Outlier 처리
데이터를 처리하다보면 데이터에 믿을 수 없는 데이터들이 섞여있기도 하다. 그럴때 해결할 수 있는 다양한 방법들을 알아보자.
데이터가 없을때
데이터에 공백이 있다면 공백을 포함하는 데이터를 제외하고 연산을 할 수도 있다.
[실습]
select restaurant_name,
avg(rating) average_of_rating,
avg(if(rating<>'Not given', rating, null)) average_of_rating2
# 조건 칼럼 rating의 값이 'Not given'이 아닐때
# 조건 O : rating 그대로
# 조건 X : Null로 변경 if 절 후 avg
from food_orders
group by 1 [결과]
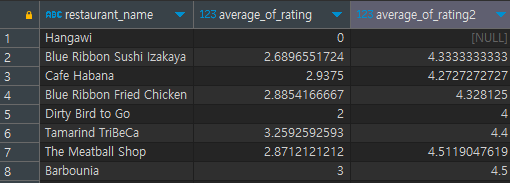
rating 에서 데이터는 숫자이지만, 입력되지 않았음을 표현한 'Not given'은 문자이기 때문에 해당 부분을 null로 변경하여 계산한 것이다. 그러나 이런 방법은 rating을 입력하지 않은 것을 0으로 처리한 후 평균을 구하기 때문에 rating이 있는 데이터간의 평균과 차이가 많이 발생하게 된다.
값을 null로 변경하는 대신 중앙값, 평균값 등 대표값을 이용하여 대체해주기도 한다.
다른 값으로 변경하고 싶을 때, 다음 두 개의 문법을 이용할 수 있다.
-
다른 값이 있을 때
if(rating>=1, rating, 대체값) -
null 값일 때
coalesce(age, 대체값)
[실습]
select a.order_id,
a.customer_id,
a.restaurant_name,
a.price,
b.name,
if(b.name is null ,'NONAME' ,b.name) "이름 null 제거",
b.age,
coalesce(b.age, 20) "나이 null 제거",
b.gender
from food_orders a left join customers b on a.customer_id=b.customer_id
where b.age is null # is [not] null로 사용해야한다.[결과]
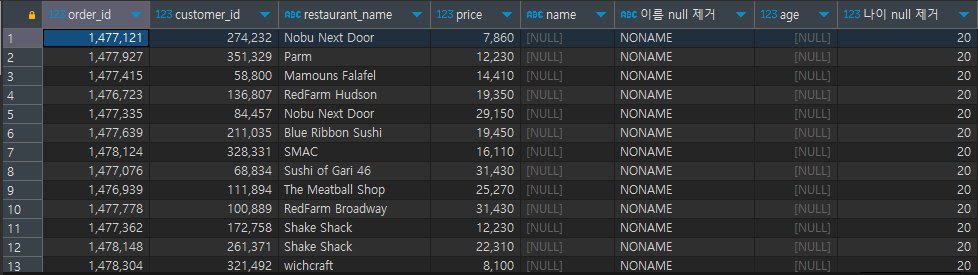
데이터 값이 이상할 때
데이터의 값이 입력되어 있기는 하지만 이상한 경우에는 조건문으로 가장 큰 값, 가장 작은 값의 범위를 지정해 줄 수 있다. 범위를 벗어난 값들을 평균, 중앙값으로 맞춰주거나, 범위내의 가장 큰 값이나 가장 작은 값으로 변경할 수도 있다.
