예외처리
에러(error)와 예외(exception)
- 에러 : 프로그램 코드에 의해서 수습될 수 없는 심각한 오류
- 예외 : 프로그램 코드에 의해서 수습될 수 있는 다소 미약한 오류
ExceptionTest01, 프로그램 실행 중에 예외가 발생하는 상황
-
Exception클래스들 : 사용자의 실수같은 외적인 요인에 의해 발생하는 예외
-
RunTimeException클래스들 : 프로그래머의 실수로 발생하는 예외
-
try~catch문
try {
예외가 발생할 가능성이 있는 코드를 try블럭 안에 정의
}catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
예외가 발생되면 실행될 코드
}catch(IOException e) {
예외가 발생되면 실행될 코드
}
package exception;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Super{
}
class Sub extends Super{
}
public class ExceptionTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//1.개발자가 실수할 수 있는 부분
System.out.println("***********프로그램시작***********");
System.out.println(10/0);//java.lang.ArithmeticException
System.out.println(args[0]);//java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:
String str = null;
str.length();//java.lang.NullPointerException
Super obj = new Super();
Sub obj2 =(Sub)obj;//java.lang.ClassCastException
System.out.println("************");
//2.외부요인이나 사용자의 실수로 발생할 수 있는 익셉션
Scanner key = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("값입력:");
int data = key.nextInt();
System.out.println("사용자가 입력한 값=>"+data);
//java.util.InputMismatchException
//숫자만 입력가능한데 문자 입력하는 경우
//3.API에서 문법적으로 예외처리를 컴파일타입에 요구하는 경우
//=>메소드 선언부에 XXXException을 throws하는 것은 이 메소드를 사용하면서 XXXException이 발생할 수 있다는 의미
//=>Exception에 대한 처리를 RuntimeException의 하위같은 경우 문법적으로 제약하지 않는다
// 그러나 RuntimeException의 하위가 아니라 Exception의 하위 Exception들은 컴파일 시점에 체크하므로
//예외처리를 할 수 있도록 문법적으로 제약하므로 반드시 익셉션에 대한 처리를 해야한다
//=> 런타임익셉션의 하위이거나 아니거나 예외발생 가능성이 있는 코드는 무조건 예외를 처리
try {
//예외가 발생할 가능성이 있는 코드를 try블럭 안에 정의
FileReader fr = new FileReader("test.txt");
System.out.println((char)fr.read());
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("100")+200);
System.out.println("step1종료");
}catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
//예외가 발생되면 실행될 코드
System.out.println("파일경로가 틀림");
System.out.println("파일을 다시 선택하세요");
}catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println("파일엑세스 오류 발생");
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
}
}
ExceptionTest02
- .getMessage() : 개발자가 실수할 수 있는 부분을 찾아서 처리할 수 있도록 메세지를 출력
- .printStackTrace() : 예외를 추적해서 화면에 예외가 발생한 메소드의 라인넘버까지 출력하므로 개발시에 많이 사용
예외발생 당시의 호출스택에 있었던 메서드의 정보와 예외 메세지를 화면에 출력한다
package exception;
public class ExceptionTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args){
try {
System.out.println("try블럭시작");
System.out.println(10/0);
System.out.println("try블럭종료");
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
//예외가 발생하면 처리할 문장을 구현
//개발자가 실수할 수 있는 부분을 찾아서 처리할 수 있도록 메세지를 출력
System.out.println("예외발생");
System.out.println("예외메세지:"+e.getMessage());
//예외를 추적해서 화면에 예외가 발생한 메소드의 라인넘버까지 출력하므로 개발시에 많이 사용
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

ExceptionTest03, while문 사용시 Exception에 대한 처리
- while문 안의 try~catch블럭-> while문이 조건이 끝날때까지 실행됨
- try~catch블럭 안의 while문->예외가 발생하는 순간 프로그램 종료
package exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
//while문 사용시 Exception에 대한 처리
public class ExceptionTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner key = new Scanner(System.in);
//while문을 사용하는 경우 while문 밖에서 예외처리를 정의하면 예외가 발생하는 경우 반복문이 모두 실행되지 않고 프로그램이 종료된다.
