1. 연산자 우선순위
<정리>
1) 괄호부터 처리
2) *, /, % 먼저 연산
3) +, - 연산
4) 우선순위가 같으면 왼쪽부터 오른쪽으로 계산
5) 이항연산자보다 단항연산자가 우선순위 높음.
6) 삼항연산자보다 이항연산자가 우선순위 높음
7) = 연산자는 오른쪽에서 왼쪽으로 순서대로 연산
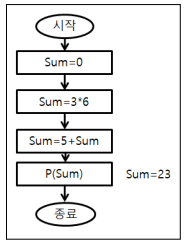
public class JavaStart00 { public static void main(String[] args) { int sum = 0; sum = 3*6; sum = 5 + sum; System.out.println(sum); } }
2. 형변환과 캐스팅 연산
- 프로그램에서 특정 자료형을 다른 자료형으로 변환해주는 것이다.
(1) 자동형 변환(묵시적 타입 변환)
- 작은 크기의 자료형을 큰 크기의 자료형을 넣을때 자동형 변환이 나타난다.
- 대입 연산이나 산술 연산에서 컴파일러가 자동으로 수행해줌.
public class JavaStart00 { public static void main { double num1 = 10; // int num2 = 3.14; double num3 = 7.0f + 3.14; System.out.println(num1); System.out.println(num3); } }
- 1번 라인: double형 변수에 int형 데이터를 대입. 즉, int형 데이터가 double형 데이터로 자동타입 변환.
- 2번 라인: int형 변수가 표현할 수 있는 범위보다 더 큰 double형 데이터 대입. 즉, 데이터 손실발생
- 3번 라인: float형 데이터와 double형 데이터를 산술연산. 이때, 데이터 손실을 최소화하기 위해 double형 자동 변환
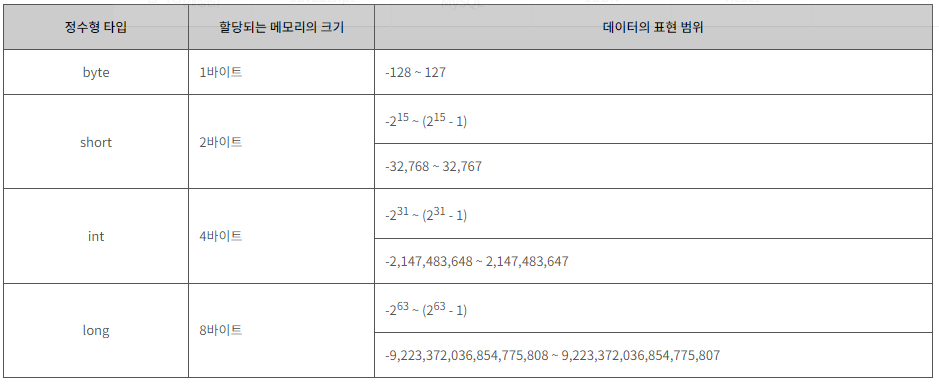
- 정리: byte -> short -> char -> int -> long -> float -> double
- int이하 자료형은 int형으로 통합한다.
byte byteValue = 10; int intValue = byteValue; System.out.println("intValue: " + intValue);char charValue = '가'; intValue = charValue; System.out.println("가의 유니코드: " + intValue);intValue = 50; long longValue = intValue; System.out.println("longValue: " + longValue);longValue = 100; float floatValue = longValue; System.out.println("floatValue: " + floatValue);floatValue = 100.5F; double doubleValue = floatValue; System.out.println("doubleValue: " + doubleValue);
(2) 강제 타입 변환(명시적 타입 변환)
- 사용자가 타입 캐스트 연산자()를 사용하여 강제적으로 수행함.
- 캐스팅 연산자의 우선순위가 높아서 먼저 실행
// 기본문법 (변환할 타입) 변환할 데이터public class JavaStart00 { public static void main { int num1 = 1; int num2 = 4; double result1= num1 / num2 double result2= (double)num1/num2 System.out.println(result1); System.out.println(result2); } }
- 1번 라인: 나눗셈 연산결과 0 반환.