[실습]
select customer_id, name, email, gender, age,
case when age<15 then 15
# 15세 미만은 15세로 지정
when age>80 then 80
#80세 초과는 80세로 지정
else age end "범위를 지정해준 age"
from customers
where age > 80 OR age <15 # 범위를 초과한 경우만 확인[결과]
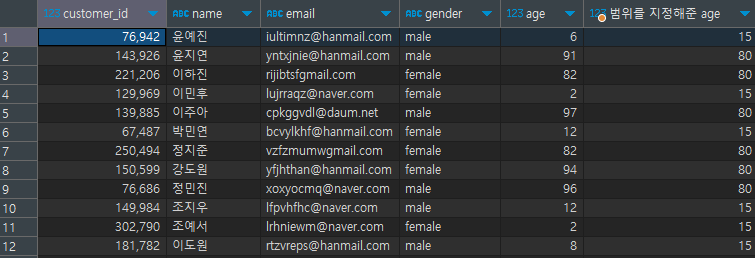
Pivot Table
Pivot table은 2개 이상의 기준으로 데이터를 집계할 때, 보기 쉽게 배열하여 보여주는 것을 의미한다.
예를 들면 레스토랑별 시간당 주문건수를 보고싶다면 아래의 실습처럼 할 수 있다.
[실습]
select restaurant_name,
max(if(hh='15', cnt_order, 0)) "15",
# 15시에 주문건수를 보여줘, 15시가 아니면 0으로 보여줘
max(if(hh='16', cnt_order, 0)) "16",
max(if(hh='17', cnt_order, 0)) "17",
max(if(hh='18', cnt_order, 0)) "18",
max(if(hh='19', cnt_order, 0)) "19",
max(if(hh='20', cnt_order, 0)) "20"
from
(
select a.restaurant_name,
substring(b.time, 1, 2) hh,
count(1) cnt_order
from food_orders a inner join payments b on a.order_id=b.order_id
where substring(b.time, 1, 2) between 15 and 20
group by 1, 2
# 이 말의 뜻은 레스토랑 이름만으로 분류하는 것이 아니라 더 세부적으로 레스토랑+ 시간으로 분류를 의미한다.
# 레스토랑만으로 분류를 하게 되면 hh는 가장 먼저 나온 것으로만 보여지고 cnt_oder는 레스토랑별 합계가 나와서 시간분류가 안된다.
) a
#서브쿼리로 테이블 join을 해준 후, time에서 시간만 가져온다(substr).
group by 1
order by 7 desc
# 이후 본쿼리에서 시간별 분류를 실시하고, 20시 기준 내림차순 정렬 [결과]
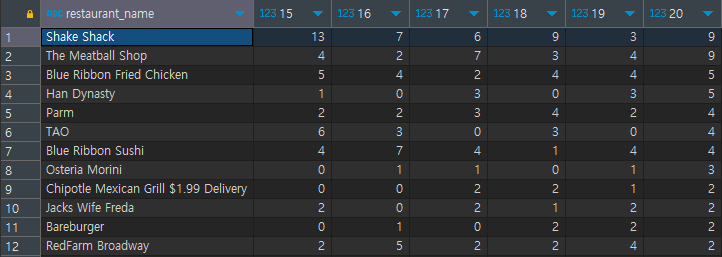
Window Function
기본 SQL 구조로 해결하기 위해서는 복잡하게 Subquery 문을 이용하거나, 여러번의 연산을 수행해줘야 한다. 따라서 자체적으로 제공해주는 기능을 이용하여 조금 더 편리하게 원하는 결과를 뽑을 수 있다.
window_function(argument) over (partition by 그룹 기준 컬럼 order by 정렬 기준)
window_function : 기능 명을 사용(ex. sum, avg)
argument : 함수에 따라 작성하거나 생략
partition by : 그룹을 나누기 위한 기준(group by 절과 유사)
order by : window function 적용시 정렬할 컬럼 기준
RANK
Rank 는 칼럼을 특정 기준으로 순위를 매겨주는 기능이다.
