Spring DI(Dependency Injection)
DI?
DI란 Dependency Injection 으로 의존성 주입을 의미한다. IoC와 같이 Spring의 주요 개념 중 하나로 Spring에게 객체의 생성 뿐 아니라 dependency관리 까지 맡겨 application의 결합도를 낮추는 방법이다. 편하다
Spring에서 DI를 활용하는 방법은 세가지가 있는데 setter injection, field injection 그리고 constructor injection이다. 결론부터 말하자면, Spring에서는 Constructor Injection을 사용할 것을 권장한다. IntelliJ 에서는 field injection을 사용하지 않는다는 inspection을 띄웠었다고 한다. 이제는 아닌것 같다. 내 설정이 잘못된건가
왜 constructor injection을 권장하며, setter와 field injection의 문제점이 무엇인지 알아보겠다
Setter Injection
우선 setter injection은 말 그대로 setter를 통해 의존성을 주입하는 것이다.
@Component
public class MemberController {
private MemberService memberService;
@Autowired
public void setMemberService(MemberService memberSerivce) {
this.memberService = memberService;
}
}위 코드와 같이 field를 선언하고 setter method를 작성한 후 @Autowired 어노테이션을 추가하면 된다.
이 방식의 가장 큰 문제점은, public한 setter method를 생성해야 하며, 쉽게 변경될 수 있다는 것이다.
Field Injection
setter injection이 field가 쉽게 변경될 수 있는 문제점을 field injection을 통해 해결하고자 했다. 아마도...? GPT 말로는 Spring 2.5에서 등장했다고 한다
@Component
public class MemberController {
@Autowired
private MemberService memberService;
}위 코드와 같이 field를 선언하고 setter method를 작성하는 것이 아닌, field 앞에 @Autowired 어노테이션을 작성해주면, Spring이 해당 bean(객체)을 주입해준다. Public한 setter를 작성하지 않지만, Spring이 bean을 주입한다는 것은 spring이 객체의 field를 변경한다는 것이고, 이는 결국 개발자도 field를 변경할 수 있다는 뜻인데 어떻게 setter의 단점을 보완하는 것인지 의문이 들었다.
private field 변경
Java에서 private field를 변경하는 방법은 setter 메소드를 작성하는 것 뿐만 존재하는 것이 아니다. Java의 reflection을 통해 private field를 변경할 수 있다. getClass()를 통해 class 정보를 얻고, getDeclaredField()를 통해 class의 field 정보를 얻을 수 있으며, setAccessible(true)과 set()을 통해 field의 값을 변경할 수 있다. Java의 reflection을 통해 객체의 field를 변경하는 코드는 아래와 같이 구현할 수 있다.
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class ClassTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConstTest constTest = new ConstTest();
System.out.println(constTest.getA());
for(Field field : constTest.getClass().getDeclaredFields()) {
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(constTest, new Integer(3));
} catch(IllegalAccessException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
System.out.println(constTest.getA());
}
}위 코드를 통해 ConstTest class의 private 필드인 a의 값을 변경할 수 있다.
Spring Field Injection 방식
아마 Spring 또한 이러한 방식으로 field injection을 수행할 것이라고 생각했다. 그래도 확인은 해봐야 하니까 Spring의 코드를 뜯어보고자 했다. Spring boot 프로젝트에서 시작점은 main 메소드의 SpringApplication.run()이다. 여기부터 시작해서 하나 하나 뜯어보고자 했지만 ... 너무 많다 실패했다. 그래도 이후에 조금 더 진행해서 포스트를 남겨보겠다.
결론 부터 말하자면 reflection을 이용하는 것이 맞는것 같다(아닐수도 있으니까...). Spring의 org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 소스 코드 중 AutowiredFieldElement class에 내용을 찾아보면 아래와 같은 코드를 발견할 수 있다.