(0.25지만 int형 자동반환)
결괏값 타입=피연산자 타입 일치.
즉, int형 데이터끼리 산술연산에 대한 결괏값은 int형 결과로 나온다.- 2번 라인: 연산결과 0이 출력되어 int형으로 반환되었지만 좀 더 정확한 결괏값을 알고싶으면 double형으로 강제 타입함.
<주의>
- (int)11.1+11.1: 11.1이 int 11로 변환.
int+double=double이여서 22.1
(int)(11.1+11.1) 22.2가 int형으로 반환
즉, 22가 됨.int var1 = 10; byte var2 = (byte) var1; System.out.println(var2); long var3 = 300; int var4 = (int) var3; System.out.println(var4); int var5 = 65; char var6 = (char) var5; System.out.println(var6); double var7 = 3.14; int var8 = (int) var7; System.out.println(var8);(3) 정리
- 자료형 저장범위 크기
byte > short > int > long > float > double- int이하 자료형은 int로 자동변환.
- int(4byte, 32bit)는 long(8byte, 64bit),float(4byte, 32bit),double(8byte, 64bit) 자동 변환
- long은 float, double 자동 변환
- float은 double로 자동변환.
- boolean 자료형은 자바에서 자동,강제변환 불가능.
- true+1: 연산결과를 같은 자료형으로 만들 수 없으면 에러 발생.
- long + (byte, short, char, int) == long형
- long + float == float
- long + double == double
- 문자열 + 모든 자료형 결과 : 문자열
- "안녕"+"하세요" : "안녕하세요"
- "1"+1 = 2가 아닌 문자열 11이 됨.
- 1 + 1 + "2"는 문자열 22가 됨.
- 문자열 연산은 +연산만 가능.
- 문자열 강제타입변환 불가능.
- 문자열 "11"를 int형변환
int a = Integer.parseInt("11"); int a = Integer.valueOf("11");
- 문자열 "11.11"를 double형 변환
String str1 = "11.11"; double a = Double.parseDouble(str1);double a = Double.valueOf(str1);boolean b = Boolean.parseBoolean("true");
- 다양한 자료형을 문자열 변경: "" + 자료형
""+123 == "123"""+5.3 == "5.3"
<이것은 자바다> 예제 코드
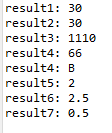
byte result1 = 10 + 20; System.out.println("result1: " + result1); byte v1 = 10; byte v2 = 20; int result2 = v1 + v2; System.out.println("result2: " + result2); byte v3 = 10; int v4 = 100; long v5 = 1000L; long result3 = v3 + v4 + v5; System.out.println("result3: " + result3); char v6 = 'A'; char v7 = 1; int result4 = v6 + v7; System.out.println("result4: " + result4); System.out.println("result4: " + (char)result4); int v8 = 10; int result5 = v8 / 4; System.out.println("result5: " + result5); int v9 = 10; double result6 = v9 / 4.0; System.out.println("result6: " + result6); int v10 = 1; int v11 = 2; double result7 = (double) v10 / v11; System.out.println("result7: " + result7);<이것은 자바다> StringConcat예제
// 숫자 연산 int result1 = 10 + 2 + 8; System.out.println("result1: " + result1); // 20 // 결합 연산 String result2 = 10 + 2 + "8"; System.out.println("result2: " + result2); // 128 String result3 = 10 + "2" + 8; System.out.println("result3: " + result3); // 1028 String result4 = "10" + 2 + 8; System.out.println("result4: " + result4); // 1028 String result5 = "10" + (2+8); System.out.println("result5: " + result5); // 1010
3. Scanner, parseInt
(1) Scanner
import java util.Scanner; public class JaveStart00 { public static void main(Stirng[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); String str1 = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.println("본인이 입력한 문자열은"+str1+"입니다."); } }
- import문과 Scanner scanner = new Scanner 부분은 java.util.Scanner 자료형 변수 scanner에 키보드 입력을 할 수 있는 데이터를 넣는 의미이다.
