✅ 오늘 한 일
- Project BCA
📝 배운 것들
🏷️ 코루틴(IEnumerator)이 네트워크 요청이나 파일 로드에 적합하지 않은 이유
코루틴이 유니티에서 비동기 처리를 쉽게 해주긴 하지만, 네트워크 요청이나 파일 로딩 같은 작업에는 적합하지 않은 이유가 몇 가지 있어.
1. 네트워크 요청은 실패할 수 있음 (에러 핸들링이 어려움)
코루틴은 기본적으로 "에러 핸들링이 불편" 해.
IEnumerator GetData()
{
UnityWebRequest request = UnityWebRequest.Get("https://example.com/data");
yield return request.SendWebRequest();
if (request.result != UnityWebRequest.Result.Success)
{
Debug.LogError("네트워크 요청 실패: " + request.error);
}
else
{
Debug.Log("데이터 받음: " + request.downloadHandler.text);
}
}- 이 방식으로 네트워크 요청을 할 수 있지만, 예외(Exception)를 잡을 수 없음.
try-catch를 못 쓰고, if 문으로 하나하나 체크해야 함.- 즉, 네트워크 오류, 타임아웃 같은 걸 관리하기 어려움.
- 게다가 코루틴은 중단(
StopCoroutine())하면 내부적으로 실행 중이던 네트워크 요청이 죽어버림.
🚀 ✅ async/await 방식이면?
async Task<string> GetData()
{
using HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
try
{
string response = await client.GetStringAsync("https://example.com/data");
return response;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Debug.LogError("네트워크 요청 실패: " + e.Message);
return null;
}
}try-catch로 네트워크 오류를 깔끔하게 처리 가능.- 비동기적으로 실행되므로 멈추거나 끊길 위험이 없음.
- 여러 개의 네트워크 요청을 병렬로 처리하는 것도 쉬움.
2. 네트워크 요청은 CPU 연산이 아니라 I/O 바운드 작업임
코루틴은 유니티의 프레임 루프에서 동작하기 때문에, CPU 바운드 작업에는 괜찮지만 I/O 바운드 작업(파일 읽기, 네트워크 요청)에는 최적화되어 있지 않음.
- 코루틴(
yield return)은 기본적으로 다음 프레임까지 기다리는 방식이라,
→ 진짜 비동기 실행이 아니라 프레임 기반 실행. - 네트워크 요청은 CPU가 아니라 네트워크 I/O를 기다리는 작업이라서, Task 기반 비동기 방식(
async/await)이 훨씬 효율적임.
🚀 ✅ async/await이면?
async Task LoadData()
{
await Task.Delay(2000); // 비동기적으로 2초 기다림
Debug.Log("데이터 로드 완료!");
}Task.Delay(2000)은 프레임에 의존하지 않고 비동기적으로 실행됨.- 코루틴(
WaitForSeconds)은 프레임 단위라서 유니티의 메인 루프에 종속됨.
3. 파일 로딩도 마찬가지 (동기 I/O 문제)
코루틴으로 파일을 로드하려면 메인 스레드에서 실행되기 때문에, 큰 파일을 읽으면 프레임이 멈출 수도 있음.
반면 async/await를 사용하면, 백그라운드에서 처리할 수 있음.
🚨 코루틴으로 파일 읽기 → 메인 스레드가 멈출 수도 있음
IEnumerator LoadFile()
{
string path = Path.Combine(Application.persistentDataPath, "save.json");
string data = File.ReadAllText(path); // 동기적으로 파일 읽기 (문제 발생 가능)
yield return null;
Debug.Log("파일 로드 완료: " + data);
}File.ReadAllText()가 실행될 때, 큰 파일이면 게임이 멈출 수 있음.- 유니티는 기본적으로 메인 스레드에서 실행되므로, 동기 I/O 연산이 위험함.
