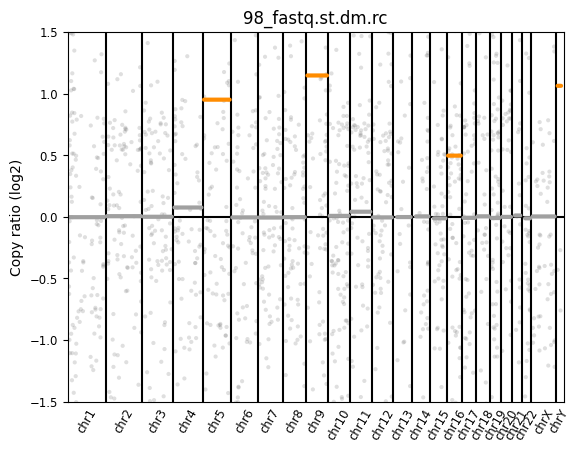
🔍 Copy Number Variation
- Germline copy number variants (CNVs)
- somatic copy number alterations (SCNAs)
🖇 PipeLine / Workflows
https://cnvkit.readthedocs.io/en/stable/pipeline.html
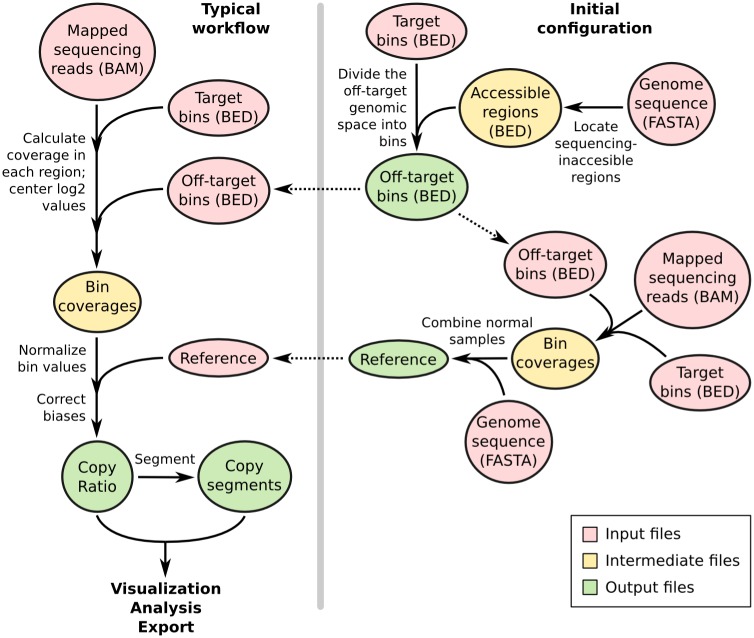
batch
=> automation of following processes
우선 input 으로 BAM 파일이 필요
< When matched normal sample, reference are available >
# From baits, and tumor / normal BAMs
cnvkit.py batch *Tumor.bam --normal *Normal.bam \
--targets my_baits.bed --annotate refFlat.txt \
--fasta hg19.fasta --access data/access-5kb-mappable.hg19.bed \
--output-reference my_reference.cnn --output-dir results/ \
--diagram --scatter
# Reusing a reference for additional samples
cnvkit.py batch *Tumor.bam -r Reference.cnn -d results/
# Reusing targets and antitargets to build a new reference, but no analysis
cnvkit.py batch -n *Normal.bam --output-reference new_reference.cnn \
-t my_targets.bed -a my_antitargets.bed \
-f hg19.fasta -g data/access-5kb-mappable.hg19.bed추가적인 옵션은 이 두개이며 결과를 그래프로 시각화 해준다. 만일 원하지 않으면 따로 써주지 않아도 된다.
- -diagram : diagram을 그려주는 옵션
- -scatter : scatter plot을 그려주는 옵션
=> equivalent to independent processes
cnvkit.py access hg19.fa -o access.hg19.bed
cnvkit.py autobin *.bam -t baits.bed -g access.hg19.bed [--annotate refFlat.txt --short-names]
# For each sample...
cnvkit.py coverage Sample.bam baits.target.bed -o Sample.targetcoverage.cnn
cnvkit.py coverage Sample.bam baits.antitarget.bed -o Sample.antitargetcoverage.cnn
# With all normal samples...
cnvkit.py reference *Normal.{,anti}targetcoverage.cnn --fasta hg19.fa -o my_reference.cnn
# For each tumor sample...
cnvkit.py fix Sample.targetcoverage.cnn Sample.antitargetcoverage.cnn my_reference.cnn -o Sample.cnr
cnvkit.py segment Sample.cnr -o Sample.cns
# Optionally, with --scatter and --diagram
cnvkit.py scatter Sample.cnr -s Sample.cns -o Sample-scatter.pdf
cnvkit.py diagram Sample.cnr -s Sample.cns -o Sample-diagram.pdf< When matched normal is not available >
cnvkit.py batch *Tumor.bam -n -t my_baits.bed -f hg19.fasta \
--split --access data/access-5kb-mappable.hg19.bed \
--output-reference my_flat_reference.cnn -d example2/- -t option; target, my_baits.bed 는 준비된 파일이어야하는지?
- --split --access ; 'calculate the sequence-accessible coordinates' , 이건 cnvkit 폴더안에 있다, 근데 나는 hg38 이용예정, 이걸 써도 될지?
- output-reference ; 생성된 FlatReference
- -d ; output directory
target
Prepare a BED file of baited regions for use with CNVkit.
cnvkit.py target my_baits.bed --annotate refFlat.txt --split -o my_targets.bed
BED file -> baited genomic regions ~ maybe unequal size, --split option would divide to the size close to specified by --average-size
- my baits.bed
- refFlat.txt ; if BED file doesn't have short, informative names for each bait interval
- -mytargets.bed
access
Calculate the sequence-accessible coordinates in chromosomes from the given reference genome, output as a BED file.