// try {
// int i = 10;
// while(i<=13) {
// System.out.println("나누기할 숫자:");
// int num = key.nextInt();
// System.out.println("값:"+i/num);
// i++;
// }
// }catch(Exception e) {
// System.out.println("예외발생");
// }
//while문 안에서 예외를 처리하면 오류가 발생되는 상황만 catch블럭의 코드가 실행되고 와일문이 멈추지않는다
//에러체크돼도 while문은 설정값까지 계속가야 끝남
int i = 10;
while(i<=13) {
System.out.println("나누기할 숫자:");
int num = key.nextInt();
try {
System.out.println("값:"+i/num);
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("0으로 나누면 error!!!");
}
i++;
}
}
}
ExceptionTest04, 다중 catch 사용하기
- 예외처리 : try~catch~catch...
- 각각의 예외가 발생할때마다 다르게 처리하고싶은 경우 catch블럭을 여러개 정의하고 사용할 수 있다.
- 단 상위 익셉션은 가장 아래에 정의한다.
- Exception 예외클래스는 모든 예외클래스의 상위클래스이므로 예외가 발생됐을때 동일한 처리를 하려면 상위타입으로 정의해서 작업
- 다 다른 종류의 익셉션을 상위 익셉션 하나로 묶음 =>다형성
package exception;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ExceptionTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner key = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = null;
try {
//예외발생 가능성이 있는 코드
System.out.println("시작");
System.out.println("숫자입력:");
int num1 = key.nextInt();
System.out.println("나눌 숫자 입력:");
int num2 = key.nextInt();
System.out.println("결과=>"+(num1/num2));
if(num1%2==0) {
System.out.println(args[0]);//짝수
}else {
System.out.println("종료:"+str.length());//홀수
}
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("0으로 나눔");
}catch(InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("사용자가 문자를 입력함");
}catch(NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("널이야......");
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("기타오류...");
}//상위타입은 앞에서 먼저 안걸러지게 마지막으로..
//Exception 예외클래스는 모든 예외클래스의 상위클래스이므로 예외가 발생됐을때 동일한 처리를 하려면 상위타입으로 정의해서 작업
// try {
// //System.out.println(10/0);
// String str = null;
// //str.lastIndexOf(10);
// System.out.println(args[0]);
// }catch(Exception e) {//다 다른 종류의 익셉션을 상위 익셉션 하나로 묶음 =>다형성
// System.out.println("예외발생");
// }
}
}
ExceptionTest04_2, 다중 catch의 다른표현
package exception;
//다중 catch의 다른표현
public class ExceptionTest04_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println(10/0);
System.out.println(args[0]);
}catch(ArithmeticException | ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("예외발생: "+e.getMessage());
if(e instanceof ArithmeticException) {
System.out.println("0으로 나누지마");
}else {
System.out.println("배열선언안함");
}
}
}
}
ExceptionTest05, try~catch~finally
- finally블럭 : 예외의 발생여부에 상관없이 실행되어야할 코드를 포함시킬 목적으로 사용
package exception;
//try~catch~finally
public class ExceptionTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println("프로그램시작");
System.out.println("디비연동");
System.out.println("디비처리진행중..."+10/0);
System.out.println("완료");
//System.out.println("자원반납코드");
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("오류코드확인");
}finally {
//예외가 발생되거나 발생되지 않거나 무조건 실행되는 코드
System.out.println("자원반납코드");
}
}
}ThrowsTest1,2 throws를 이용해서 예외를 처리하는 방법
- 예외가 발생한 곳에서 예외를 처리
- 호출한 곳에서 예외가 발생된 것을 알 수 없다.
