1. 배열
- 같은 타입의 숫자들을 관리하기 위해 배열을 생성함.
1) 배열의 선언과 생성
package array;
public class Array1Ref1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] students;
students = new int[5];
System.out.println(students);
students[0] = 90;
students[1] = 80;
students[2] = 70;
students[3] = 60;
students[4] = 50;
System.out.println("학생 1 점수: " + students[0]);
System.out.println("학생 2 점수: " + students[1]);
System.out.println("학생 3 점수: " + students[2]);
System.out.println("학생 4 점수: " + students[3]);
System.out.println("학생 5 점수: " + students[4]);
}
}
(1) 구조분석
- 배열 변수 선언. int[] students;
- 배열을 사용하려면 int[] students와 같이 배열 변수 선언
- 일반적 변수: 단순한 값. 배열 변수는 대괄호[ ] 포함.
- 배열을 선언해도 아직 사용할 수 있는 배열은 아니다.
- 배열 생성: students = new int[5]
- 배열을 사용하려면 배열 생성
- new int[5]는 새로 생성한 int형의 5개 들어있는 배열
- 배열에 들어있는 값은 0으로 자동초기화
- System.out.println(students)
- 코드를 출력하면 [I@b4c966a 형태가 나옴.
- I는 int형태의 자료타입이라고 함.
- @b4c966a는 배열의 참조값이라고 함.
- new int[5] 라고 하면 총 5개의 int형 변수가 만들어짐.
- 자바는 자동적으로 0으로 초기화
- 배열 참조값 보관 students = new int[5]
- new int[5]을 생성하면 배열의 크기만큼 메모리 생성(4byte * 5)
- 배열을 생성하면 자바에서는 1개의 배열값의 참조값이 나온다.
- 그 참조값이 students 변수에 대입된다.
2) 배열 사용
(1) 인덱스
students[0] = 90;
students[1] = 80;
System.out.println("학생 1 점수: " + students[0]);
System.out.println("학생 2 점수: " + students[1]);
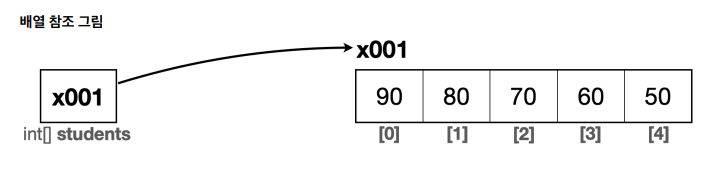
- 배열은 0부터 시작한다.
- int[] students의 참조값은 x001이며 그 참조값을 int형의 배열의 첫번째 참조값인 x001에 해당 값을 대입해라.
System.out.println("학생1 점수: " + students[0]);
System.out.println("학생1 점수: " + x001[0]);
System.out.println("학생1 점수: " + 90);
(2) 기본형, 참조형
- int, double, boolean형처럼 변수에 사용할 수 있는 값을 직접 넣을 수 있음.
- int[] students와 같이 데이터에 접근할 수 있는 참조를 저장하는 데이터 타입
- 기본형은 선언과 동시에 크기를 결정하지만 참조형은 동적으로 크기를 결정할 수 있음.
- 참조형은 Scanner클래스의 사용자 입력을 통해서 동적으로 크기를 결정.
3) 배열 리팩토링
- 기존의 코드 기능을 유지하면서 내부 구조를 개선하여 가독성을 높이고 유지보수 용이
package array;
public class Array1Ref2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] students;
students = new int[5];
System.out.println(students);
System.out.println(students.length);
students[0] = 90;
students[1] = 80;
students[2] = 70;
students[3] = 60;
students[4] = 50;
for(int i=0; i<students.length; i++) {
System.out.println("학생" + (i + 1) + " 점수: " + students[i]);
}
}
}
- 변수 값 대입은 for문을 이용해서 배열을 통해 값을 사용하는 부분으로 변경
- 배열의 인덱스는 0부터 시작
- students.length는 int형이 5개가 있는 배열의 크기라고 한다.
(1) students.length
- 배열의 길이를 제공하는 역할.
- 조회 기능만 가능하지만 대입할 수 없다.
- for문 조건이 i<students.length이기 때문에 0,1,2,3,4 배열값이 출력
(2) 배열 리팩토링-초기화
- 배열은 { }를 사용하여 편리하게 초기화 할 수 있는 기능.
int[] students;
students[] = new int[] {90, 80, 70, 60, 50};
(3) 배열 리팩토링 - 간단한 배열 생성
int[] students = {90, 80, 70, 60, 50};
- 이때, 배열 변수의 선언을 한 줄에 함께 사용할때만 가능함.
- 자바는 위 코드를 작성하더라도 new int[5]를 사용해서 배열 생성
- 코드를 수정하지 않아도 배열 값만 배경하면 동적으로 배열 값 출력
4) 2차원 배열 - 시작
- 2차원 배열은 int[][] arrr = new int[2][3]와 같이 선언.
- 행은 row, 열은 column
- 2차원 배열 구조는 다음과 같다.
arr[행][열], arr[row][column]
package array;
public class ArrayDi0 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = new int[2][3];
arr[0][0] = 1;
arr[0][1] = 2;
arr[0][2] = 3;
arr[1][0] = 4;
arr[1][1] = 5;
arr[1][2] = 6;
System.out.print(arr[0][0] + " ");
System.out.print(arr[0][1] + " ");
System.out.print(arr[0][2] + " ");
System.out.println();
System.out.print(arr[1][0] + " ");
System.out.print(arr[1][1] + " ");
System.out.print(arr[1][2] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
(1) 2차원 배열-리팩토링1(행 출력 반복)
- 0행과 1행 출력을 for문을 이용해서 리팩토링한다.
for(int row=0; row<2; row++) {
System.out.print(arr[row][0] + " ");
System.out.print(arr[row][1] + " ");
System.out.print(arr[row][2] + " ");
}
(2) 2차원 배열-리팩토링2(열 출력 반복)
for(int row=0; row<2; row++) {
for(int column=0; column<3; column++) {
System.out.print(arr[row][column] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
(3) 2차원 배열-초기화, 배열의 길이
int[][] arr = {
{1,2,3},
{4,5,6}
};
for(int row=0; row<arr.length; row++) {
for(int column=0; column<arr[row].length; column++) {
System.out.print(arr[row][column] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
(4) 2차원 배열 동적으로 받기
int[][] arr = new int[2][3];
int i = 1;
for(int row=0; row<arr.length; row++) {
for(int column=0; column<arr[row].length; column++) {
arr[row][column] = i++;
}
}
for(int row=0; row<arr.length; row++) {
for(int column=0; column<arr[row].length; column++) {
System.out.print(arr[row][column] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
5) 향상된 for문
package array;
public class EnhancedFor1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {1,2,3,4,5};
for(int i=0; i<numbers.length; i++) {
int number = numbers[i];
System.out.println(number);
}
for(int number : numbers) {
System.out.println(number);
}
for(int i=0; i<numbers.length; i++) {
System.out.println("number" + i +"번의 결과는: " + numbers[i]);
}
}
}
(1) 일반 for문
- 배열에 있는 값을 순서대로 읽어서 number 변수에 넣고 출력
(2) 향상된 for문
- 배열의 인덱스를 사용하지 않고 배열의 요소를 순회할 수 있음.
- 하지만, int i와 같은 카운터 변수가 존재할 경우 향상된 for문을 사용하지 못한다.