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);위 코드와 유사하다. 그래도 직접 봐야하니 해당 부분에 breakpoint를 걸어두고 Spring을 실행 해봤다. Debug 모드에서 method stack을 보니 직접 찾으려면 한참 걸렸을 것 같더라.
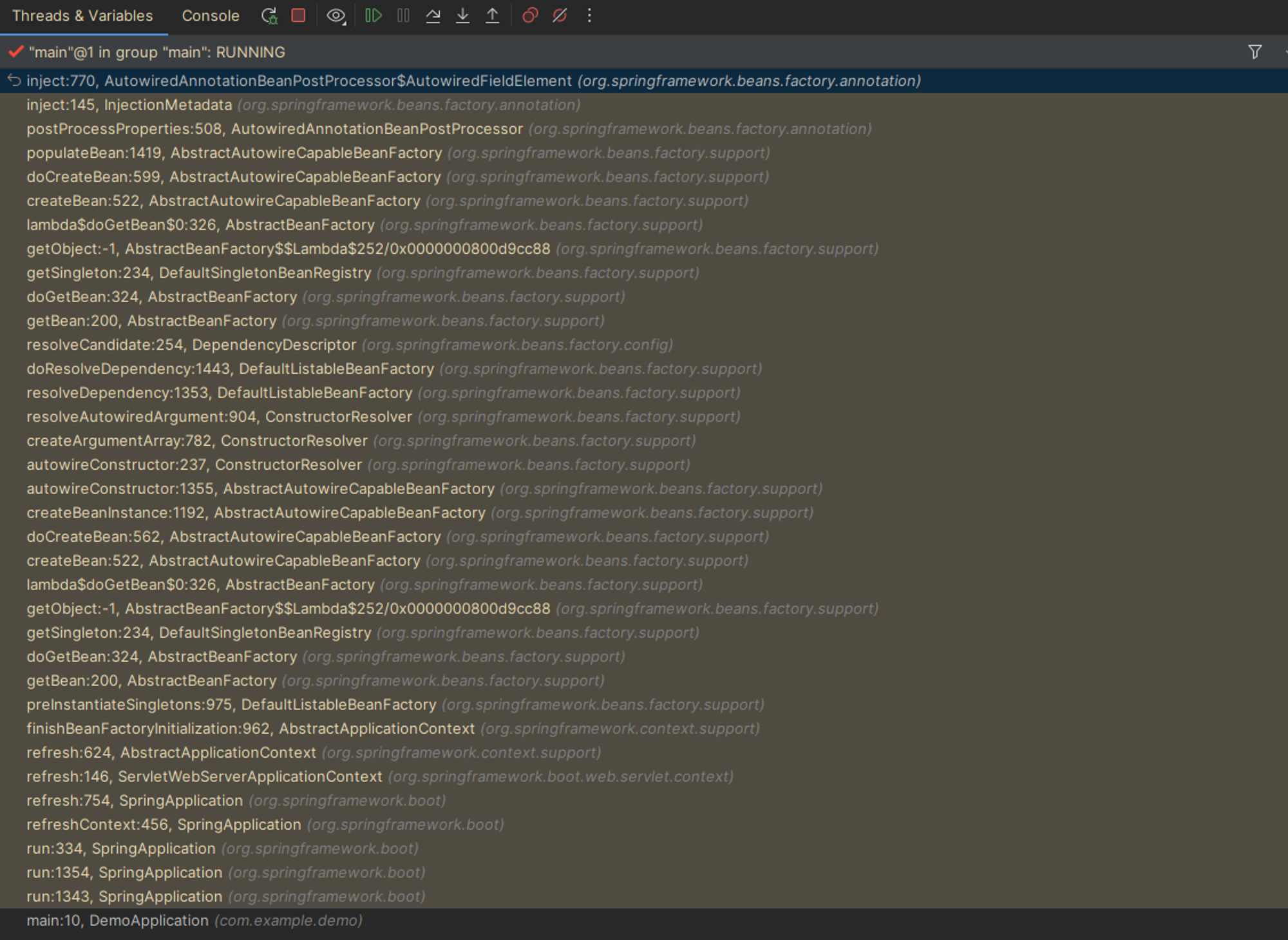
이걸 어떻게 찾냐
무튼 코드를 보면 inject 메소드에서 bean은 field injection이 필요한 객체이며, value는 해당 객체에 주입할 객체(bean)이다. inject 메소드 코드는 아래에 첨부하겠다.
