JPA
What it is:
JPA is a specification (a standard) for object-relational mapping (ORM) in Java.
Purpose:
It allows you to map Java objects → database tables, and database rows → Java objects, so you can work with databases using Java classes, not raw SQL.
Common JPA Implementations:
JPA is just an interface/spec. You need a library that implements it:
-
Hibernate (most popular, often used by Spring Boot)
-
EclipseLink
-
OpenJPA
Hibernate
Hibernate is a popular Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) framework for Java. It simplifies database interactions by mapping Java objects to relational database tables, abstracting away the complexities of JDBC and raw SQL.
While Hibernate is widely used and powerful, it's not always the best choice for every project. Here's a comparison of Hibernate with some of its alternatives:
Hibernate Strengths:
- Object-Relational Mapping (ORM): Automatically handles the mapping between Java objects and database tables, reducing boilerplate code.
- JPA Implementation: Hibernate is the most widely used implementation of the Java Persistence API (JPA) specification, making it a standard choice for Java enterprise applications.
- Productivity: Speeds up development by automating many data persistence tasks (CRUD operations, transaction management, schema generation).
- Caching: Provides first-level (session-level) and second-level (application-level) caching to improve performance by reducing database hits.
- Lazy Loading: Loads data on demand, improving performance by avoiding the loading of unnecessary data.
- Database Independence: With minimal configuration changes, you can switch between different relational databases.
- Rich Features: Supports complex mappings, inheritance, polymorphism, and various query mechanisms (HQL, Criteria API, native SQL).
- Large Community & Ecosystem: Mature project with extensive documentation, tutorials, and a large, active community for support.
Hibernate Weaknesses:
- Learning Curve: Can be complex to learn and configure, especially for beginners or for projects with very specific needs.
- Performance Overhead: While offering many optimizations, ORMs can sometimes introduce performance overhead due to the abstraction layer and automatic query generation.
- Loss of SQL Control: Can abstract away too much SQL, making it harder to fine-tune complex queries or leverage database-specific features.
- "Leaky Abstraction": In complex scenarios, the underlying database model can "leak" through the ORM, requiring developers to understand both the object model and the relational model.
- Complex Debugging: Debugging issues related to generated SQL or unexpected behavior can be challenging.
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop
👉 This is the Hibernate schema management setting.
It controls what Hibernate does with the database schema (tables, columns, constraints, etc) on application startup and shutdown:
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
| none | Hibernate does nothing — assumes schema already exists |
| validate | Hibernate validates that schema matches the entity definitions |
| update | Hibernate will update schema if entity changes are detected |
| create | Hibernate drops existing schema and creates it fresh on startup |
| create-drop | Hibernate creates schema on startup, drops schema on shutdown |
Here's why ddl-auto=create is considered bad for anything but the most ephemeral of use cases:
Data Loss: This is the absolute biggest reason. When ddl-auto=create is set, Hibernate will drop all existing tables and then recreate them based on your current entity model every time your application starts.
In production: This means all your valuable user data, orders, historical records, etc., would be instantly wiped out on every application restart. This is catastrophic for a production system.
Even in development/testing: If you have any data you want to persist between application restarts (e.g., test data you set up manually, or data you're using for debugging), create will destroy it.
spring.sql.init.mode=always
👉 This controls whether SQL scripts (like schema.sql, data.sql) are run.
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
| never | Do not run SQL init scripts |
| embedded | Run scripts only for embedded databases (H2, HSQLDB, etc.) |
| always | Run scripts always — even for production databases (PostgreSQL, etc.) |
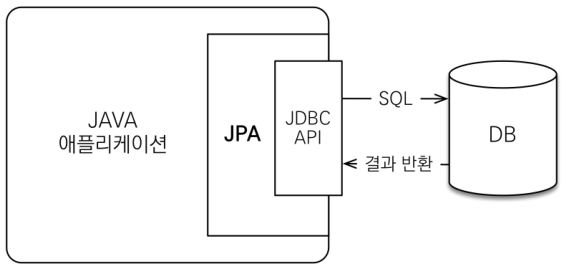
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
What it is:
JDBC is a low-level Java API for interacting with relational databases using raw SQL.
Purpose:
It gives you a way to connect to a database and execute SQL commands manually.
