below to find out about it.
emHolder.requested();
return emHolder.getEntityManager();
}
else {
// unsynchronized EntityManager demanded
if (emHolder.isTransactionActive() && !emHolder.isOpen()) {
if (!TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
return null;
}
// EntityManagerHolder with an active transaction coming from JpaTransactionManager,
// with no synchronized EntityManager having been requested by application code before.
// Unbind in order to register a new unsynchronized EntityManager instead.
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(emf);
}
else {
// Either a previously bound unsynchronized EntityManager, or the application
// has requested a synchronized EntityManager before and therefore upgraded
// this transaction's EntityManager to synchronized before.
return emHolder.getEntityManager();
}
}
}
else if (!TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
// Indicate that we can't obtain a transactional EntityManager.
return null;
}
// Create a new EntityManager for use within the current transaction.
logger.debug("Opening JPA EntityManager");
EntityManager em = null;
if (!synchronizedWithTransaction) {
try {
em = emf.createEntityManager(SynchronizationType.UNSYNCHRONIZED, properties);
}
catch (AbstractMethodError err) {
// JPA 2.1 API available but method not actually implemented in persistence provider:
// falling back to regular createEntityManager method.
}
}
if (em == null) {
em = (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(properties) ? emf.createEntityManager(properties) : emf.createEntityManager());
}
try {
// Use same EntityManager for further JPA operations within the transaction.
// Thread-bound object will get removed by synchronization at transaction completion.
emHolder = new EntityManagerHolder(em);
if (synchronizedWithTransaction) {
Object transactionData = prepareTransaction(em, emf);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(
new TransactionalEntityManagerSynchronization(emHolder, emf, transactionData, true));
emHolder.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
}
else {
// Unsynchronized - just scope it for the transaction, as demanded by the JPA 2.1 spec...
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(
new TransactionScopedEntityManagerSynchronization(emHolder, emf));
}
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(emf, emHolder);
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
// Unexpected exception from external delegation call -> close EntityManager and rethrow.
closeEntityManager(em);
throw ex;
}
return em;
}- 의존관계를 주입할 때 메타정보를 토대로 주입합니다. 이 때 실제
EntityManager가 아닌 공유 싱글톤 프록시 인스턴스를 반환합니다. - 공유할 싱글톤 프록시 인스턴스가 호출될 때
SharedEntityManagerInvocationHandler.invoke()가EntityManager인터페이스의 모든 메서드 호출을 처리합니다. (코드가 길어서 첨부는 생략하였습니다) SharedEntityManagerInvocationHandler.invoke()에서는EntityManagerFactoryUtils.doGetTransactionalEntityManager()메소드를 통해 현재 트랜잭션에 연결된 실제EntityManager인스턴스를 얻습니다.(가져오거나 생성합니다)EntityManagerFactoryUtils.doGetTransactionalEntityManager()메소드에서 현재 트랜잭션에 연결된EntityManager가 있다면 동기화시켜주고 없다면 새로운EntityManager를 생성해줍니다.
Spring에서 @PersistenceContext의 동작 원리 - Programming is Fun
프록시 클래스 - baeldung
SharedEntityManagerCreator - Spring docs
@PersistContext는 정말 트랜잭션 별로 다른 EntityManager를 사용하나?
코드를 통해 @PersistContext 어노테이션을 사용하는 경우 트랜잭션 별로 다른 EntityManager 를 사용하는 것을 확인했습니다.
실제 예제를 만들고 디버깅을 통해 확인한 내용이 맞는지 검증해보겠습니다.