- 예외가 발생되면 예외에 대한 모든 처리가 모두 끝난 상태로 실행되므로 호출한 곳에서 다양하게 처리할 수 없다.
- 예외가 발생된 곳에서 처리하지 않고 호출한 곳에서 처리하도록 예외를 넘기기
- public void 메소드명() throws 예외클래스1, 예외클래스2,...{}
package exception;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
//throws를 이용해서 예외를 처리하는 방법
public class ThrowsTest1 {
//1.예외가 발생한 곳에서 예외를 처리
//=>호출한 곳에서 예외가 발생된 것을 알 수 없다.
//=>예외가 발생되면 예외에 대한 모든 처리가 모두 끝난 상태로 실행되므로 호출한 곳에서 다양하게 처리할 수 없다.
//=>
public void test(String fileName) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
}catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
//예외를 처리
System.out.println("지정한 파일을 찾을 수 없습니다.!!");
}
}
//2.예외가 발생된 곳에서 처리하지 않고 호출한 곳에서 처리하도록 예외를 넘기기
//public void 메소드명() throws 예외클래스1, 예외클래스2,...{}
public void test2(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException,ArithmeticException{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
System.out.println(10/0);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//예외가 발생될 메소드인 test()를 호출해서 사용하는곳
//1.예외가 발생되지만 이미 발생된 곳에서 예외처리가 끝난 test 메소드를 호출
ThrowsTest1 obj = new ThrowsTest1();
obj.test("test2.txt");
//2.예외를 발생한 곳에서 처리하지 않고 호출한 곳에서 처리
try {
obj.test2("test2.txt");
}catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
//호출한 곳에서 상황에 맞게 예외에 대한 처리를 할 수 있다.
System.out.println("파일명이 틀렸으므로 파일을 다시 선택할 수 있는 대화상자를 출력");
}
}
}package exception;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class ThrowsTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThrowsTest1 obj = new ThrowsTest1();
obj.test("test2.txt");
//2.예외를 발생한 곳에서 처리하지 않고 호출한 곳에서 처리
try {
obj.test2("test2.txt");
}catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
//호출한 곳에서 상황에 맞게 예외에 대한 처리를 할 수 있다.
System.out.println("파일선택의 기회는 한번..종료");
}
}
}MyException, Test, 사용자정의로 클래스를 예외클래스의 하위클래스로 작업
- 예외가 발생되는 상황 : JVM이 인지하는 예외상황이 아니므로 인위적으로 exception을 발생시킬것
- 문법
throw new Exception클래스생성자()
package exception;
//잔액이 0원일때 발생하는 exception
//사용자정의로 클래스를 예외클래스의 하위클래스로 작업
public class MyException extends Exception{
public MyException(String message) {
super(message);
//Exception 생성자중 메세지호출있어서 슈퍼로받음
}
}package exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MyExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner key = new Scanner(System.in);
int money = 1000;
System.out.println("********인터넷뱅킹**********");
System.out.println("출금하기");
System.out.println("출금할 금액 입력:");
int money2 = key.nextInt();//출금금액
//money2가 money보다 크면 출금을 할 수 없는 상황이므로 익셉션 발생시키기
if(money2>money) {
//예외가 발생되는 상황 - JVM이 인지하는 예외상황이 아니므로 인위적으로 익셉션을 발생시킬것
//문법 throw new Exception클래스생성자()
try{
throw new MyException("잔액이 0원, 출금불가");
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("잔액이없어서 출금할수없습니다.");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}else {
//정상상황
System.out.println("정상상황의 step");
}
}
}ExceptionExam01 -> 다시 해보기 아직 헷갈림

package exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ExceptionExam01 {
//필요할 경우 다음의 메서드 선언부분(메서드 시그너처)을 수정하시기 바랍니다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan= new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("숫자로 변환할 문자열을 입력바랍니다.");
String str= scan.nextLine();
//여기를 작성하십시오.
