From
https://blog.cloudflare.com/how-to-drop-10-million-packets/
Set up Bench
Needs to:
1. set up packets to be forwarded to one RX queue:
ethtool -N ext0 flow-type udp4 dst-ip 198.18.0.12 dst-port 1234 action 2 
--> solved using ethtool -L ens6f0 combined 1
- show result as below
$ tcpdump -ni vlan100 -c 10 -t udp and dst port 1234
IP 198.18.40.55.32059 > 198.18.0.12.1234: UDP, length 16
IP 198.18.51.16.30852 > 198.18.0.12.1234: UDP, length 16
IP 198.18.35.51.61823 > 198.18.0.12.1234: UDP, length 16
IP 198.18.44.42.30344 > 198.18.0.12.1234: UDP, length 16
IP 198.18.106.227.38592 > 198.18.0.12.1234: UDP, length 16
IP 198.18.48.67.19533 > 198.18.0.12.1234: UDP, length 16
IP 198.18.49.38.40566 > 198.18.0.12.1234: UDP, length 16
IP 198.18.50.73.22989 > 198.18.0.12.1234: UDP, length 16
IP 198.18.43.204.37895 > 198.18.0.12.1234: UDP, length 16
IP 198.18.104.128.1543 > 198.18.0.12.1234: UDP, length 16when using "packit"
https://manpages.ubuntu.com/manpages/focal/man8/packit.8.html
tcpdump:
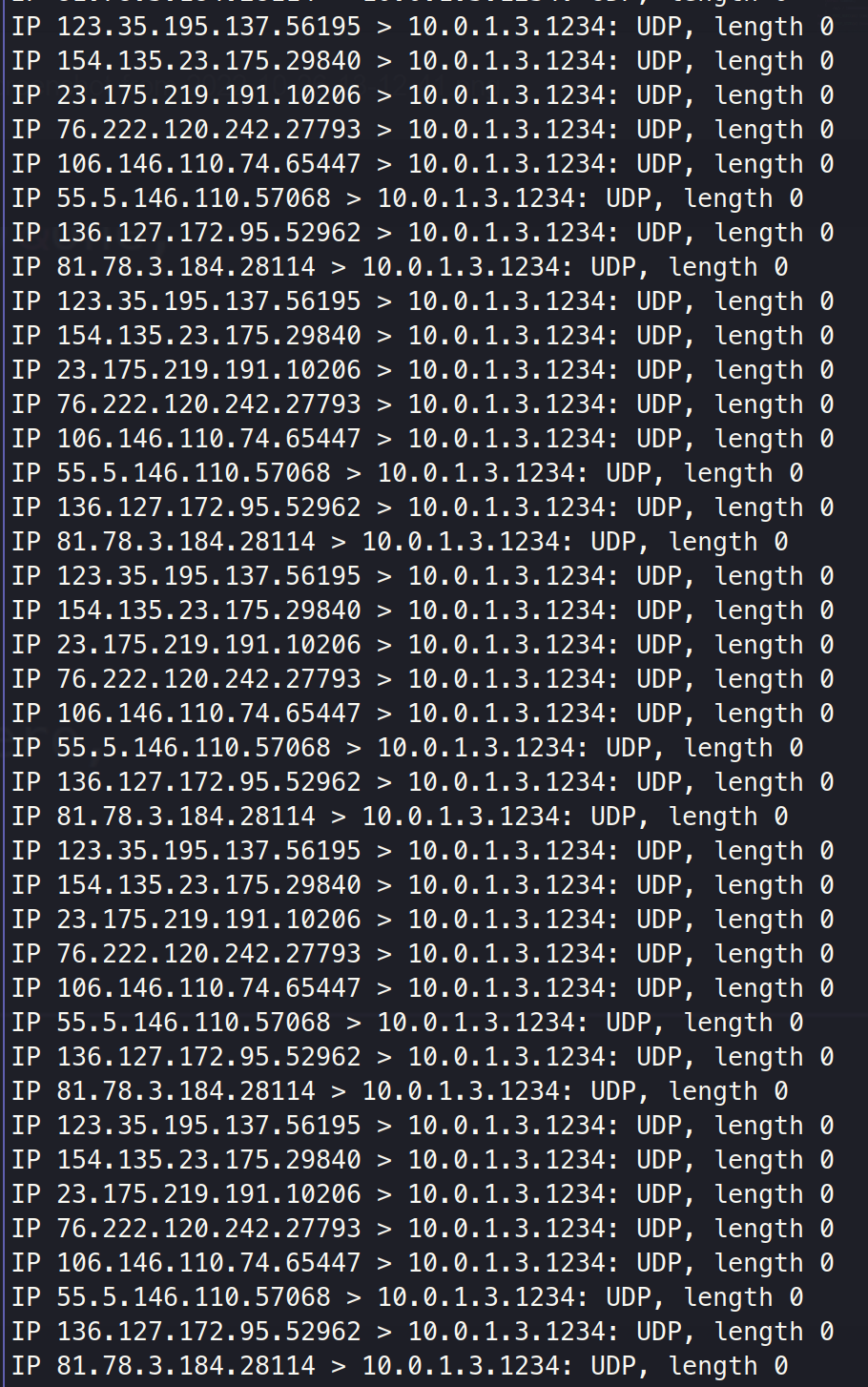
sudo packit -m inject -t udp -i enp3s0f1 -b 0 -c 0 -sR -d 10.0.1.3 -D 1234why length = 0?