예제
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.2.2'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.4'
}
group = 'com.example'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
java {
sourceCompatibility = '17'
}
configurations {
compileOnly {
extendsFrom annotationProcessor
}
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
// jpa
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
// h2
runtimeOnly 'com.h2database:h2'
// lombok
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
// test
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
tasks.named('test') {
useJUnitPlatform()
}@Entity
@Getter
@Setter
public class Memeber {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
}@Service
@Slf4j
public class MemberService {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
@Transactional
public Long save(String name) {
Memeber memeber = new Memeber();
memeber.setName(name);
// 디버깅 지점, 내부에서 어떤 엔티티 매니저를 통해 수행하는지 확인
entityManager.persist(memeber);
return memeber.getId();
}
}@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class EntitymanagerAutowiredApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private MemberService memberService;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EntitymanagerAutowiredApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
memberService.save("멤버 생성1");
memberService.save("멤버 생성2");
}
}
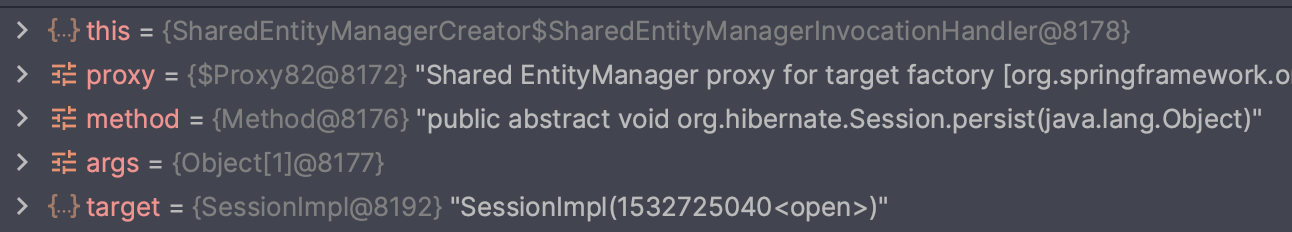
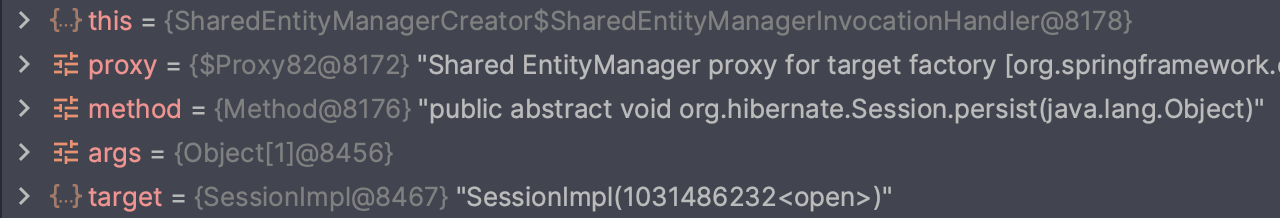
트랜잭션 별로 다른 EntityManager 가 사용되는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
@Autowired는 어떻게 동작하는가?
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MemberService {
@Autowired
private EntityManager entityManager;
@Transactional
public Long save(String name) {
Memeber memeber = new Memeber();
memeber.setName(name);
entityManager.persist(memeber);
return memeber.getId();
}
}의존관계 주입 어노테이션만 @Autowired 로 변경하여 @Autowired 로 주입했을 경우 동작 방식도 보도록 하겠습니다.


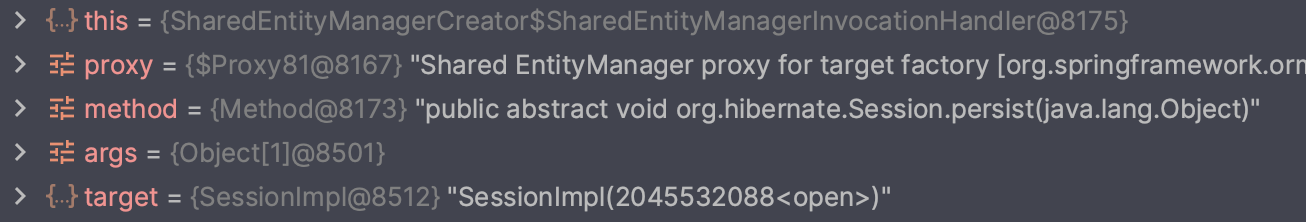
@Autowired 도 프록시 인스턴스를 주입받아 트랜잭션 별로 다른 EntityManager 를 사용합니다.
추측: 스프링 부트에서 EntityManager 빈이 아닌 프록시 빈을 주입해주는 것 같습니다.
결론
- JPA의
@PersistContext어노테이션을 사용할 경우EntityManager에 프록시 인스턴스를 주입시켜준다. - 프록시 인스턴스로 트랜잭션 별로 실제 다른
EntityManager를 사용하여 tread-safe하다. - 스프링 부트 환경에서는
@Autowired어노테이션을 통한 의존관계 주입시에서도EntityManger에 프록시 인스턴스를 주입시켜주는 것 같다. (추측) - 스프링 부트(3.2.2) 환경에서는
EntityManager에@Autowired를 사용하여도 tread-safe하다.
참조
자바 ORM 표준 JPA 프로그래밍 - 김영한
JPA/Hibernate Persistence Context - baeldung
