Basic BFS & DFS
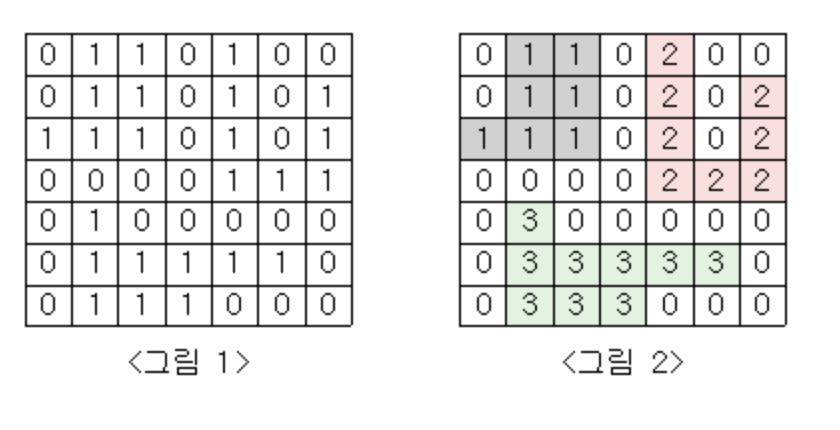
Q. <그림 1>과 같이 정사각형 모양의 지도가 있다. 1은 집이 있는 곳을, 0은 집이 없는 곳을 나타낸다. 철수는 이 지도를 가지고 연결된 집의 모임인 단지를 정의하고, 단지에 번호를 붙이려 한다. 여기서 연결되었다는 것은 어떤 집이 좌우, 혹은 아래위로 다른 집이 있는 경우를 말한다. 대각선상에 집이 있는 경우는 연결된 것이 아니다. <그림 2>는 <그림 1>을 단지별로 번호를 붙인 것이다. 지도를 입력하여 단지수를 출력하고, 각 단지에 속하는 집의 수를 오름차순으로 정렬하여 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
예제:
input:
7
0110100
0110101
1110101
0000111
0100000
0111110
0111000
output:
3
7
8
9BFS
from collections import deque
# 1. Loop through each cell in the grid.
# 2. If the cell contains a house (i.e., 1) and has not been visited yet, initiate a BFS from that cell.
# 3. Store the count of houses in each cluster found by the BFS.
# WHY? you have to perform multiple BFS
# bfs with multiple start points is for when in the end, they should be considered together like tomato problem
def bfs(start, grid, visited, n):
queue = deque([(start[0], start[1])])
visited[start[0]][start[1]] = True
house_count = 0
directions = [(-1,0), (1,0), (0, 1), (0, -1)]
while queue:
r, c = queue.popleft()
house_count += 1
for direction in directions:
next_r, next_c = r + direction[0], c + direction[1]
if 0 <= next_r < n and 0 <= next_c < n and not visited[next_r][next_c]:
if grid[next_r][next_c] == 1:
visited[next_r][next_c] = True
queue.append((next_r, next_c))
return house_count
n = int(input())
apartments = []
# this does NOT work since there is no space between the input map
# for i in range(n):
# row = map(int, input().split())
# print(row)
for i in range(n):
row = input().strip() # read each row as a string
apartments.append([int(char) for char in row])
visited = [[False] * n for _ in range(n)]
house_counts = []
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if apartments[i][j] == 1 and not visited[i][j]:
count = bfs((i, j), apartments, visited, n)
house_counts.append(count)
house_counts.sort()
print(len(house_counts))
for i in house_counts:
print(i)
DFS - Iterative
def dfs(start, grid, visited, n):
stack = [(start[0], start[1])]
visited[start[0]][start[1]] = True
house_count = 0
directions = [(-1,0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]
while stack:
r, c = stack.pop()
house_count += 1
for direction in directions:
next_r, next_c = r + direction[0], c + direction[1]
if 0 <= next_r < n and 0 <= next_c < n and not visited[next_r][next_c]:
if grid[next_r][next_c] == 1:
stack.append((next_r, next_c))
visited[next_r][next_c] = True
return house_count
n = int(input())
apartments = []
for i in range(n):
row = input().strip()
apartments.append([int(char) for char in row])
visited = [[False]* n for _ in range(n)]
house_counts = []
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if apartments[i][j] == 1 and not visited[i][j]:
count = dfs((i, j), apartments, visited, n)
house_counts.append(count)
house_counts.sort()
print(len(house_counts))
for i in house_counts:
print(i)DFS - Recursive
def dfs(start, grid, visited, n, count):
r, c = start[0], start[1]
visited[r][c] = True
count[0] += 1 # Increment the count of apartments in this connected component
directions = [(-1,0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]
for dx, dy in directions:
next_r, next_c = r + dx, c + dy
if 0 <= next_r < n and 0 <= next_c < n and not visited[next_r][next_c]:
if grid[next_r][next_c] == 1:
dfs((next_r, next_c), grid, visited, n, count)
n = int(input())
apartments = []
for i in range(n):
row = input().strip()
apartments.append([int(char) for char in row])
visited = [[False]* n for _ in range(n)]
house_counts = []
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if apartments[i][j] == 1 and not visited[i][j]:
# use list for variable scope and mutability issue.
# immutable integer & mutable containers
count = [0] # Initialize the count for this new connected component
dfs((i, j), apartments, visited, n, count)
house_counts.append(count[0])
house_counts.sort()
print(len(house_counts))
for i in house_counts:
print(i)variable scope and mutability issue:
count = [0], count[0] += 1