✅ async/await로 해결 (백그라운드 스레드에서 실행)
async Task LoadFileAsync()
{
string path = Path.Combine(Application.persistentDataPath, "save.json");
if (File.Exists(path))
{
string data = await File.ReadAllTextAsync(path); // 비동기적으로 파일 읽기
Debug.Log("파일 로드 완료: " + data);
}
else
{
Debug.LogError("파일이 없음!");
}
}- 비동기 파일 로딩 (
File.ReadAllTextAsync())을 사용하면 메인 스레드가 멈추지 않음. - 유니티의
IEnumerator코루틴으로는 이런 걸 백그라운드에서 처리할 수 없음.
🚀 결론: 네트워크 & 파일 로드는 async/await가 더 적합!
| 작업 유형 | 코루틴 (IEnumerator) | async/await |
|---|---|---|
| 애니메이션, 연출, 타이머 | ✅ 사용 가능 | ❌ 필요 없음 |
| 네트워크 요청 (API 호출) | ⚠ 가능하지만 비효율적 | ✅ 최적화됨 |
| 파일 읽기/쓰기 | ⚠ 가능하지만 멈출 수도 있음 | ✅ 백그라운드 처리 가능 |
| 멀티스레딩 연산 (AI, 데이터 처리) | ❌ 안됨 | ✅ 가능 |
📌 정리하면...
- 코루틴은 "게임 루프와 관련된 비동기 작업" (애니메이션, 타이머 등)에 적합
- 네트워크 요청 & 파일 로딩 같은 I/O 작업에는
async/await이 더 효율적이고 안정적 - 멀티스레드에서 실행되는 연산이 필요하면
Task.Run()같은 걸 고려해야 함.
그래서 네트워크 요청 & 파일 로드에는 async/await 쓰는 게 정석! 🚀
🎮 Project BCA
좌표계 변환
처음 만들 때 유니티 좌표 (1,1)을 배열 (1,1)에 대응되도록 코드를 짜놨었는데,
유니티 좌표 (1,1)이 아니더라도 배열 (1,1)에 대응될 수 있도록 코드를 바꿔야 한다.
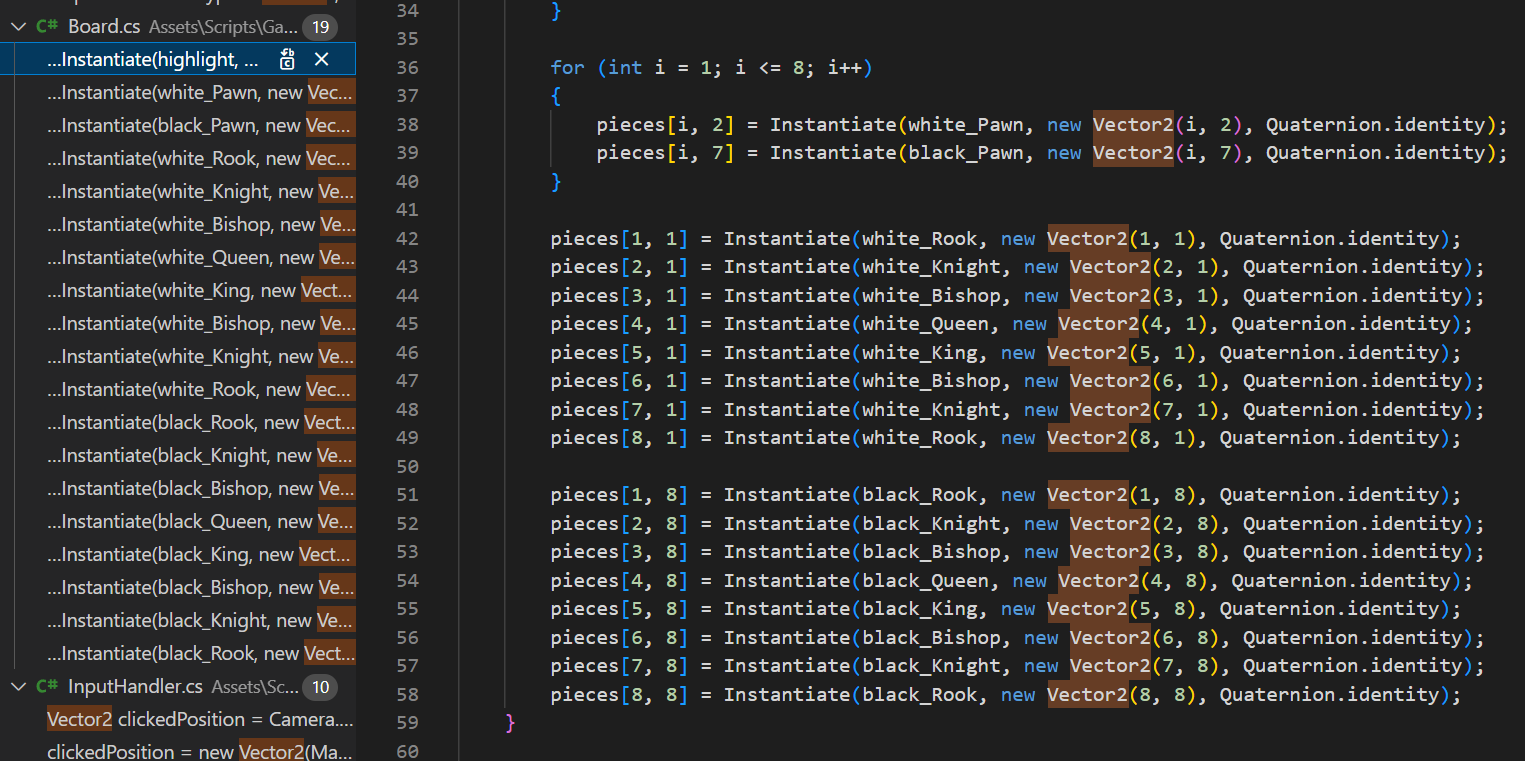
Vector2, transform.position으로 검색된 코드들 전부 바꿔주기
// 초기화 코드
public void SetBoard()
{
TILE_WIDTH_ORIGIN = board_object.transform.position.x;
TILE_HEIGHT_ORIGIN = board_object.transform.position.y;
SpriteRenderer board_sr = board_object.GetComponent<SpriteRenderer>();
TILE_DW = board_sr.bounds.size.x / 16;
