✅ 한 것들
- 윤성우의 열혈 TCP/IP 소켓 프로그래밍
- 프로그래머스
📖 윤성우의 열혈 TCP/IP 소켓 프로그래밍
10-3 시그널 핸들링
시그널 핸들링: signal()로 자식이 종료되면 실행할 함수를 운영체제에 등록
시그널과 signal 함수
signal()
- 매개변수 :
int signo,void(*func)(int) - 반환형 : 매개변수가 int고 반환형이 void인 함수 포인터
- int로 특정 상황에 대한 정보를, 함수 포인터로 특정 상황에 호출될 함수 포인터 전달
- SIGARLM : alarm()으로 등록된 시간이 지난 상황
- SIGINT : CTRL+C가 입력된 상황
- SIGCHLD : 자식 프로세스가 종료된 상황
- 예시 : signal(SIGCHLD, mychild);
alarm()
- 지정한 시간 이후 SIGALRM 시그널 발생
- 0을 인자로 전달하면 이전에 설정된 SIGALRM 시그널 예약 취소
- alarm()으로 예약만 해두고 signal()로 함수 호출 지정 안 하면 프로세스 그냥 종료됨
void timeout(int sig)
{
if(sig==SIGALRM)
puts("Time out!");
alarm(2);
}
void keycontrol(int sig)
{
if(sig==SIGINT)
puts("CTRL+C pressed");
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i;
signal(SIGALRM, timeout);
signal(SIGINT, keycontrol);
alarm(2);
for(i=0; i<3; i++)
{
puts("wait...");
sleep(100);
}
return 0;
}- 100초를 3번, 300초를 기다리지 않고 10초 이내에 종료된다
- alarm()이 프로세스를 깨운 뒤에 다시 재워주진 않기 때문이다
- CTRL+C를 누르면 더 빨리 끝난다
sigaction 함수를 이용한 시그널 핸들링
sigaction()
- signal() 대체 가능
- signal()과 달리 운영체제 별 동작 방식에 차이가 없다
- 그래서 대부분 sigaction() 쓴다
struct sigaction
{
void (*sa_handler)(int);
sigset_t sa_mask;
int sa_flags;
}sigaction() 호출하려면 sigaction이라는 구조체 선언 및 초기화해야 함
- sa_handler에 시그널 핸들러 함수 포인터 지정
- sa_mask는 모든 비트를 0으로 초기화
- sa_flags는 0으로 초기화
- sa_mask와 sa_flag는 시그널 관련 옵션 및 특성 지정에 사용됨
void timeout(int sig)
{
if(sig==SIGALRM)
puts("Time out!");
alarm(2);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i;
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler=timeout;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
act.sa_flags=0;
sigaction(SIGALRM, &act, 0);
alarm(2);
for(i=0; i<3; i++)
{
puts("wait...");
sleep(100);
}
return 0;
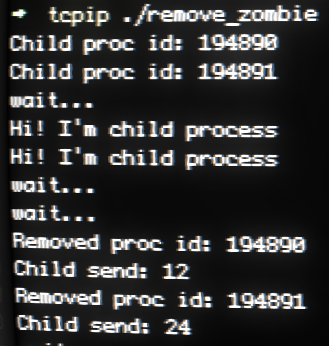
}시그널 핸들링을 통한 좀비 프로세스의 소멸
void read_childproc(int sig)
{
int status;
pid_t id=waitpid(-1, &status, WNOHANG);
if(WIFEXITED(status))
{
printf("Removed proc id: %d \n", id);
printf("Child send: %d \n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pid_t pid;
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler=read_childproc;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
act.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction(SIGCHLD, &act, 0);
pid=fork();
if(pid==0) /* 자식 프로세스 실행 영역 */
{
puts("Hi! I'm child process");
sleep(10);
return 12;
}
else /* 부모 프로세스 실행 영역 */
{
printf("Child proc id: %d \n", pid);
pid=fork();
if(pid==0) /* 또 다른 자식 프로세스 실행 영역 */
{
puts("Hi! I'm child process");
sleep(10);
exit(24);
}
else
{
int i;
printf("Child proc id: %d \n", pid);
for(i=0; i<5; i++)
{
puts("wait...");
sleep(5);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
⚔️ 프로그래머스
리틀 프렌즈 사천성
string solution(int m, int n, vector<string> board) {
string answer = "";
// 시작
// 전체를 훑는다
// 흰 칸은 전부 visited 처리
// 바로 짝이 연결되는 문자들은 우선순위 큐에 넣고 visited 처리
// 흰 칸에 노출된 문자는 알파벳 배열에 기록한 뒤 visited 처리
// 제거 시도
// 알파벳 배열을 훑으며 두번째 배열이 차 있으면 제거 시도한다
// (하우, 우하 두 방향 시도)
// 제거가 가능하다면 우선순위 큐에 넣는다
// 우선순위 큐에서 하나를 꺼내고 제거 가능한지 확인한다.