- scanner.nextLine()은 실제 사용자가 입력하면 실행된다. (해당 코드 연속으로 입력이 가능하다)
- String str1 = scanner.nextLine()에서 = 연산자는 오른쪽에서 왼쪽으로 실행.
- 사용자 입력은 문자열이기에 String에 담아야 한다.
(2) parseInt
public class JavaStart00 { public static void main(String[] args) { java.util.Scanner sc = new java.util.Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("정수입력>>"); String st = sc.nextLine(); int i = Integer.parseInt(st); System.out.println(i); } }
- 사용자 입력을 String이 아닌 숫자로 변환한다면 java.lang.NumberFormatException 에러 발생
<이것은 자바다> 예제
- 기본타입 값을 문자열 변경
String str = String.valueOf(기본타입값);
변환 타입 사용 예 String → byte String str = "10"; byte value = Byte.parseByte(str); String → short String str = "10"; short value = Short.parseShort(str); String → int String str = "10"; int value = Integer.parseInt(str); String → long String str = "10"; long value = Long.parseLong(str); String → float String str = "10"; float value = Float.parseFloat(str); String → double String str = "10"; double value = Double.parseDouble(str); String → boolean String str = "10"; boolean value = Boolean.parseBoolean(str); int value1 = Integer.parseInt("10"); double value2 = Double.parseDouble("3.14"); boolean value3 = Boolean.parseDouble("true"); System.out.println("value1: " + value1); System.out.println("value2: " + value2); System.out.println("value3: " + value3); String str1 = String.valueOf(10); String str2 = String.valueOf(3.14); String str3 = String.valueOf(true); System.out.println("str1: " + str1); System.out.println("str2: " + str2); System.out.println("str3: " + str3);
(3) scanner, parseInt 예제
- 세로와 가로를 입력 받아 사각형의 넓이를 구현하는 프로그램 만들기
package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("사각형의 넓이를 구현하는 프로그램입니다."); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("가로를 입력해주세요> "); int a = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("세로를 입력해주세요> "); int b = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); int area = a*b; System.out.println("사각형의 넓이는 " + area + " 제곱미터입니다."); } }
- 세로 가로 높이를 입력 받아 사각기둥의 부피를 만드는 프로그램 만들기
package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("사각기둥의 부피를 구현하는 프로그램입니다."); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("가로를 입력해주세요> "); int a = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("세로를 입력해주세요> "); int b = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("높이를 입력해주세요> "); int c = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); int volume = a*b*c; System.out.println("사각기둥의 부피는 " + volume + " 세제곱미터입니다."); } }
- a 센치미터가 몇 m 몇 cm인지 출력하는 프로그램 구현
package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("a 센치미터를 몇 미터 몇센치인지 구현하는 프로그램입니다."); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("길이 입력(cm→m)> "); double a = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.println(a/100 + " m입니다."); } }
- 잔디의 가격은 1 제곱 미터에 a원일 때 윗변이 b,아래변이 c, 높이d인 사다리꼴에
잔디를 심으려면 얼마의 비용이 드는지 구하는 순서도를 작성하시오.package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("잔디를 심으려면 얼마나 비용이 드는지를 구현하는 프로그램입니다."); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("윗변 입력> "); int b = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("아랫변 입력> "); int c = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("높이 입력> "); int d = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("잔디의 가격 입력> "); int a = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); int result = ((b+c)*d/2)*a; System.out.println("잔디의 가격은 " + result + "원입니다."); } }