Also, packet does not arrive for the socket program.
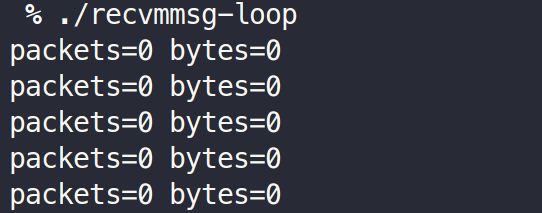
./recvmsg-loop
when using "nping"
https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/nping.1.html
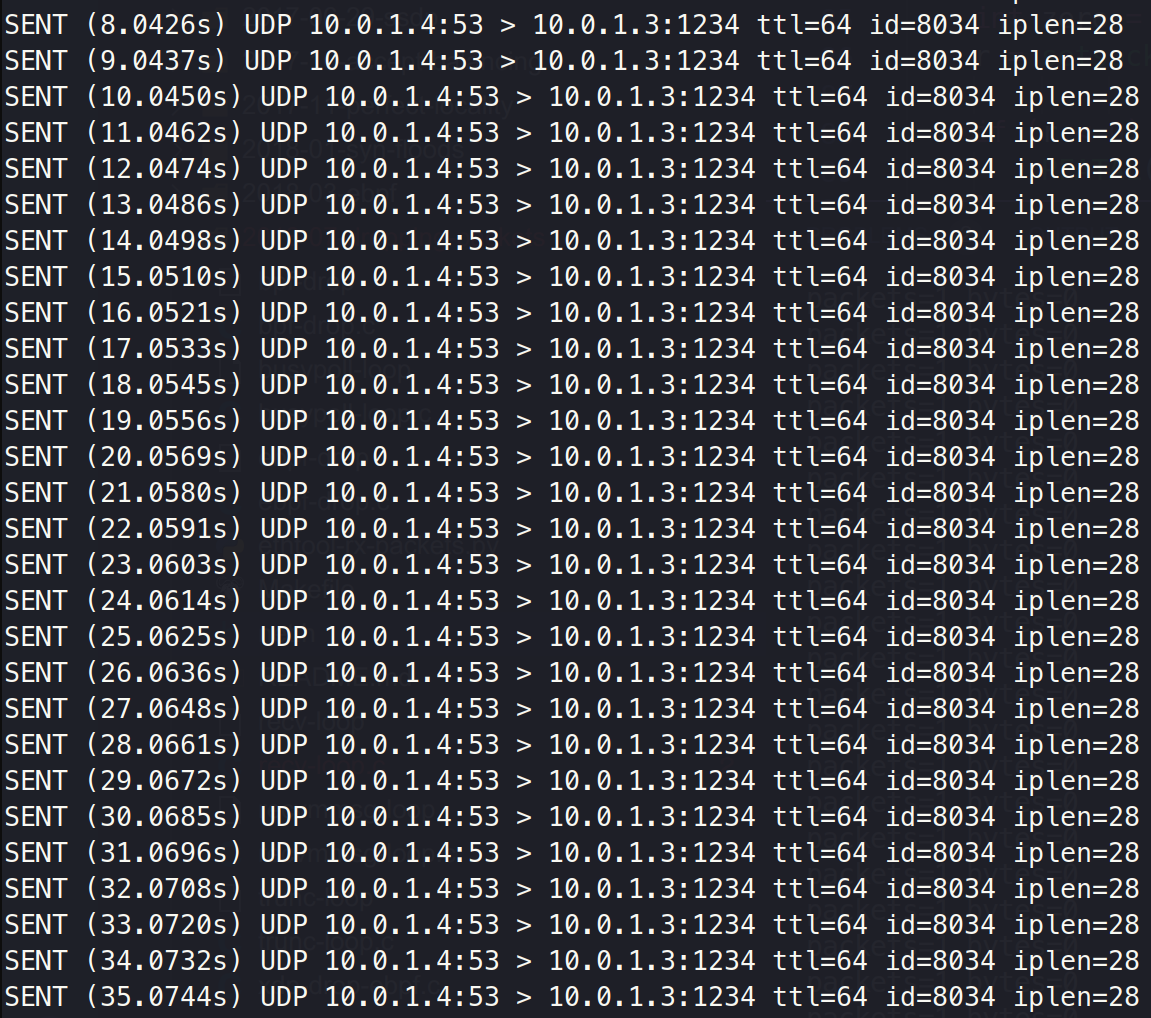