TILE_DH = board_sr.bounds.size.y / 16;체스판은 8*8이니, 각 칸의 중심을 (2x - 1) * di 라고 두고
x를 칸으로, di를 board_width / 16 으로 두면 된다
/// <summary>
/// 가로 인덱스 x, 세로 인덱스 y에 해당하는 씬 위치 반환
/// </summary>
public Vector2 GridIdxToBoardPos((int, int) idx)
{
int x = idx.Item1;
int y = idx.Item2;
float x_pos = TILE_WIDTH_ORIGIN + (2 * x - 1) * TILE_DW;
float y_pos = TILE_HEIGHT_ORIGIN + (2 * y - 1) * TILE_DH;
return new Vector2(x_pos, y_pos);
}
/// <summary>
/// 씬에서의 위치 좌표에 해당하는 가로 인덱스 x, 세로 인덱스 y 반환
/// </summary>
public (int, int) BoardPosToGridIdx(Vector2 pos)
{
int x = (int)((pos.x - TILE_WIDTH_ORIGIN) / (2 * TILE_DW) + 1);
int y = (int)((pos.y - TILE_HEIGHT_ORIGIN) / (2 * TILE_DH) + 1);
return (x, y);
}
/// <summary>
/// 해당 오브젝트의 x 인덱스 반환
/// </summary>
public int PieceToGridX(GameObject piece)
{
return BoardPosToGridIdx(piece.transform.position).Item1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 해당 오브젝트의 y 인덱스 반환
/// </summary>
public int PieceToGridY(GameObject piece)
{
return BoardPosToGridIdx(piece.transform.position).Item2;
}
/// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 이 아래부터는 전부 그리드 인덱스 기반으로 작성된 함수들
/// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public bool IsIdxInBoard((int, int) idx)
{
return idx.Item1 >= 1 && idx.Item1 <= 8 && idx.Item2 >= 1 && idx.Item2 <= 8;
}기존 체계는 좌표 자체가 그리드라는 걸 가정하고 만든 거라
좌표 체계를 migration하는 과정에서 수많은 혼란이 야기됨.
