동적계획법 (Dynamic Programming)
DP는 복잡한 문제를 간단한 여러 개의 문제로 나누어 푸는 방법이다.
DP 사용 방법
정답을 구한 작은 문제의 답은 어딘가에 저장해 놓고 그 보다 큰 문제를 풀어나갈 때, 똑같은 작은 문제가 나타나면 앞서 메모한 작은 문제에 대한 결과값을 이용하는 것이다.
조건
- 작은 문제가 반복이 일어나는 경우
- 같은 문제는 구할 때마다 정답이 같을 경우
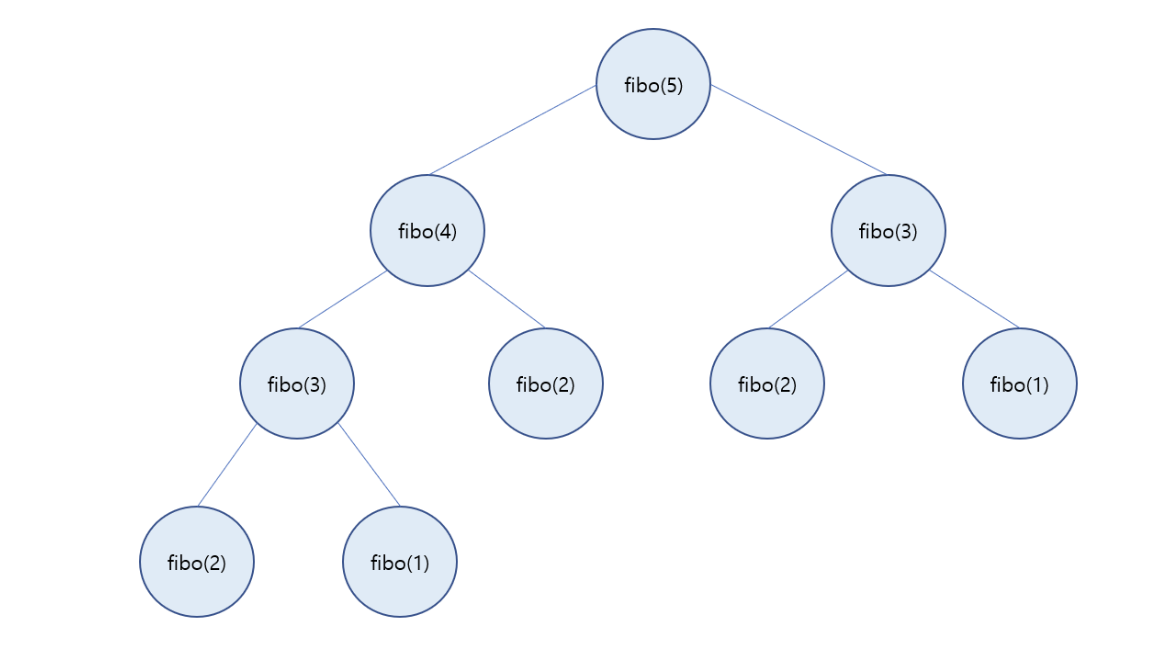
예시) 피보나치 함수
재귀 사용
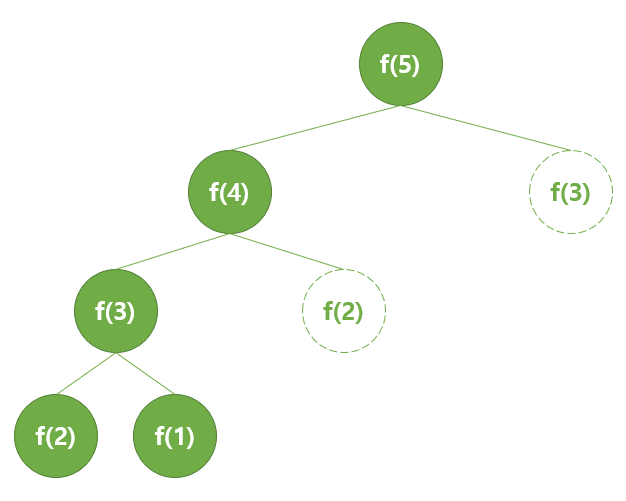
DP 사용
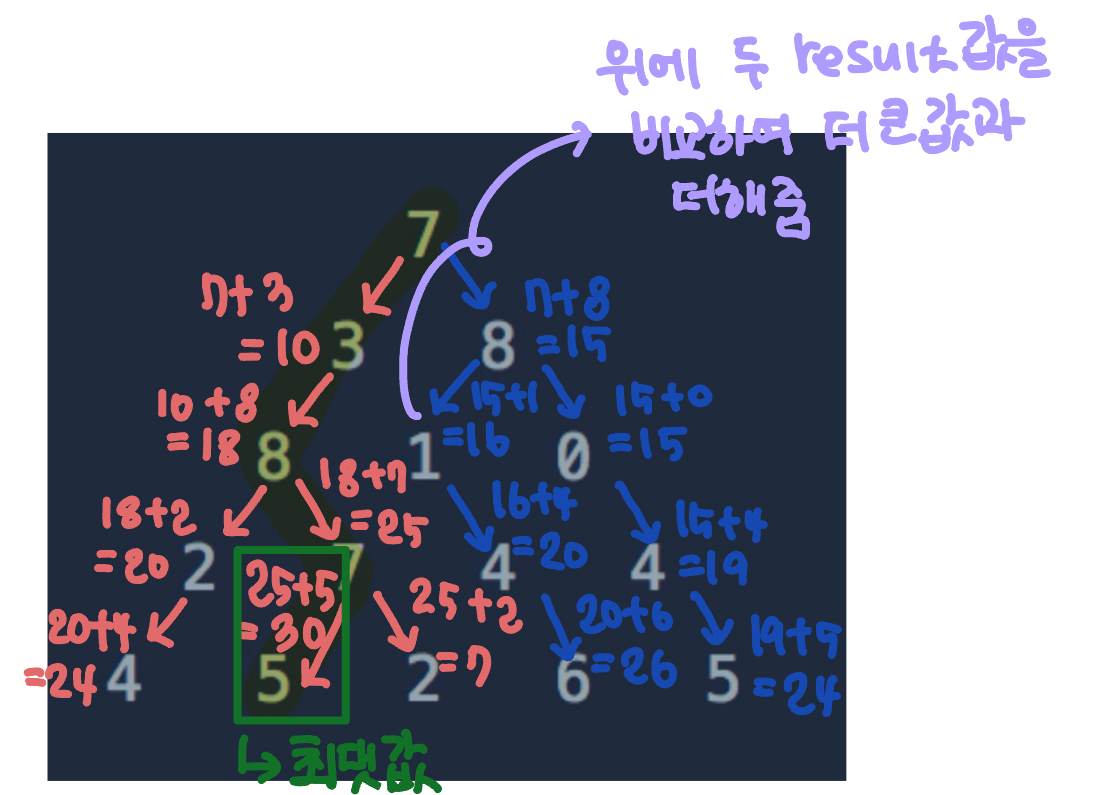
알고리즘 생각흐름
2차원 result 배열을 하나 더 만들어주고 거기까지 도달할 때의 최댓값을 정해주었다.
그리고 배열의 마지막 행만 sort로 내림차순으로 정렬하여 최댓값을 answer에 저장하여 구해주었다.
코드
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int solution(vector<vector<int>> triangle){
int answer = 0;
vector<vector<int>> result(triangle.size());
result[0].push_back(triangle[0][0]);
for(int i=1;i<triangle.size();i++){
for(int j=0;j<triangle[i].size();j++){
if(j == 0){
result[i].push_back(triangle[i][j] + result[i-1][j]);
} else if(j == triangle[i].size()-1){
result[i].push_back(triangle[i][j] + result[i-1][j-1]);
} else{
result[i].push_back(max(result[i-1][j-1],result[i-1][j]) + triangle[i][j]);
}
}
}
sort(result[triangle.size()-1].begin(),result[triangle.size()-1].end(),greater<>());
answer = result[triangle.size()-1][0];
return answer;
}
int main(void){
vector<vector<int>> triangle = {{7}, {3, 8}, {8, 1, 0}, {2, 7, 4, 4}, {4, 5, 2, 6, 5}};
int s = solution(triangle);
cout<<s<<'\n';
}