- 복습: 이것이 자바다 예제에 있는 내용 확인 후 코드 쳐보기.1. 예외 처리
- 예외처리는 프로그램 동작 중 문제가 발생시 프로그램이 종료되지만 종료되지 않고 작업이 계속 이어나갈 수 있도록 적절한 처리.
- 런타임 오류는 실행 중에 프로그램이 오류를 만나 프로그램이 종료되는 것.
- 예: 숫자를 입력 > 문자를 다른 배열의 인덱스를 벗어났다든지 사용자 입력이 잘못되었을때 발생.
(1) try ~ catch ~ finally문
try {
// 예외 발생 가능한 지점
} catch(처리할 예외 클래스 변수명) {
// 예외처리할 내용
} catch(처리할 예외 클래스 변수명) {
// 예외처리할 내용
} finally {
// 예외 발생 유무와 상관없이 항상 실행하는 코드 입력
}-
try문의 중괄호 안에 예외가 발생할 수 있는 코드 작성. 예외가 발생하면 catch문의 예외 처리.
-
catch문은 switch문 case처럼 여러개 정의 가능
-
발생한 예외 클래스 인스턴스가 할당되고 인스턴스를 사용하여 catch문에서 여러가지 작업 진행
-
finally 부분은 예외 유무 상관없이 반드시 실행해야 할 코드를 기술함.
<예외처리 예시 코드>
try {
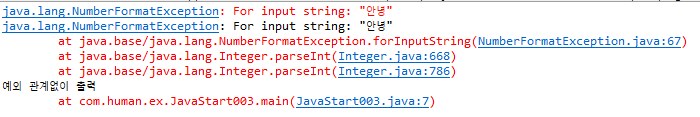
int num = Integer.parseInt("안녕");
System.out.println("정상 동작시만 출력");
} catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println(e); // 예외 문자 출력
e.printStackTrace(); // 예외내용 뿐만 아니라 예외가 발생한 함수들의 호출관계를 모두 찍음
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("예외 관계없이 출력");
}
}
}-
문자를 수로 바꿀 수 없을때 발생하는 예외 클래스는 NumberFormatException 클래스.
-
try문 안에서 예외가 발생하면 catch(NumberFormatException e) { 의 catch블록으로 이동해 실행해 나감.
-
만약, try문 안에서 배열 인덱스가 벗어날 경우 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 발생.
-
예외 처리하고 싶다면 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { 를 기술.

int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
int index = 10;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
try {
System.out.println("출력하고 싶은 배열의 인덱스 입력>>");
index = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine());
System.out.println(arr[index]);
break;
} catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("잘못된 인덱스를 입력하였습니다");
} catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("숫자를 입력하였습니다");
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("알 수 없는 예외 발생");
}
}
try {
int[] numbers = {1,2,3};
int index = 4;
int value = numbers[index];
System.out.println("배열 요소 값: " + value);
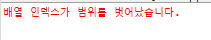
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.err.println("배열 인덱스가 범위를 벗어났습니다");
}- 없는 클래스를 접근하려고 할때 ClassNotFoundException 발생.
- 정수를 0으로 나누면 ArithmeticException 발생.
- 즉, switch문에서 default처럼 Exception 클래스는 모든 예외를 받아 처리하는 클래스.
try {
int a = 4/0;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
}- 수학적 예외를 발생시키고 싶다면
int a = 15;
try {
if(a>10) {
//강제로 예외 발생
throw new Exception();
} else {
a = a+5;
}
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("a가 10보다 커서 예외 발생");
}
System.out.println(a);(2) throws
- 메소드 안의 코드중 예외가 발생하면 해당 메소드에서 하지 않고 해당 메소드를 호출한 부분에서 예외처리.
리턴타입 메소드명 throws 예외클래스1, 예외클래스2 { }
try {
findClass();
} catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
// 호출한 곳에서 예외처리
System.out.println("예외 처리: " + e.toString());
}
}
public static void findClass() throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class.forName("java.lang.String2");
}
}public static void exceptionFunction1() throws Exception {
throw new Exception();
}
public static void exceptionFunction2() throws Exception {
throw new NumberFormatException();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, NumberFormatException {
try {
exceptionFunction1();
} catch(Exception e) { };
exceptionFunction2();
}(3) 예외 구문 다른 예시
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 15;
int b = 5;
try {
int additionResult = add(a,b);
System.out.println("덧셈결과: " + additionResult);
int subtractResult = subtract(a,b);
System.out.println("뺄셈결과: " + subtractResult);
int multiplicationResult = multiply(a,b);
System.out.println("곱셈결과: " + multiplicationResult);
int divideResult = divide(a,b);
System.out.println("나눗셈결과: " + divideResult);
} catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.err.println("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.");
}
}
public static int add(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
public static int subtract(int a, int b) {
return a-b;
}
public static int multiply(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
public static int divide(int a, int b) {
return a / b;
}(4) NullPointerException
- 참조변수가 null인 상태에서 필드나 메소드에 접근할 경우 발생
public static void printLength(String data) {
try {
int result = data.length;
System.out.println("문자 수: " + result);
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
// 예외 정보를 얻는 방법
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("[마무리 실행]\n");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("[프로그램 시작]\n");
printLength("ThisIsJava");
printLength(null);
System.out.println("[프로그램 종료]");
}
}