이건 그리드 좌표인가 위치 좌표인가? 계속 헷갈림.
3분만 시간 더 써서 어떻게 할지 계획했으면 이렇게 쩔쩔매지 않아도 됐었을 것.
초반에 설계할 때 향후 많이 쓰일 부분이라면 최대한 확장성, 가독성 좋게 만들어야 한다는 교훈을 얻음.
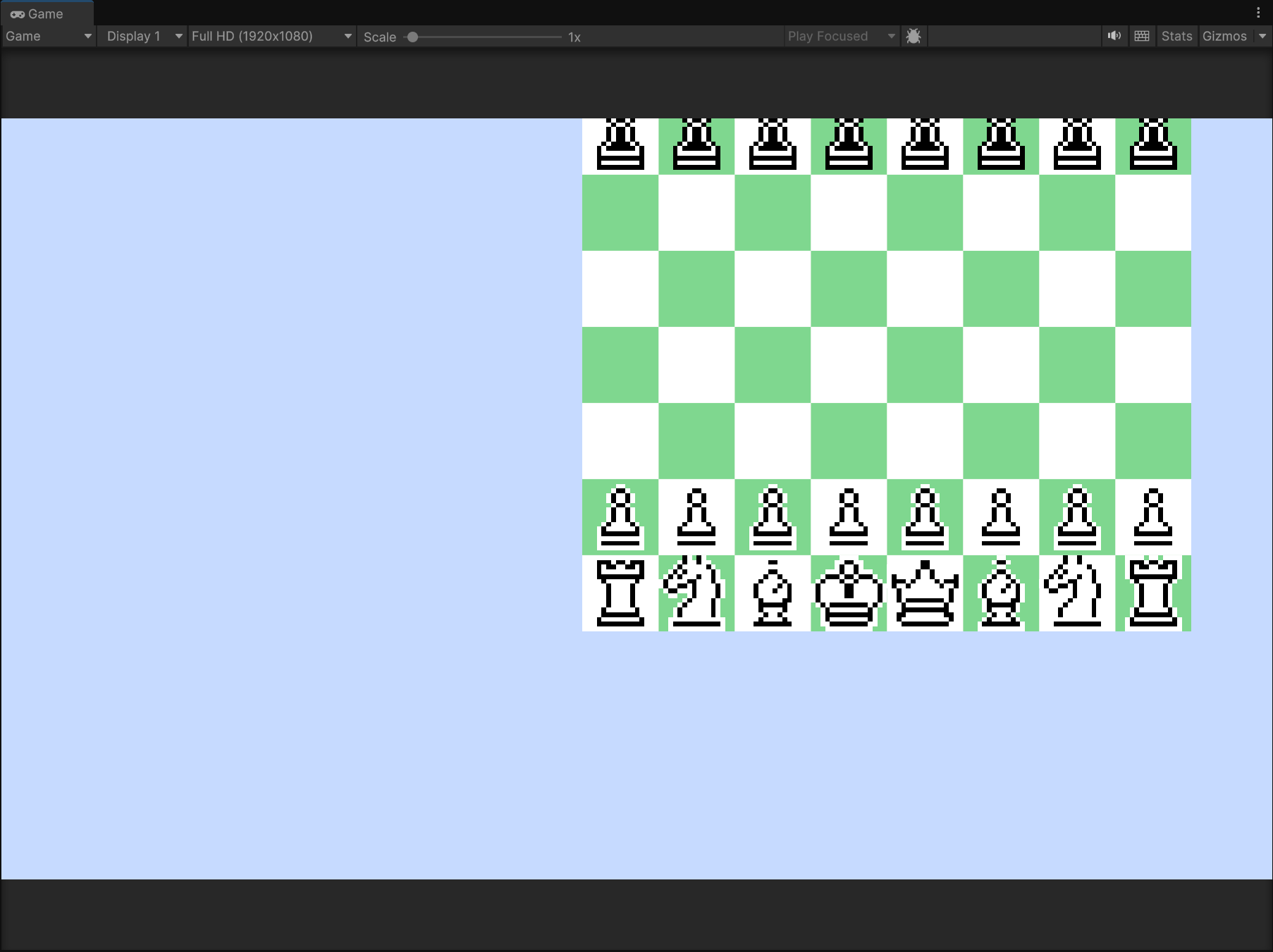
이제 보드의 위치를 바꿔도 해당 위치에서 기물들이 생성되고 게임도 정상적으로 돌아간다
좌표가 기물에 저장돼있는게 아니고 기물의 위치를 기반으로 그리드 인덱스를 추출해내는 거라
수 불법 판단 과정에서 비효율이 발생할 수 있는 점은 염려됨.