try {
int result= convert(str);
System.out.println("변환된 숫자는 "+result+" 입니다.");
}catch(IllegalArgumentException e){
// System.out.println("예외가 발생되었습니다. 문자열을 입력하지 않고 Enter키를 누르셨습니다.");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
//필요할 경우 다음의 메서드 선언부분(메서드 시그너처)을 수정하시기 바랍니다.
private static int convert(String str) throws IllegalArgumentException{
int result = 0;
if(str==null | str.length()==0) {
// throw new IllegalArgumentException();//예외발생시키는 코드
throw new IllegalArgumentException("예외가 발생되었습니다. 문자열을 입력하지 않고 Enter키를 누르셨습니다.");
}
result = Integer.parseInt(str);
return result;
}
}TestAccount
Account
package exception;
public class Account {
private String accId;
private long balance;
private String ownerName;
public Account() {
}
public Account(String accId, long balance, String ownerName) {
super();
this.accId = accId;
this.balance = balance;
this.ownerName = ownerName;
}
//입금하기
public void deposit(long amount) {
balance = balance + amount;
}
//출금하기
public void withdraw(long amount) {
balance = balance - amount;
}
public String getAccId() {
return accId;
}
public void setAccId(String accId) {
this.accId = accId;
}
public long getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(long balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public String getOwnerName() {
return ownerName;
}
public void setOwnerName(String ownerName) {
this.ownerName = ownerName;
}
}BankException
package exception;
public class BankException extends Exception {
public BankException(String msg) {
super(msg);//Exception을 발생시키면서 전달하는 문자열이 Exception객체의 message로 셋팅될 수 있도록 처리
//1. Exception이 발생될때 메세지로 출력될수있도록 하기 위해
//2. getMessage()메소드 호출하면 출력
}
}CheckingAccount
package exception;
public class CheckingAccount extends Account {
private String cardNo;
public CheckingAccount() {
}
public CheckingAccount(String accId, long balance, String ownerName,String cardNo) {
super(accId,balance,ownerName);
this.cardNo = cardNo;
}
public void pay(long amount,String cardNo) throws BankException {//여기
//String은 참조형이니까 ==은 주소 비교하는것
//문자열을 비교하는 경우 무조건 equals=>대소문자까지 비교
if(amount<=getBalance() & this.cardNo.equals(cardNo)) {
//super는 메소드명이 부모클래스와 동일할때 쓰면댕
//구매가 가능하도록 - 지불할수있도록 작업
withdraw(amount);
}
else{
//오류가 발생하는 상황
//step1 Exception객체를 생성
BankException exception = new BankException("지불이 불가능 합니다.");
//step2 스텝원에서 생성한 객체를 익셉션이 ㅏㄹ생된 것으로 처리
throw exception;
// throw new BankException("지불이 불가능합니다.")
