This series will be followed a more advanced series in mathematical statistics which I'm still getting the hang of!
This post is meant to be a refresher on the topic!
If this is your first time with these topics, please checkout more thorough materials.
Hypothesis Testing
Terminology
Hypothesis : A statement on something we are trying to investigate. It's normally a statement that is based on a belief about the population.
Null Hypothesis : The originial statement. The statement about the population we want to test.
Alternative Hypothesis : The opposite of the null hypothesis.
Type I Error : Thee probability of rejecting the null hypothesis although it is true. If we say tht the possibility of rejecting H0 is then type I error is .
Type II Error : The probability of accepting the H0 despite the fact that it is wrong.
P-Value : The probability that the H0 will be true. It is a number between 0 ~ 1.
Two-side Test v.s. One-side Test
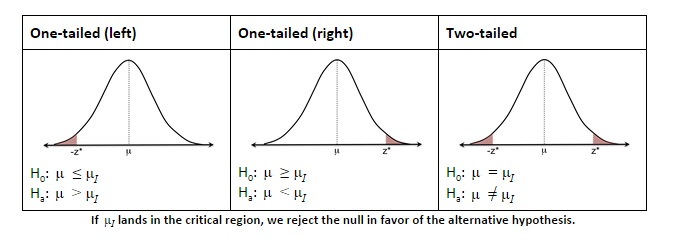
| Two-tailed test | Left-tailed test | Right-tailed test | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sign in rejection region | < | > |
One Sample Hypothesis Test
Assumptions about the population mean - population variance is KNOWN
If we know the population variance we can utilize the regardless of the size of the population.
,
a) Reject
b) Reject
c) Reject
Otherwise we FAIL to reject
Assumptions about the population mean - the population variance is UNKNOWN
, ~
The T-distribution becomes similar to a normal distribution as the degree of freedom increases
Assumptions about the population proportion
Remember that the sampling distribution of has a mean of and a standard deviation of