하지만 기물들이 이미 저장된 배열 + 기물 위치 2가지를 로직에 맞게 관리하는 것만으로 복잡했는데
기물에 그리드 인덱스까지 저장하면 복잡성이 더 올라갈 것 같아서 어쩔 수 없었음.
-> gpt한테 transform.position 접근하는거 비용 비싸냐고 물어봤는데 아니라고 하긴 함
AI Integration
- 비동기 출력 읽기: BeginOutputReadLine()와 BeginErrorReadLine()를 사용하여 Stockfish의 출력을 비동기적으로 읽습니다.
- 이벤트 핸들러 활용: OutputDataReceived와 ErrorDataReceived 이벤트에서 데이터를 받아옵니다.
- 메인 스레드로 데이터 전달: Unity의 메인 스레드에서 안전하게 데이터를 처리하기 위해 ConcurrentQueue(혹은 다른 쓰레드 안전한 방법)를 사용합니다.
- 주의점: 이벤트 핸들러는 별도 스레드에서 실행되므로, Unity 객체를 직접 수정하는 작업은 메인 스레드로 옮겨서 처리해야 합니다.
일반적으로 프로세스를 RedirectStandardOutput = true, RedirectStandardError = true로 설정하고,
StandardOutput과 StandardError 모두를 계속 읽어주지 않으면,
어느 한쪽이 꽉 차서 프로세스가 쓰레드를 멈추는 데드락(deadlock) 현상이 나타날 수 있습니다.
라고는 하는데, 이거 만들면서 비동기 때문에 게임 멈추는 문제에 헛소리를 내놓은 전적이 있어서 이것도 진짠지 의심스러워졌다.
- 스톡피시를 켜고 uci 보내고 uciok 받으면 ucinewgame 보낸다
- 플레이어가 착수하고 AI 턴으로 넘겨준다 (AI 턴엔 클릭이 막힌다)
- 플레이어가 착수한 걸 UCI 명령어로 바꾸고 스톡피시에 보낸다
- 스톡피시에서 응답이 오면 그거 기반으로 배열이랑 기물 위치 바꾼다
- 플레이어 턴으로 다시 넘어온다
stockfish에 수 넘겨줄 땐 이전 수를 다 포함해야 함.
position [fen <fenstring> | startpos ] moves <move1> .... <movei>
position: 수를 둘 거임[fen <fenstring> | startpos ]: fen이면 특정 보드 상태에서부터, startpos면 처음부터의 수를 둘거임moves <move1> .... <movei>: 플레이어와 AI가 착수했던 문자열 기록 + 이번 착수- 이전 수에서 이어지는게 아니라 새 게임 할거면 ucinewgame 보내야 함
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using UnityEngine;
public class AIManager : MonoBehaviour
{
private Process stockfish;
private StreamWriter input;
// 별도의 큐를 이용해 이벤트 핸들러에서 받은 메시지를 메인 스레드로 전달
private ConcurrentQueue<string> outputQueue = new ConcurrentQueue<string>();
private InputHandler inputHandler;
private string moves = " moves "; // 플레이어의 수를 기록하는 변수
void Start()
{
GameObject serviceLocator = GameObject.FindGameObjectWithTag("ServiceLocator");
inputHandler = serviceLocator.GetComponentInChildren<InputHandler>();
StartStockfish();
}
void StartStockfish()
{
stockfish = new Process();
stockfish.StartInfo.FileName = Path.Combine(Application.streamingAssetsPath, "stockfish/stockfish-windows-x86-64-avx2.exe");
stockfish.StartInfo.RedirectStandardInput = true;
stockfish.StartInfo.RedirectStandardOutput = true;
stockfish.StartInfo.RedirectStandardError = true;
stockfish.StartInfo.UseShellExecute = false;
stockfish.StartInfo.CreateNoWindow = true;
// 이벤트 핸들러 등록
stockfish.OutputDataReceived += StockfishOutputHandler;
stockfish.ErrorDataReceived += StockfishErrorHandler;
stockfish.Start();
input = stockfish.StandardInput;
// 비동기 읽기 시작
stockfish.BeginOutputReadLine();
stockfish.BeginErrorReadLine();
// UCI 프로토콜 초기화
input.WriteLine("uci");
input.Flush();
}
// StandardOutput에서 데이터가 들어올 때마다 호출됨