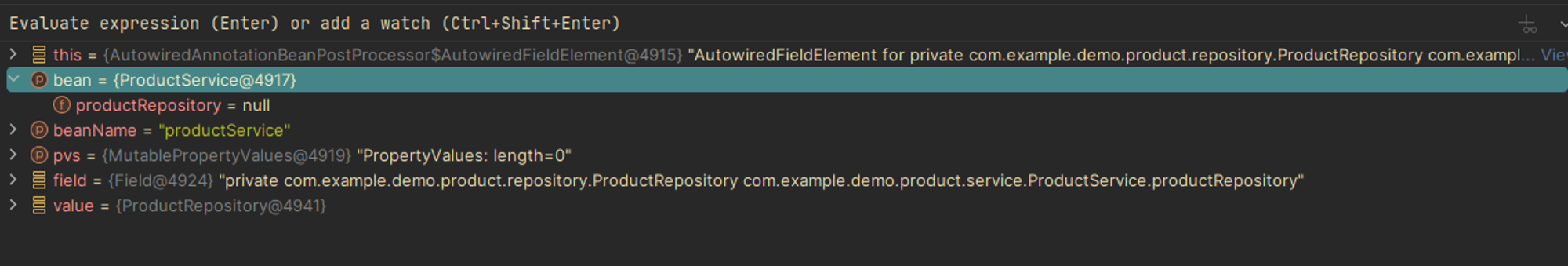
method 코드 전문
private class AutowiredFieldElement extends AutowiredElement {
private volatile boolean cached;
@Nullable
private volatile Object cachedFieldValue;
public AutowiredFieldElement(Field field, boolean required) {
super(field, (PropertyDescriptor)null, required);
}
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field)this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
try {
value = AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.resolveCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
} catch (BeansException var7) {
this.cached = false;
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.logger.debug("Failed to resolve cached argument", var7);
value = this.resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);
}
} else {
value = this.resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);
}
if (value != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
}Setter vs. Field
위 코드를 확인하고 든 의문점은 그럼 결국 개발자가 field의 값을 reflection을 통해 수정할 수 있는데, Setter injection과 field injection의 차이가 무엇인가? 였다. 굳이 field injection이라는 방식을 만들어야 했는지, 코드가 간결해지는 것 말고도 다른 이점이 있는지 의문이 생겼다.
확실한 답은 spring 개발자에게 물어보지 않는 이상 정확한 답을 얻을 수는 없지만(window의 host 파일에 localhost가 사라진 이유처럼), 감히 추측을 하자면 injection 방식을 개발자에서 온전히 Spring으로 옮긴것 아닐까 싶다. 그냥 의미 차이 같은 느낌이다
Java의 reflection을 통해 private field에 접근할 수 있다고 해서 reflection이 OOP의 Encapsulation을 위반한다고 할 수 있을까? 아니라고 생각한다. Reflection은 하나의 도구일 뿐이다. Spring이 개발자에게 DI를 위해 setter를 작성하도록(사실 롬복이)한 방식에서 this.xxService = xxService 이 코드 한 줄마저 Spring에게 넘기고, 값이 변경될 수 있을지언정 개발자에게서 떠나가게 한 행동..?에 의의를 둔 것이 아닐까 싶다.
Constructor Injection
Spring에서 DI를 구현하는 마지막 방법은 생성자(Constructor)를 통한 주입이다. 생성자 주입(Constructor Injection)이라 부르며, 세가지 방법 중 Spring에서 권장하는 방식이다.