sudo nping --udp -c 0 -p 1234 10.0.1.3without randomizing source IP
SENT:
tcpdump:
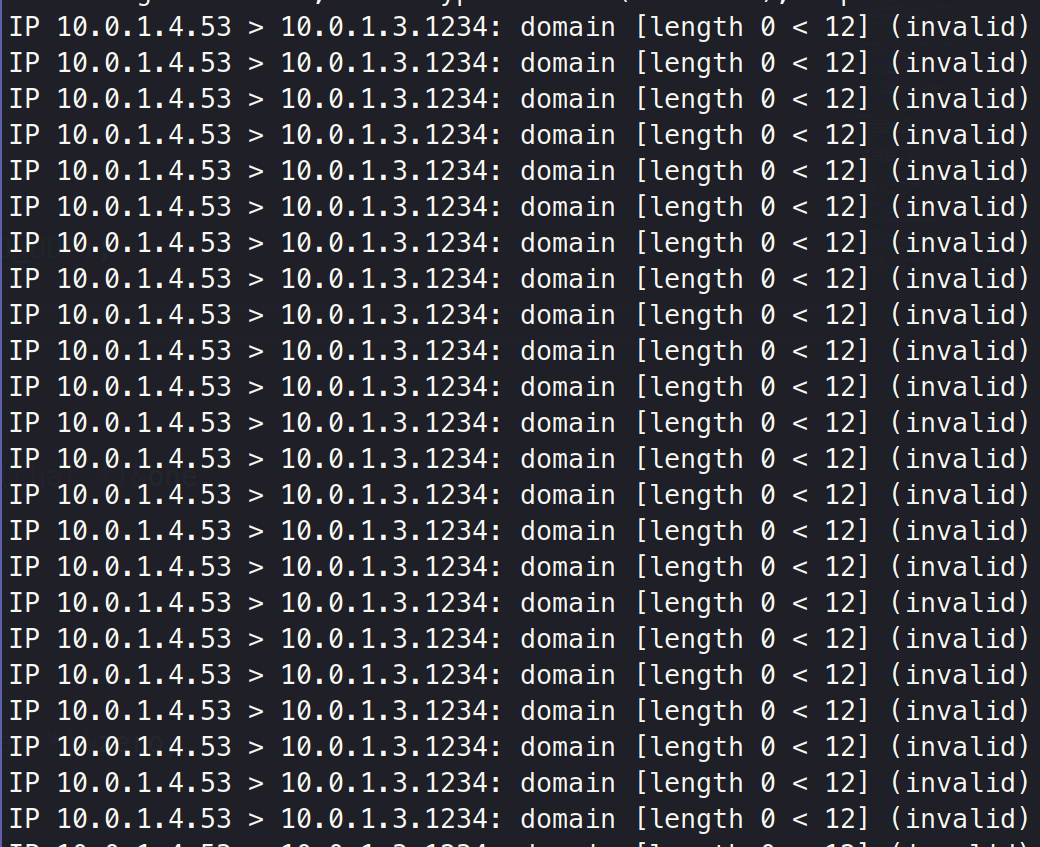
but,
./recvmsg-loop
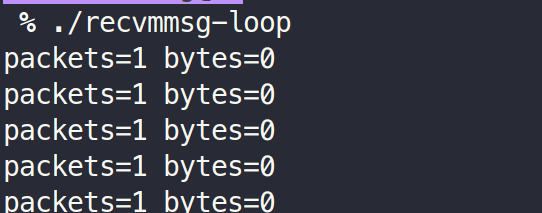
recvmsg-loop:
// recvmmsg-loop
//
// Copyright (c) 2018 CloudFlare, Inc.