private void StockfishOutputHandler(object sendingProcess, DataReceivedEventArgs outLine)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(outLine.Data))
{
outputQueue.Enqueue(outLine.Data);
}
}
// StandardError에서 데이터가 들어올 때마다 호출됨
private void StockfishErrorHandler(object sendingProcess, DataReceivedEventArgs errLine)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(errLine.Data))
{
outputQueue.Enqueue(errLine.Data);
}
}
void Update()
{
// 메인 스레드에서 큐를 확인하고 처리
while (outputQueue.TryDequeue(out string response))
{
UnityEngine.Debug.Log("Stockfish 응답: " + response);
ProcessResponse(response);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// stockfish의 응답에 따라 다르게 처리
/// </summary>
void ProcessResponse(string response)
{
if (response.Contains("uciok"))
{
input.WriteLine("ucinewgame");
input.Flush();
UnityEngine.Debug.Log("uciok를 받았고, ucinewgame를 stockfish에게 보냈다.");
}
else if (response.StartsWith("bestmove"))
{
string bestMove = response.Split(' ')[1];
moves += " " + bestMove;
UnityEngine.Debug.Log("Stockfish가 선택한 수: " + bestMove);
SendAIMoveToGameManager(bestMove);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 플레이어의 착수를 Stockfish에게 전달
/// </summary>
public void SendPlayerMoveToStockfish(int x, int y, int mx, int my)
{
string playermove = GridToUCI(x, y, mx, my);
UnityEngine.Debug.Log("플레이어의 수 : " + playermove);
moves += " " + playermove;
input.WriteLine("position startpos" + moves);
input.Flush();
input.WriteLine("go depth 10");
input.Flush();
}
/// <summary>
/// Stockfish의 착수를 게임 매니저에게 전달
/// </summary>
void SendAIMoveToGameManager(string move)
{
(int x, int y) = StringToGrid(move.Substring(0, 2));
(int mx, int my) = StringToGrid(move.Substring(2, 2));
inputHandler.AIMoveTo(x, y, mx, my);
}
/// <summary>
/// UCI 프로토콜을 게임 내 그리드 좌표로 변환
/// </summary>
(int, int) StringToGrid(string move)
{
int x = move[0] - 'a' + 1;
int y = move[1] - '1' + 1;
return (x, y);
}
/// <summary>
/// 게임 내 그리드 좌표를 UCI 프로토콜로 변환
/// </summary>
string GridToUCI(int x, int y, int mx, int my)
{
return GridToString(x, y) + GridToString(mx, my);
}
/// <summary>
/// 게임 내 그리드 좌표를 UCI 프로토콜 문자열로 변환
/// </summary>
string GridToString(int x, int y)
{
char xChar = (char)('a' + x - 1);
char yChar = (char)('1' + y - 1);
return xChar.ToString() + yChar.ToString();
}
/// <summary>
/// 게임 종료 시 Stockfish 프로세스 종료
/// </summary>
void OnApplicationQuit()
{
if (stockfish != null)
{
try
{
if (!stockfish.HasExited)
{
stockfish.Kill();
}
stockfish.Dispose();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
UnityEngine.Debug.LogWarning("Stockfish 종료 중 오류 발생: " + e.Message);
}
}
}
}