RANK() over (partition by 컬럼 order by 정렬 기준)
[실습]
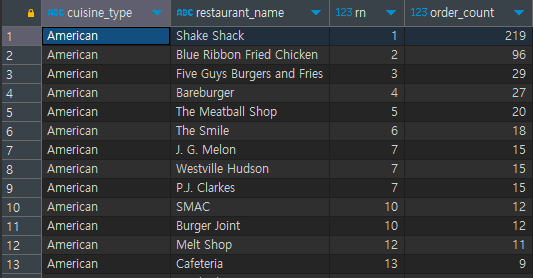
select cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
rank() over (partition by cuisine_type order by order_count desc) rn,
#cuisine_type 칼럼을 oder_count로 정렬하여 순위를 구해줌
order_count
from
(
select cuisine_type, restaurant_name, count(1) order_count
from food_orders
group by 1, 2 # cuisine_type별 restaurant_name으로 그룹
# count로 각 그룹별 주문건수 세기
) a [결과]
SUM
Sum 은 그대로 합계를 구하는 기능이다. 특히 누적합이 필요하거나 카테고리별 합계컬럼와 원본 컬럼을 함께 이용할 때 유용하게 사용한다.
SUM(칼럼) over (partition by 컬럼 order by 정렬 기준)
order by로 정렬하게 되면 누적합이 출력.
[실습]
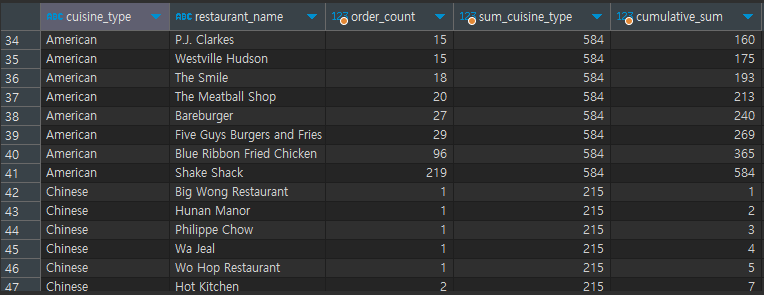
select cuisine_type,
restaurant_name,
order_count,
sum(order_count) over (partition by cuisine_type) sum_cuisine_type,
# cuisine_type별 oder_count 합계을 구한 후 sum_cuisine_type 지정
sum(order_count) over (partition by cuisine_type order by order_count,restaurant_name) cumulative_sum
# cuisine_type별 oder_count을 구한 후 order_count,restaurant_name 정렬순으로 누적합, cumulative_sum 지정
from
(
select cuisine_type, restaurant_name, count(1) order_count
from food_orders
group by 1, 2
) a[결과]
DATE_Type
문자타입, 숫자타입과 같이 날짜 데이터도 특정한 타입을 가지고 있다. 년, 월, 일, 시, 분, 초 등의 값을 모두 갖고 있으며 목적에 따라 ‘월’, ‘주’, ‘일’ 등으로 포맷을 변경할 수도 있다.
date(칼럼)
date_format에서 요일을 볼때 , 1 : 월, 2 : 화....6:토 0 : 일
[실습]
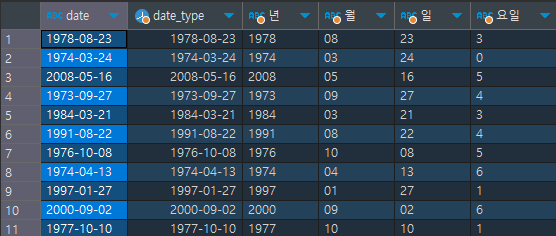
select date , # 기존의 문자 형식이던 date 칼럼을
date(date) date_type, # date형으로 변경
date_format(date(date), '%Y') "년", # date_format으로 년, 월, 일, 요일 추출
date_format(date(date), '%m') "월",
date_format(date(date), '%d') "일",
date_format(date(date), '%w') "요일"
from payments[결과]
Point to check
- is 와 = 의 차이
- Null의 특징
- Pivot Table Max가 포함되는 이유
- sum, max와 같이 계산해주는 것을 한다면 grouop by를 무조건 해줘야 한다.
(코드가 길어질 때 놓치지 않기)