#define _GNU_SOURCE // recvmmsg
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "net.h"
#define MTU_SIZE 2048
#define MAX_MSG 32
static uint64_t packets = 0;
static uint64_t bytes = 0;
static void timer_handler()
{
printf("packets=%lu bytes=%lu\n", packets, bytes);
packets = 0;
bytes = 0;
}
int main()
{
struct sigaction sa = {0};
sa.sa_handler = &timer_handler;
sigaction(SIGALRM, &sa, NULL);
struct itimerval timer = {0};
timer.it_value.tv_sec = 1;
timer.it_interval.tv_sec = 1;
setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &timer, NULL);
struct sockaddr_storage listen_addr;
net_gethostbyname(&listen_addr, "::", 1234);
int fd = net_bind_udp(&listen_addr);
struct mmsghdr messages[MAX_MSG] = {0};
char buffers[MAX_MSG][MTU_SIZE];
struct iovec iovecs[MAX_MSG] = {0};
/* Setup recvmmsg data structures. */
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_MSG; i++)
{
char *buf = &buffers[i][0];
struct iovec *iovec = &iovecs[i];
struct mmsghdr *msg = &messages[i];
msg->msg_hdr.msg_iov = iovec;
msg->msg_hdr.msg_iovlen = 1;
iovec->iov_base = &buf[0];
iovec->iov_len = MTU_SIZE;
}
while (1)
{
int r = recvmmsg(fd, messages, MAX_MSG, MSG_WAITFORONE, NULL);
if (r == 0)
{
return 0;
}
if (r < 0)
{
