1. 최댓값
최댓값
자료구조에서 가장 큰 값을 찾는다.
실습
리스트에서 아스키코드가 가장 큰 값을 찾는 알고리즘을 만들어보자.
chars = ['c', 'x', 'Q', 'A', 'e', 'P', 'p']
print(f'chars: {chars}')
max_chars = chars[0]
for i in range(len(chars)-2):
if max_chars < chars[i]:
max_chars = chars[i]
print(max_chars)2. 최솟값
최솟값
자료구조에서 가장 작은 값을 찾는다.
실습
리스트에서 아스키코드가 가장 작은 값을 찾는 알고리즘을 만들어보자.
chars = ['c', 'x', 'Q', 'A', 'e', 'P', 'p']
print(f'chars: {chars}')
min_chars = chars[0]
for i in range(len(chars)-2):
if min_chars > chars[i]:
min_chars = chars[i]
print(min_chars)3. 최빈값
최빈값
데이터에서 빈도수가 가장 많은 데이터를 최빈값이라고 한다.
실습
최빈값 알고리즘을 이용해서 학생 100명의 점수 분포를 다음과 같이 나타내 보자.
import random
scores = []
sc_item=[]
sc_dist=[]
for i in range(100):
sc_rand = random.randrange(70,100,5)
scores.append(sc_rand)
print(scores)
for i in scores:
if i not in sc_item:
sc_item.append(i)
for it in sc_item:
count_num = scores.count(it)
sc_dist.append(count_num)
for i in range(len(sc_item)):
for j in range(i,len(sc_item)-1):
if sc_dist[j]< sc_dist[j+1]:
sc_dist[j], sc_dist[j+1] = sc_dist[j+1], sc_dist[j]
sc_item[j], sc_item[j + 1] = sc_item[j + 1], sc_item[j]
for i in range(len(sc_item)-1):
print(f'{i}. {sc_item[i]}빈도수: {sc_dist[i]} \t','+'*(sc_dist[i]))[75, 80, 75, 95, 80, 85, 85, 85, 95, 70, 70, 95, 85, 75, 80, 90, 85, 95, 80, 80, 80, 85, 95, 80, 70, 85, 95, 75, 90, 70, 90, 75, 70, 90, 75, 85, 70, 80, 75, 85, 75, 85, 80, 70, 90, 75, 90, 95, 75, 90, 70, 80, 95, 70, 85, 80, 85, 80, 75, 90, 90, 75, 70, 85, 80, 70, 85, 85, 95, 95, 95, 75, 70, 85, 95, 70, 80, 90, 95, 95, 80, 75, 80, 80, 75, 95, 80, 75, 90, 85, 75, 80, 85, 80, 80, 85, 70, 80, 85, 95] 0. 80빈도수: 22 ++++++++++++++++++++++ 1. 85빈도수: 20 ++++++++++++++++++++ 2. 75빈도수: 17 +++++++++++++++++ 3. 95빈도수: 16 ++++++++++++++++ 4. 70빈도수: 14 ++++++++++++++
4. 근삿값
근삿값
특정 값(참값)에 가장 가까운 값을 근삿값이라고 한다.
실습
근삿값 알고리즘을 이용해서 시험 점수를 입력하면 학점이 출력되는 프로그램을 만들어보자. 평균 점수에 따른 학점 기준 점수는 다음과 같다.
- 95에 근삿값이면 A
- 85에 근삿값이면 B
- 75에 근삿값이면 C
- 65에 근삿값이면 D
- 55에 근삿값이면 F
kor_score = int(input('input kor score: '))
eng_score = int(input('input eng score: '))
mat_score = int(input('input mat score: '))
sci_score = int(input('input sci score: '))
his_score = int(input('input his score: '))
totalScore = kor_score + eng_score + mat_score + sci_score + his_score
avgScore = totalScore / 5
print('totalScore:',totalScore)
print('avgScore:',avgScore)
grade = [95, 85, 75, 65, 55]
nearest = 55
nearIdx = 0
for i in range(len(grade)-1):
if abs(grade[i] - avgScore) < nearest:
nearest = abs(grade[i] - avgScore)
nearIdx = i
print(nearest)
print(nearIdx)
if grade[nearIdx] == 95:
print('grade: A')
elif grade[nearIdx] == 85:
print('grade: B')
elif grade[nearIdx] == 75:
print('grade: C')
elif grade[nearIdx] == 65:
print('grade: D')
elif grade[nearIdx] == 55:
print('grade: F')5. 평균
평균
여러 수나 양의 중간값을 갖는 수를 평균이라 한다.
실습
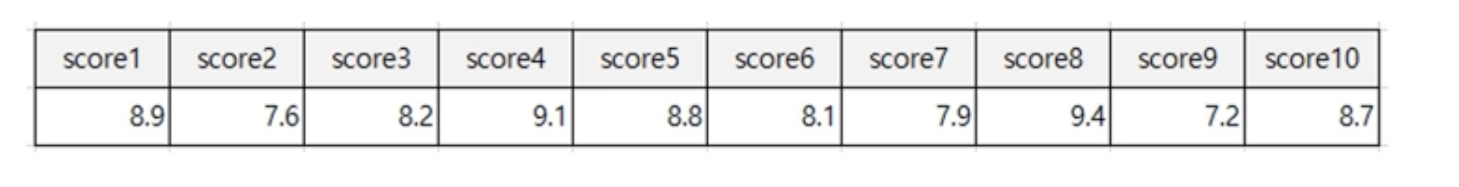
다음은 어떤 체조선수의 점수이다. 평균을 구하고 순위를 정하는 알고리즘을 만들어보자.
scores = [8.9, 7.6, 8.2, 9.1, 8.8, 8.1, 7.9, 9.4, 7.2, 8.7]
top5 = [9.12, 8.95, 8.12, 7.90, 7.88]
totalScore = 0
for score in scores:
totalScore += score
avgScore = round(totalScore / len(scores),2)
top5.append(avgScore)
top5.sort(reverse=True)
for i in range(5):
print(f'{i+1}위 ➡️ {top5[i]}')