✅ 한 것들
- 백준
- 프로그래머스
⚔️ 백준
- N과 M (2)
- N과 M (3)
- N과 M (4)
- N과 M (5)
- N과 M (6)
- N과 M (7)
- N과 M (8)
- N과 M (10)
- N과 M (11)
- N과 M (12)
1662 압축
#include"1662.h"
using namespace std;
typedef pair<char, int> pii;
typedef long long ll;
void B1662::Solution()
{
string s;
cin >> s;
stack<pii> st;
for (char c : s)
{
// 숫자나 괄호는 그냥 넣음
// 닫는 괄호 찾으면
// 스택 안에 왼쪽 괄호 찾을 때까지 꺼냄
// 왼쪽 괄호와 오른쪽 괄호 사이에 있는 수들의 개수를 집계하고
// 왼쪽 괄호 앞에 있는 값만큼 개수를 곱함
// 닫는 괄호 앞에 있는 수를 넣음
if (c == ')')
{
char tc;
ll count;
tie(tc, count) = st.top();
st.pop();
char lastN = tc;
ll total = 0;
while (tc != '(')
{
total += count;
tie(tc, count) = st.top();
st.pop();
}
// 왼쪽 괄호 앞에 있는 값을 꺼낸다
tie(tc, count) = st.top();
st.pop();
if (isdigit(lastN))
{
// 괄호가 아니라 숫자라면 스택에 최종 계산된 값을 넣는다
total *= tc - '0';
st.push({ lastN,total });
}
}
else
{
st.push({ c,1 });
}
}
ll total = 0;
while (!st.empty())
{
total += st.top().second;
st.pop();
}
cout << total;
}내 풀이
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
cin >> s;
stack<pair<int,int>> st; //시작 위치, 문자열 길이
st.push({-1, 0});
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s[i] == '(') {
st.top().second--;
st.push({i,0});
}
else if (s[i] == ')') {
int len = (s[st.top().first-1] - '0') * st.top().second;
st.pop();
st.top().second += len;
}
else
st.top().second++;
}
cout << st.top().second << endl;
return 0;
}남의 풀이
- 숫자 나오면 스택 맨 위의 데이터에 count 추가
- 왼쪽 괄호 나오면 K가 추가했던 count를 취소하고 새로운 데이터 추가
- 오른쪽 괄호 나오면 스택에 넣어놨던 데이터로 왼쪽 괄호 옆의 K에 접근하여 count와 곱한 뒤, 이전 top에 결과를 더함
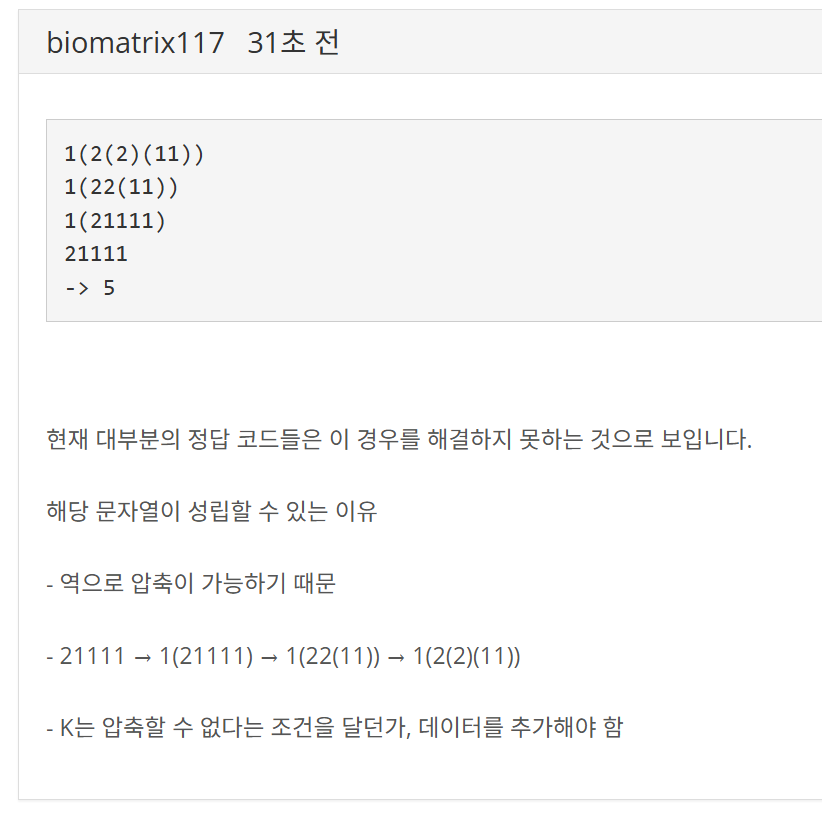
나는 이 테케 생각하고 짰는데, 이 사람은 아예 그 부분은 고려 안 하고 짠 것 같음. 근데 나도 이 테케 돌려보면 틀리긴 한다. 어차피 오래된 문제라 반영은 안되겠지만 만약 반영되면 2(132434)(242)(23)(34) 이런 것도 해결해야 해서 문제 난이도 떡상할듯.