if (errno == EINTR)
{
continue;
}
PFATAL("recv()");
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i < MAX_MSG; i++)
{
struct mmsghdr *msg = &messages[i];
bytes += msg->msg_len;
msg->msg_len = 0;
}
packets += r;
}
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}Also, not even close to max performance?
Solved via : https://velog.io/@brian11hwang/Random-IP-Random-Port
Start Experiment
Step 1. Dropping packets in application
--> Using 20 rx queue : 7.8 m packets arrive
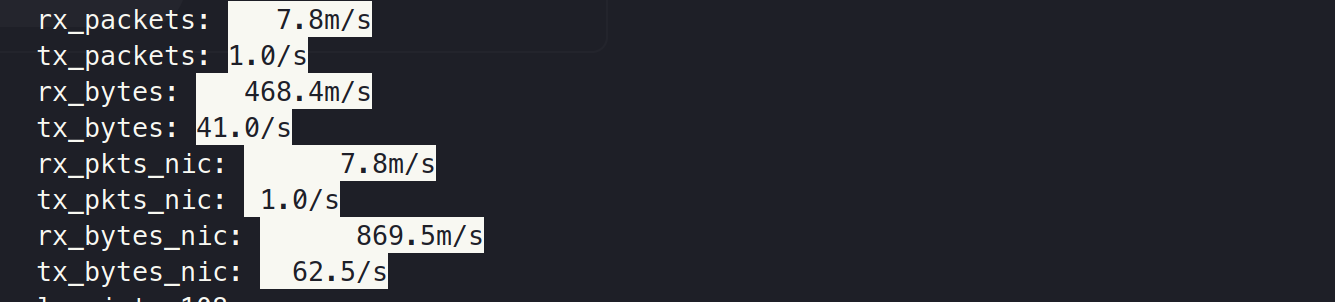
--> Using 1 rx queue(#0) : 1.7 million packets arrive
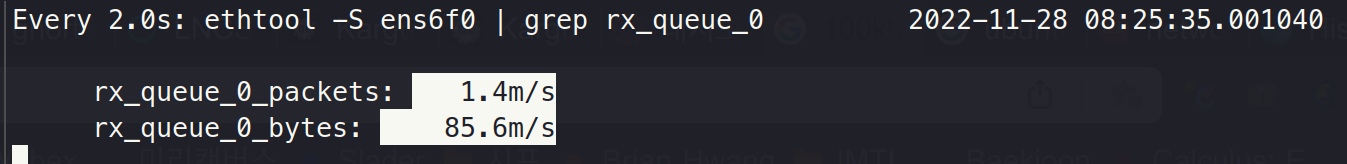
Step 2. Slaughter conntrack
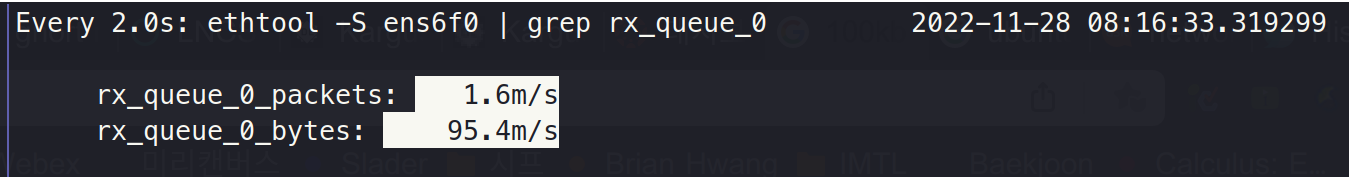
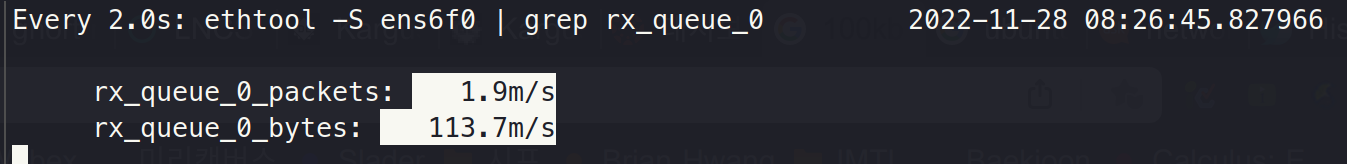
Step 3. BPF drop on a socket
static int net_setup_bpf(int sd)
{
struct sock_filter code[] = {
// ret #0
{0x06, 0, 0, 0x00000000},
};
struct sock_fprog bpf = {
.len = ARRAY_SIZE(code),
.filter = code,
};
int r = setsockopt(sd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_ATTACH_FILTER, &bpf, sizeof(bpf));
if (r < 0) {
PFATAL("setsockopt(SO_ATTACH_FILTER)");
}
return sd;
}
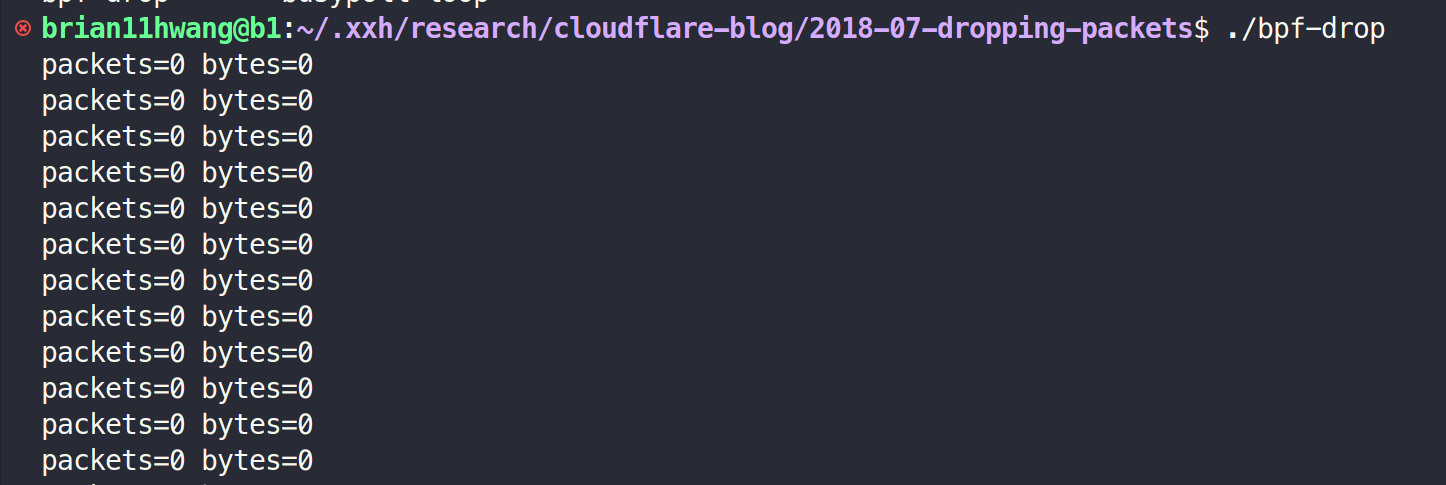
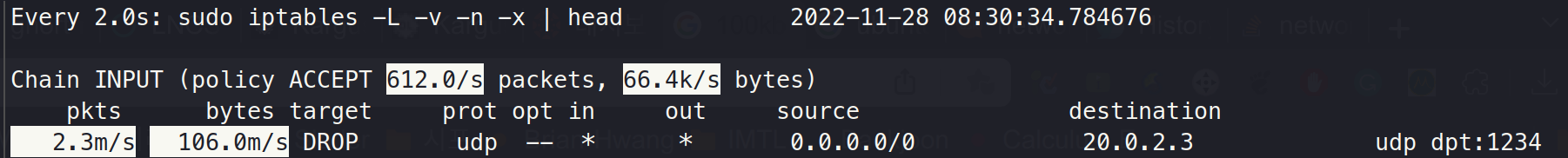
Step 4. iptables DROP after routing