- 이름 나이 키를 입력받은 화면에 출력하는 프로그램을 작성해 보자. 출력결과:
당신의 이름은 홍길동 입니다.당신의 나이는 23입니다. 당신의 키는 165.5 입니다.package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("이름, 나이, 키를 입력하고 구현하는 프로그램입니다."); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("이름 입력> "); String a = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.print("나이 입력> "); int b = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("키 입력> "); double c = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.println("당신의 이름은 " + a + " 입니다. 당신의 나이는 " + b + "입니다. 당신의 키는 " + c + " 입니다."); } }
- 두수를 입력받아 두수의 차를 출력하는 프로그램을 작성해보자
package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("두 수를 입력받아 두수의 차를 구현하는 프로그램입니다."); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("첫번째 수 입력> "); int a = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("두번째 수 입력> "); int b = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.println("두 수의 차는 " + (a-b) + "입니다."); } }
- 다음은 국어,영어,수학 점수를 입력 받아 평균을 구하여 다음과 같이 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어보자. 출력결과: 국어:80 영어:70 수학:90 평균:80
package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("세 과목의 평균점수를 구현하는 프로그램입니다."); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("국어점수 입력> "); double a = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("영어점수 입력> "); double b = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("수학점수 입력> "); double c = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine()); double avg = (a+b+c)/3; System.out.println("세 과목의 평균 점수는 " + avg + "입니다."); } }
- 키를 m로 소수점 2째 자리까지 입력받아 cm로 바꿔주는 프로그램을 만들어 보자.
package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("키를 m로 소수점 2자리까지 입력받아 cm로 구현하는 프로그램입니다."); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("키 입력> "); double a = Double.parseDouble(scanner.nextLine()); double height = a*100; System.out.println("키는 " + height + "cm 입니다."); } }
- 상장의 가로, 세로, 높이를 입력받아 부피를 구하는 프로그램을 만들어 보자.
package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("상장의 부피를 구현하는 프로그램입니다."); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("가로 입력> "); int a = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("세로 입력> "); int b = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("높이 입력> "); int c = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); int volume = a*b*c; System.out.println("상장의 부피는 " + volume + "세제곱미터입니다."); } }
- 연필 한박스에 12자루의 연필이 들어 있고 연필 1자루는 1000원 이다. 소비자가 몇박스와 연필 몇자루를 구매할 것인지 입력 받아 지불해야 할 돈을 계산해주는 프로그램을 만들어 보자
package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("소비자가 몇박스와 연필 몇자루를 구매할 것인지 입력받아 지불해야할 돈을 구현하는 프로그램입니다."); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("구매할 박스 입력> "); int a = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("구매할 연필자루 입력> "); int b = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("가격 입력> "); int c = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); int result = (a*12+b)*c; System.out.println("소비자는 " + a + "박스와 " + b + "자루를 구매하여 총 " + result + "원을 지불하였습니다."); } }
4. String.Format
- 매개변수를 가지고 새로운 문자열을 만드는 메소드
- 메소드: 필요한 기능을 미리 만들어놓고 필요할때 호출하여 사용.
- 매개변수: 메소드에서 필요한 기능을 실행할때 필요한 데이터를 넘겨줄때 사용함.