}
}
public String getCardNo() {
return cardNo;
}
public void setCardNo(String cardNo) {
this.cardNo = cardNo;
}
}
TestAccount
package exception;
public class TestAccount {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CheckingAccount acc1 =
new CheckingAccount("111-222-333",1000000,"장동건","1234-5647-8888");
try{
acc1.pay(500000,"1234-5678-8888");
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("현재잔액====>"+acc1.getBalance());
String cardNo = new String("1234-5647-8888");//객체방식
String cardNo2 = "1234-5647-8888";//리터럴
try{
acc1.pay(500000,cardNo);
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("현재잔액====>"+acc1.getBalance());
// try {
// acc1.pay(500000,cardNo);
// } catch (BankException e) {
// // TODO Auto-generated catch block
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
}
}
GUI
GUITest
package gui;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Container;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTextArea;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
//로그인창 클래스
class MyLoginView extends JFrame{//is a관계
JTextField text;
JButton btn;
JTextArea content;
MyLoginView(String title) {
super(title);
//화면디자인
display();
//이벤트연결
eventStart();
this.setSize(400, 300);//JFrame의 사이즈 결정
this.setVisible(true);//JFrame창을 화면에 출력
//x버튼 누르면 프로그램이 종료되도록 작업하기
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public void display() {
Container c = this.getContentPane();
content = new JTextArea(5,30);
JScrollPane scroll = new JScrollPane(content);
c.add(scroll,BorderLayout.CENTER);
JPanel p1 = new JPanel();
JLabel label = new JLabel("텍스트입력");
text = new JTextField(20);
btn = new JButton("전송");
p1.add(label);
p1.add(text);
p1.add(btn);
c.add(p1,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
}
public void eventStart() {
//이벤트연결
btn.addActionListener(new ActionEventListener(this));
}
}
public class GUITest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLoginView loginview = new MyLoginView("로그인");
}
}
ActionEventListener
package gui;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
//버튼을 클릭하는 이벤트가 발생하면 호출될 메소드를 갖고있는 클래스
public class ActionEventListener implements ActionListener{
MyLoginView mainView;
public ActionEventListener(MyLoginView mainView) {
super();
this.mainView = mainView;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if(e.getSource()==mainView.text |
e.getSource()==mainView.btn){
mainView.content.append(mainView.text.getText()+"\n");
mainView.text.setText("");
}
}
}
API.lang
ObjectTest, Person
package api.lang;
public class Person {
private String name;
private String addr;
private int age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, String addr, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.addr = addr;
this.age = age;
}
// public String toString() {
// return "name:"+name+",addr:"+addr+",age"+age;
// }
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", addr=" + addr + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
//source-제너레이트 투스트링
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddr() {
return addr;
}
public void setAddr(String addr) {
this.addr = addr;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
package api.lang;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Random;
public class ObjectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// equals는 하위클래스에서 객체의 속성을 비교해서 같은 객체인지 여부를 boolean으로 리턴하도록 재정의해서 주로 사용
Object obj1 = new Object();
Object obj2 = new Object();
Person p1 = new Person("BTS","서울",30);
Person p2 = new Person("BTS","서울",30);
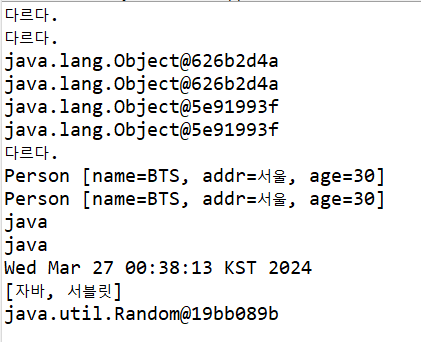
if(obj1==obj2) {
System.out.println("같다.");
}else {
System.out.println("다르다.");
}
if(obj1.equals(obj2)) {
System.out.println("같다.");
}else {
System.out.println("다르다.");
}
//Object클래스의 메소드
//toString메소드가 객체가 갖는 기본메소드 - 기본메소드는 생략이 가능
System.out.println(obj1);
System.out.println(obj1.toString());//위와같은데 그냥 생략된거, 출력해보면 주소같음을 알 수 있음.
System.out.println(obj2);
System.out.println(obj2.toString());
if(p1.equals(p2)) {
System.out.println("같다.");
}else {
System.out.println("다르다.");
}
System.out.println(p1);
System.out.println(p2);
String str = new String("java");
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(str.toString());//세임세임~ 투스트링 생략되어있는것뿐, 얘는 이미 오버라이딩 api에서 되어있음..그래서
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date);
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("자바");
list.add("서블릿");
System.out.println(list);
Random rand = new Random();
System.out.println(rand);//toString 오버라이팅 api에서 안되어있는애들은 주소값뜸
}
}
본 포스팅은 멀티캠퍼스의 멀티잇 백엔드 개발(Java)의 교육을 수강하고 작성되었습니다.