iptables -I INPUT -d 20.0.2.3 -p udp --dport 1234 -j DROP
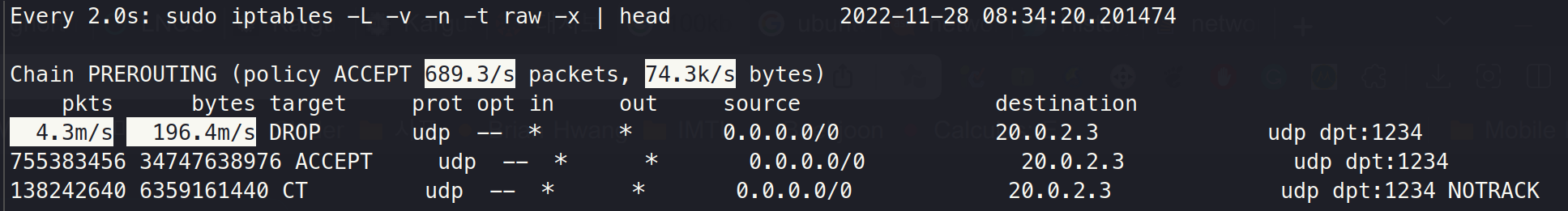
Step 5. iptables DROP in PREROUTING
iptables -I PREROUTING -t raw -d 198.18.0.12 -p udp --dport 1234 -j DROP
Step 7. tc ingress handler DROP
tc qdisc add dev ens6f0 ingress
tc filter add dev ens6f0 parent ffff: prio 4 protocol ip u32 match ip protocol 17 0xff match ip dport 1234 0xffff match ip dst 20.0.2.3/24 flowid 1:1 action drop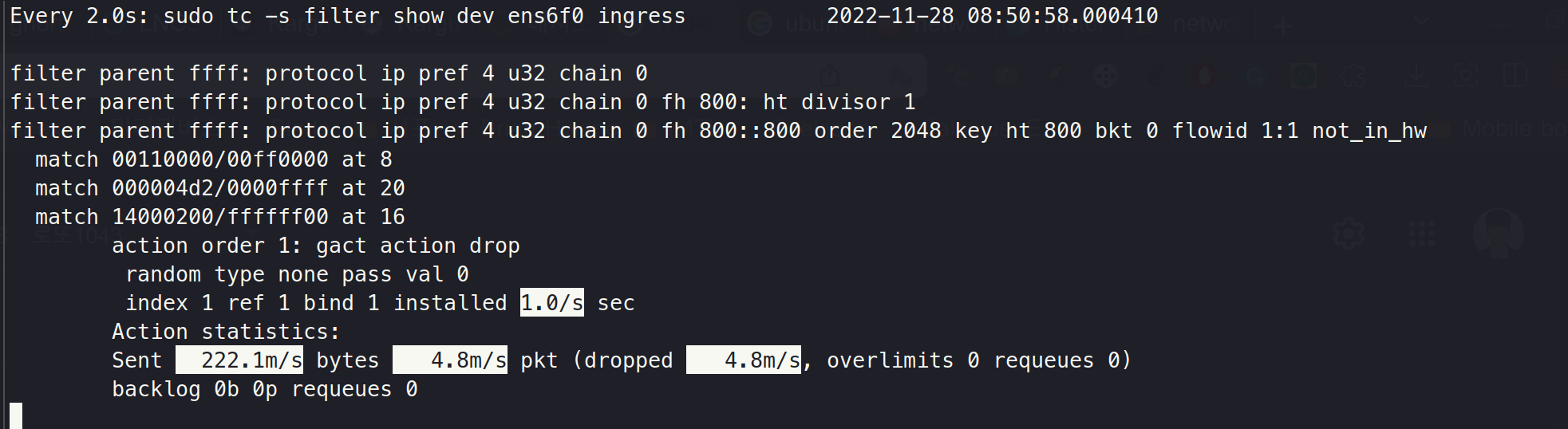
About 4.9mpps
Step 8. XDP_DROP
#include <linux/bpf.h>
#include <linux/if_ether.h>
#include <linux/in.h>
#include <linux/ip.h>
#include <linux/ipv6.h>
#include <linux/udp.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#define SEC(NAME) __attribute__((section(NAME), used))
#define htons(x) ((__be16)___constant_swab16((x)))
#define htonl(x) ((__be32)___constant_swab32((x)))
struct vlan_hdr {
__be16 h_vlan_TCI;
__be16 h_vlan_encapsulated_proto;
};
SEC("prog")
int xdp_drop_benchmark_traffic(struct xdp_md *ctx)
{
void *data_end = (void *)(long)ctx->data_end;
void *data = (void *)(long)ctx->data;
struct ethhdr *eth = data;
uint64_t nh_off = sizeof(*eth);
if (data + nh_off > data_end) {
return XDP_PASS;
}
uint16_t h_proto = eth->h_proto;