// 제거 가능 여부 확인 중 벽을 만났다면 바로 IMPOSSIBLE
// 추가 탐색
// 우선순위 큐에서 하나 뺀 후에 제거한다
// 제거 시 해당 문자의 알파벳 배열 값은 초기화한다
// 제거된 문자 두개와 붙어있고 visited하지 않은 타일들을 알파벳 배열에 기록한다
// 알파벳 배열을 다시 훑으며 연결이 가능한 값이 있는지 확인한다
// 종료
// 우선순위 큐가 비었으면 while문을 종료한다
// 알파벳 배열을 확인하고, 아직 값이 남아있다면 IMPOSSIBLE
vvp alpbt = vvp(26, vp(2, {-1,-1}));
vvb visited = vvb(m,vb(n));
vi diri = {0,0,1,-1};
vi dirj = {1,-1,0,0};
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
{
if(visited[i][j]) continue;
char b = board[i][j];
if(b=='.' || b=='*')
{
visited[i][j] = true;
}
else
{
for(int k=0; k<4; k++)
{
int newi = i+diri[k];
int newj = j+dirj[k];
if(newi<0||m<=newi||newj<0||n<=newj) continue;
int idx = b-'A';
if(board[newi][newj] == b)
{
alpbt[idx][0] = {i,j};
alpbt[idx][1] = {newi, newj};
visited[i][j]==true;
visited[newi][newj]=true;
pq.push(idx);
break;
}
else if (board[newi][newj] == '.')
{
if(alpbt[idx][0].first == -1)
{
}
}
}
}
}
}
return answer;
}코드가 말도 안되게 길어지길래 정답을 봤더니
내 코드는 과최적화를 하고 있었다.
타일들 기록해두고 계속 순회하면서 제거 가능한지만 보면 됐다.
그럼 시간 복잡도는 O((알파벳개수^2*(m+n)) 라서, 충분히 가능
배열도 알파벳을 인덱스로 그대로 사용하고, 순서대로 훑으니까 우선순위 큐로 억지 정렬 해줄 필요도 없다
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef vector<pii> vp;
typedef vector<vp> vvp;
bool HorizontalEmpty(int li, int hi, int j, vector<string>& board, char tileC)
{
for(int i=li; i<=hi; i++)
{
char b = board[i][j];
if(b!='.'&&b!=tileC) return false;
}
return true;
}
bool VerticalEmpty(int i, int lj, int hj, vector<string>& board, char tileC)
{
for(int j=lj; j<=hj; j++)
{
char b = board[i][j];
if(b!='.'&&b!=tileC) return false;
}
return true;
}
bool CanPop(pii t1, pii t2, vector<string>& board)
{
int t1i, t1j, t2i, t2j;
tie(t1i, t1j) = t1;
tie(t2i, t2j) = t2;
char tileC = board[t1i][t1j];
bool f1 = t1i <= t2i;
bool f2 = t1j <= t2j;
int li, hi, lj, hj;
li = f1 ? t1i : t2i;
hi = f1 ? t2i : t1i;
lj = f2 ? t1j : t2j;
hj = f2 ? t2j : t1j;
bool leftEmpty = VerticalEmpty(li,lj,hj,board,tileC);
bool rightEmpty = VerticalEmpty(hi,lj,hj,board,tileC);
bool downEmpty = HorizontalEmpty(li,hi,lj,board,tileC);
bool topEmpty = HorizontalEmpty(li,hi,hj,board,tileC);
if((f1&&f2) || (!f1&&!f2)) // 좌상 대각선
{
// 좌+상이 비었거나, 우+하가 비었거나
if(leftEmpty&&topEmpty) return true;
if(rightEmpty&&downEmpty) return true;
}
else // 우하 대각선
{
// 좌+하가 비었거나, 우+상이 비었거나
if(leftEmpty&&downEmpty) return true;
if(rightEmpty&&topEmpty) return true;
}
return false;
}
// 전역 변수를 정의할 경우 함수 내에 초기화 코드를 꼭 작성해주세요.
string solution(int m, int n, vector<string> board) {
string answer = "";
vvp tiles = vvp(26,vp());
int idx = 0;
// 타일을 전부 순회하면서 vvp에 정보를 기록해둔다
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
{
char b=board[i][j];
if(b!='.'&&b!='*')
{
tiles[b-'A'].push_back({i,j});
idx++;
}
}
}
// 알파벳을 계속 훑으면서, 터진게 있는지 확인
// 터졌다면 vvp를 초기화시키고 터진 char 반환
// 아무것도 안 터졌으면 종료
// 종료됐을 때 cnt!=0이면 IMPOSSIBLE 출력, cnt면 이제까지 모았던 char 출력
bool explosion = true;
while(explosion)
{
explosion = false;
for(int i=0; i<size(tiles); i++)
{
if(size(tiles[i])==0) continue;
int t1i, t1j, t2i, t2j;
tie(t1i, t1j) = tiles[i][0];
tie(t2i, t2j) = tiles[i][1];
if(CanPop(tiles[i][0],tiles[i][1],board))
{
explosion = true;
answer+=board[t1i][t1j];
board[t1i][t1j] = '.';
board[t2i][t2j] = '.';
tiles[i]=vp();
idx-=2;
break;
}
}
}
cout << answer;
if(idx==0) return answer;
else return "IMPOSSIBLE";
}실수
- idxMap으로 억지 최적화 하다가 알파벳 순서대로 정렬 놓침. 어차피 continue하면 나머지 연산 안 해서 거의 의미도 없으니 알파벳 범위 매번 전부 순회해줘도 괜찮다.