','로 구분하여 여러 데이터 넘김.- 즉, System.out.println("hello world");
메소드 : System.out.println
매개변수: "hello world"
public class JavaStart00 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "홍길동"; String str2 = String.format("이름 : %s", str1); String str3 = "이름 : " + str1; System.out.println(String.format("이름 : %s", str1)); System.out.println(str2); System.out.println(str3); } }
<참고: printf>
- printf("형식문자열", 값1, 값2, ...") : 형식 문자열에 맞춰서 뒤의 값을 출력
System.out.printf("이름: %s", "감자바");System.out.printf("이름: %1$s, 나이:%2$d", "감자바", 25);
타입 형식화된 문자열 설명 출력형태 정수 %d 정수 123 정수 %6d 6자리 정수, 왼쪽 빈자리 공백 ___123 정수 %-6d 6자리 정수, 오른쪽 빈자리 공백 123___ 정수 %06d 6자리 정수, 왼쪽 빈자리 0채움 000123 실수 %10.2f 정수 7자리 + 소수점 + 소수 2자리. 왼쪽 빈자리 공백 ____123.45 실수 %-10.2f 정수 7자리 + 소수점 + 소수 2자리. 오른쪽 빈자리 공백 123.45____ 실수 %010.2f 정수 7자리 + 소수점 + 소수 2자리. 왼쪽 빈자리 0 채움 0000123.45 문자열 %s 문자열 abc 문자열 %6s 6자리 문자열, 왼쪽 빈자리 공백 ___abc 문자열 %-6s 6자리 문자열, 오른쪽 빈자리 공백 abc___ 특수문자 \t 탭 특수문자 \n 줄바꿈 특수문자 %% % %
(1) String.Format 이해하기
String.format("문자: %s" 숫자: %d 실수:%f ...", 첫번째 %문자에 넣을 값1, 두번째 문자열에 넣을 값2...)
- 첫번째 매개변수의 문자열 데이터 안에 %문자는(%s,%d,%f)의 개수만큼 다음 매개변수에 %문자를 대처할 데이터들을 순서대로 추가.
- 첫번째 매개변수의 문자열의 %문자 부분에 두번째 매개변수부터 순서대로 삽입.
String.format(">%s %s %d %f", "문자열1", "문자열2", 10, 12.2);
(2) String.format 연습
- int age= 156, String name = "hong" double height=175.3 다음 데이터와 String.format을 이용해서 문자열로 만들어 출력해보자.
package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = String.format("나이는 %d", 156); String str2 = String.format("이름은 %s", "hong"); String str3 = String.format("키는 %.1f", 175.3); System.out.println(str1); System.out.println(str2); System.out.println(str3); } }
- 사용자로부터 2개의 정수를 받아서 첫번째 정수를 두번째 정수로 나누었을때의 몫과 나머지를 계산하는 프로그램
package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("사용자로부터 2개의 정수를 받아 첫번째 정수와 두번째 정수를 나눌때 몫과 나머지를 계산하는 프로그램입니다."); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("첫번째 정수를 입력해주세요> "); int a = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("두번째 정수를 입력해주세요> "); int b = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); int result1 = a / b; int result2 = a % b; String str1 = String.format("몫은 %d 나머지는 %d이다", result1, result2); System.out.println(str1); } }
- 3자리 숫자를 입력하여 각 자리의 숫자를 출력하시오.
힌트) %연산자와 /연산자를 이용하여 만들 수 있다. 555를 100으로 나누면 몫은 5고 나머지는 55다. 423을 입력하였다면 백의자리:4 십의자리:2 일의자리:1이 되도록 출력하라.package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("3자리 숫자를 입력하여 각 자리의 숫자를 구현하는 프로그램입니다."); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("백의 자리를 입력해주세요> "); int a = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("십의 자리를 입력해주세요> "); int b = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("일의 자리를 입력해주세요> "); int c = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); String str1 = String.format("백의 자리는 %d 십의 자리는 %d 일의 자리는 %d", a, b, c); System.out.println(str1); } }
- 두 점을 입력 받아 두 점의 거리를 구하는 프로그램을 만들어보자.
힌트) Math.sqrt(25) = 5.package com.human.ex; import java.util.Scanner; public class Practice { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("두 점을 입력받아 두 점의 거리를 구하는 프로그램입니다."); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("첫번째 점의 x좌표를 입력해주세요> "); int a = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("첫번째 점의 y좌표를 입력해주세요> "); int b = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("두번째 점의 x좌표를 입력해주세요> "); int c = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.print("두번째 점의 y좌표를 입력해주세요> "); int d = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); double distance = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(b-a, 2) + Math.pow(d-c, 2)); System.out.println("두 점 사이의 거리는 " + distance +"입니다."); } }