N과 M (9)
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int N, M;
vector<int> table;
vector<int> seq;
map<int, int> cnt;
void pm(int remain)
{
if (remain == 0) {
for (int s : seq) cout << s << ' ';
cout << '\n';
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < table.size(); i++) {
if (cnt[table[i]] == 0) continue;
seq.push_back(table[i]);
cnt[table[i]]--;
pm(remain - 1);
seq.pop_back();
cnt[table[i]]++;
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> N >> M;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int temp;
cin >> temp;
bool alreadyE = false;
for (int t : table)
if (temp == t) alreadyE = true;
if(!alreadyE)
table.push_back(temp);
cnt[temp]++;
}
sort(table.begin(), table.end());
pm(M);
}- cnt 말고 count로 하면 map에 count 함수 있어서 오류
- 동일한 숫자가 여러 번 입력될 때 별개의 인덱스로 받아버리면 dfs로 생각했을 때 서로 다른 노드로 판단되므로 중복이 생김. cnt == 0인지로 조건 확인해야 한다.
if (find(table.begin(), table.end(), temp) == table.end())
table.push_back(temp);alreadyE 개선
DFS와 BFS
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int N, M, V;
map<int, vector<int>> edge;
vector<bool> visited;
void dfs(int node)
{
cout << node << ' ';
if (edge[node].empty()) return;
for (int to : edge[node]) {
if (visited[to]) continue;
visited[to] = true;
dfs(to);
// return을 여기에 넣어서 틀렸습니다 떴었음
// '어떤 정점에서' 방문 할 수 있는 점이 없는 경우 종료가 아니라
// '어떤 곳도' 방문 할 수 있는 점이 없는 경우 종료니까...
}
}
void bfs(int start)
{
visited = vector<bool>(N + 1, false);
queue<int> q;
q.push(start);
visited[start] = true;
while (!q.empty())
{
int node = q.front(); q.pop();
cout << node << ' ';
for (int nn : edge[node]) {
if (visited[nn]) continue;
visited[nn] = true;
q.push(nn);
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> N >> M >> V;
visited = vector<bool>(N+1, false);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
edge[a].push_back(b);
edge[b].push_back(a);
sort(edge[a].begin(), edge[a].end());
sort(edge[b].begin(), edge[b].end());
}
visited[V] = true;
dfs(V);
cout << '\n';
bfs(V);
}- 문제 조건 잘못 생각해서 dfs할 때 return 넣어버림
⚔️ 프로그래머스
뒤에 있는 큰 수 찾기
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
vector<int> solution(vector<int> numbers) {
// stack에 인덱스들 담는다
// 담을 때 안에 있는 인덱스들 확인하면서
// 자기보다 작은 놈이면 answer의 해당 인덱스에 자기 인덱스 박아버림
// 뽑았으면 계속 뽑고, 못 뽑았으면 끝
vector<int> answer = vector<int>(numbers.size(),-1);
stack<int> idxST;
for(int i=0; i<numbers.size(); i++) {
while(!idxST.empty()) {
int topIdx = idxST.top();
if(numbers[topIdx] < numbers[i]) {
answer[topIdx] = numbers[i];
idxST.pop();
}
else break;
}
idxST.push(i);
}
return answer;
}