int i;
/* Handle double VLAN tagged packet. See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.1ad */
for (i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
if (h_proto == htons(ETH_P_8021Q) || h_proto == htons(ETH_P_8021AD)) {
struct vlan_hdr *vhdr;
vhdr = data + nh_off;
nh_off += sizeof(struct vlan_hdr);
if (data + nh_off > data_end) {
return XDP_PASS;
}
h_proto = vhdr->h_vlan_encapsulated_proto;
}
}
if (h_proto == htons(ETH_P_IP)) {
struct iphdr *iph = data + nh_off;
struct udphdr *udph = data + nh_off + sizeof(struct iphdr);
if (udph + 1 > (struct udphdr *)data_end) {
return XDP_PASS;
}
if (iph->protocol == IPPROTO_UDP &&
(htonl(iph->daddr) & 0xFFFFFF00) ==
0x14000203 // 198.18.0.0/24
&& udph->dest == htons(1234)) {
return XDP_DROP;
}
} else if (h_proto == htons(ETH_P_IPV6)) {
struct ipv6hdr *ip6h = data + nh_off;
struct udphdr *udph = data + nh_off + sizeof(struct ipv6hdr);
if (udph + 1 > (struct udphdr *)data_end) {
return XDP_PASS;
}
if (ip6h->nexthdr == IPPROTO_UDP &&
ip6h->daddr.s6_addr[0] == 0xfd // fd00::/8
&& ip6h->daddr.s6_addr[1] == 0x00 // fd00::/8
&& udph->dest == htons(1234)) {
return XDP_DROP;
}
}
return XDP_PASS;
}
char _license[] SEC("license") = "GPL";