If your reference genome is the UCSC human genome hg19, a BED file of the sequencing-accessible regions is included in the CNVkit distribution as data/access-5kb-mappable.hg19.bed. If you’re not using hg19, consider building the “access” file yourself from your reference genome sequence (say, mm10.fasta) using the access command:
cnvkit.py access mm10.fasta -s 10000 -o access-10kb.mm10.bed
=> use this file in the next step to ensure off-target bins (“antitargets”) are allocated only in chromosomal regions that can be mapped.if there are ohter known unmappable, variable, poorly sequenced regions that should be excluded
cnvkit.py access hg19.fa -x excludes.bed -o access-excludes.hg19.bed
- hg38 과 같이 주어져있는 Referece file 이 있을때, 이 ref으로부터 interval list를 포함한 genomic coordinates 가 기록된 bed 파일이 access 명령어를 통해 만들어짐
~/GATK_best_practice/cnvkit.py access /BiO/Share/Tools/gatk-bundle/hg38/Homo_sapiens_assembly38.fasta -o access.hg38.bedantitarget
Given "target" BED , derive BED file off-target/"antitarget" regions
cnvkit.py antitarget my_targets.bed -g data/access-5kb-mappable.hg19.bed -o my_antitargets.bed
autobin
quicly estimate read counts/ depth in BAM => estimate resonable on/off target bin size
cnvkit.py autobin *.bam -t my_targets.bed -g access.hg19.bed cnvkit.py autobin *.bam -m amplicon -t my_targets.bed cnvkit.py autobin *.bam -m wgs -b 50000 -g access.hg19.bed --annotate refFlat.txtThe BAM index (.bai) is used to quickly determine the total number of reads present in a file, and random sampling of targeted regions (-t) is used to estimate average on-target read depth much faster than the coverage command.
coverage
calculate coverage in given regions from read depth
pileup ~ - ountnone optioncnvkit.py coverage Sample.bam targets.bed -o Sample.targetcoverage.cnn cnvkit.py coverage Sample.bam antitargets.bed -o Sample.antitargetcoverage.cnn
reference
compile CN reference from given files, given reference genome ( -f) calculate GC content, repeat-masked proportion
( A reference should be constructed specifically for each target capture panel, using a BED file listing the genomic coordinates of the baited regions. Ideally, the control or “normal” samples used to build the reference should match the type of sample (e.g. FFPE-extracted or fresh DNA) and library preparation protocol or kit used for the test (e.g. tumor) samples.)cnvkit.py reference *coverage.cnn -f ucsc.hg19.fa -o Reference.cnn
BUT 나는 paired/pooled normal 이 없다! => "Flat" reference of neutral copy number
cnvkit.py reference -o FlatReference.cnn -f ucsc.hg19.fa -t targets.bed -a antitargets.bed1) extract copy number information from one / small # of tumor sample
2) create 'dummy' reference to use as input to batch command
3) evaluate suitablity for analysis by repeating CNVkit analysisfix
combine uncorrected target & antitarget coverage tables (.cnn), correct for biases in regional coverage and GC content
cnvkit.py fix Sample.targetcoverage.cnn Sample.antitargetcoverage.cnn Reference.cnn -o Sample.cnr
how it works ;
A weight is assigned to each remaining bin depending on:
1. The size of the bin;
2. The deviation of the bin’s log2 value in the reference from 0;
3. The “spread” of the bin in the reference.segment
infer discrete copy number segments from give coverage table
cnvkit.py segment Sample.cnr -o Sample.cns
call
Given segmented log2 ratio estimates (.cns), derive each segment’s absolute integer copy number using either:
cnvkit.py call Sample.cns -o Sample.call.cns cnvkit.py call Sample.cns -y -m threshold -t=-1.1,-0.4,0.3,0.7 -o Sample.call.cns cnvkit.py call Sample.cns -y -m clonal --purity 0.65 -o Sample.call.cns cnvkit.py call Sample.cns -y -v Sample.vcf -m clonal --purity 0.7 -o Sample.call.cns
cnvkit.py call Sample.cns -y -v Sample.vcf -o Sample.call.cns
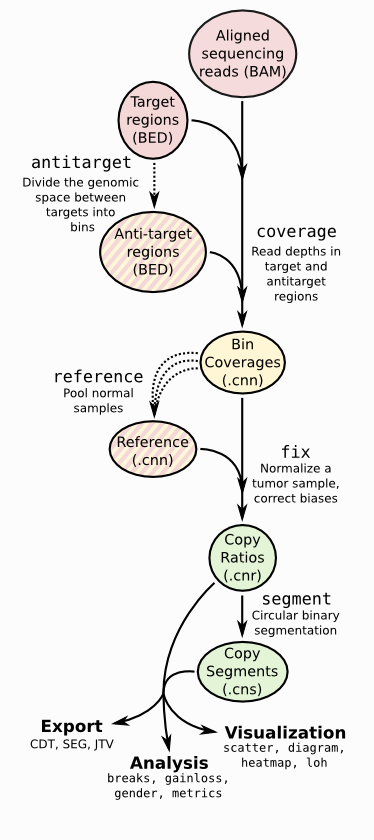
🗂 Review from Paper
Calculation of off-target intervals
- antitarget command ; accepts a list of targeted regions,
- Browser Extensible Data (BED) or GATK/Picard interval list format, and divides the off-target regions between each target into large bins