생성자 주입을 활용하는 방법은 constructor에 @Autowired annotation을 작성하면 된다.
@Component
public class MemberController {
private final MemberService memberService;
@Autowired
public MemberController(MemberService memberService) {
this.memberService = memberService
}
}위와 같이 field를 선언하고, 생성자를 작성하여 annotation을 써주면 Spring이 bean(객체)을 생성하는 과정에서 의존성을 주입할 대상(memberService)을 찾아 주입해준다.
Spring은 생성자의 매개변수 타입을 통해 필요한 bean을 찾으며, setter/field injection 또한 타입을 통해 bean을 찾지만 두 방식과 가장 큰 차이점은 의존성을 주입하는 시점이 다르다. Java에서 객체를 생성하는 것은 생성자를 호출하는 것인데, field/setter injection은 생성자를 호출하여 bean을 생성하고 이후 reflection api/setter method를 통해 의존성을 주입하고, constructor injection은 bean을 생성하는 시점에 의존성을 주입한다.
Constructor Injection을 권장하는 이유
Field injection 대신 constructor injection을 권장하는 이유에 대해 찾아보면, 단일 책임 원칙, 순환 참조, test 용이 등 여러 이유가 있다. 각 이유에 대한 설명은 여러 블로그에서 잘 정리 해 두었으니 각 장점에 대해 쓰기 보다는 개인적인 생각에 대해 써보고자 한다.
위에서 끄적였듯이 field/setter 주입과 constructor 주입의 가장 큰 차이는 주입 시점이라 생각한다. Bean을 생성하는 과정에서 의존성을 주입하기에 spring application이 실행되기 전 순환 참조를 찾아 에러를 발생시킬 수 있으며, final 키워드를 통해 불변성을 보장할 수 있다.
그 외에도 Spring에게 주입을 일임하는 setter/field 주입과 달리 constructor를 통해 직접 주입할 수 있다는 점에서 Spring container와 결합도를 줄이고 test code를 쉽게 작성할 수 있다는 장점도 있다.
하지만, field injection과 달리 생성자를 작성해야 하는 귀찮음이 있다. 롬복이 도와줄것이다
@RequiredArgsConstructor
생성자 주입의 단점은 field에 @Autowired만 작성해주는 field injection과 달리 생성자를 작성해야 하는 귀찮음일 것이다. Lombok의 @RequiredArgsConstructor annotation을 통해 필요한 의존성을 주입할 수 있는 생성자를 자동으로 생성할 수 있다.
@RequiredArgsConstructorgenerates a constructor with 1 parameter for each field that requires special handling. All non-initializedfinalfields get a parameter, as well as any fields that are marked as@NonNullthat aren't initialized where they are declared. For those fields marked with @NonNull, an explicit null check is also generated. The constructor will throw a NullPointerException if any of the parameters intended for the fields marked with @NonNull contain null. The order of the parameters match the order in which the fields appear in your class.
그렇다고 한다. 무튼, 의존성 주입이 필요한 field를 final 또는 @NonNull을 통해 선언하면 lombok이 해당 field들을 매개변수로 하는 생성자를 만들어주고, null check 까지 해준다. 또 Spring은 Constructor injection을 권장하는 만큼 하나의 생성자가 존재하는 경우 @Autowired annotation을 생략할 수 있다.
여러 생성자가 존재하고 @Autowired annotation이 여러 생성자에 작성된 경우에 대해서도 생각해볼 수 있는데, 이는 Spring container가 @Autowired의 required option이나 의존성 등을 고려하여 생성자를 선택하며 자세한 내용은 추후에 코드 뜯어보며 알아보겠다. 아직 멀었다
무튼, @RequiredArgsConstructor 와 final 키워드를 통해 아래와 같이 쉽게 class를 작성할 수 있다.
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class MemberController {
private final MemberService memberService;
}쉽다